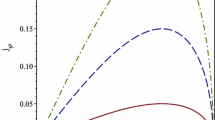
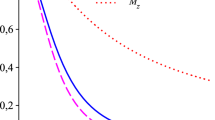
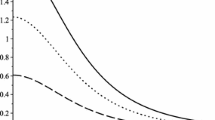
Abstract
Applying the Horský-Mitskievitch conjecture to the empty space solutions of Morgan and Morgan due to the gravitational field of a finite disk, we have obtained the corresponding solutions of the Einstein-Maxwell equations. The resulting expressions are simply written in terms of oblate spheroidal coordinates and the solutions represent fields due to magnetized static thin disk of finite extension. Now, although the solutions are not asymptotically flat, the masses of the disks are finite and the energy-momentum tensor agrees with the energy conditions. Furthermore, the magnetic field and the circular velocity show an acceptable physical behavior.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonnor, W.B., Sackfield, A.: Commun. Math. Phys. 8, 338 (1968)
Morgan, T., Morgan, L.: Phys. Rev. 183, 1097 (1969)
Morgan, L., Morgan, T.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 2, 2756 (1970)
Voorhees, B.H.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 5, 2413 (1972)
Lynden-Bell, D., Pineault, S.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 185, 679 (1978)
Chamorro, A., Gregory, R., Stewart, J.M.: Proc. - Royal Soc., Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 413, 251 (1987)
Letelier, P.S., Oliveira, S.R.: J. Math. Phys. 28, 165 (1987)
Lemos, J.P.S.: Class. Quantum Gravity 6, 1219 (1989)
Bičák, J., Lynden-Bell, D., Katz, J.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 47, 4334 (1993)
Bičák, J., Lynden-Bell, D., Pichon, C.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 265, 126 (1993)
González, G.A., Letelier, P.S.: Class. Quantum Gravity 16, 479 (1999)
González, G.A., Espitia, O.A.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 68(10), 104028 (2003)
González, G.A., Gutiérrez-Piñeres, A.C., Viña-Cervantes, V.M.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 79(12), 124048 (2009)
Lynden-Bell, D., Pineault, S.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 185, 695 (1978)
Bičák, J., Ledvinka, T.: Phys. Rev. Lett. 71, 1669 (1993)
Pichon, C., Lynden-Bell, D.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 280, 1007 (1996)
González, G.A., Letelier, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 62(6), 064025 (2000)
Lemos, J.P.S., Letelier, P.S.: Class. Quantum Gravity 10, L75 (1993)
Lemos, J.P.S., Letelier, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 49, 5135 (1994)
Lemos, J.P.S., Letelier, P.S.: Int. J. Mod. Phys. D 5, 53 (1996)
Semerák, O., Žáček, M.: Class. Quantum Gravity 17, 1613 (2000)
Semerák, O.: Class. Quantum Gravity 19, 3829 (2002)
Žáček, M., Semerák, O.: Czechoslov. J. Phys. 52, 19 (2002)
Semerák, O.: Class. Quantum Gravity 20, 1613 (2003)
Semerák, O.: Class. Quantum Gravity 21, 2203 (2004)
Karas, V., Huré, J., Semerák, O.: Class. Quantum Gravity 21, 1 (2004)
Feinstein, A., Ibañez, J., Lazkoz, R.: Astrophys. J. 495, 131 (1998)
Vogt, D., Letelier, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 68(8), 084010 (2003)
Ujevic, M., Letelier, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 70(8), 084015 (2004)
Ledvinka, T., Žofka, M., Bičák, J.: In: Piran T., Ruffini, R. (eds.), Recent Developments in Theoretical and Experimental General Relativity, Gravitation, and Relativistic Field Theories (1999)
García-Reyes, G., González, G.A.: Braz. J. Phys. 37, 1094 (2007)
Letelier, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 60(10), 104042 (1999)
Vogt, D., Letelier, P.S.: Class. Quantum Gravity 21, 3369 (2004)
Katz, J., Bičák, J., Lynden-Bell, D.: Class. Quantum Gravity 16, 4023 (1999)
González, G.A., Gutiérrez-Piñeres, A.C., Ospina, P.A.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 78(6), 064058 (2008)
García, G.R., González, G.A.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 69(12), 124002 (2004)
Vogt, D., Letelier, P.S.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 70(6), 064003 (2004)
García-Reyes, G., González, G.A.: Class. Quantum Gravity 21, 4845 (2004)
García-Reyes, G., González, G.A.: Phys. Rev. D, Part. Fields 70(10), 104005 (2004)
Horský, J., Mitskievitch, N.V.: Czechoslovak. J. Phys. 39, 957 (1989)
Stephani, H., Kramer, D., MacCallum, M., Hoenselaers, C., Herlt, E.: Exact solutions of Einstein’s field equations, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003)
Papapetrou, A., Hamoui, A.: Ann. Inst. Henri Poincaré, a Phys. Théor. 9, 179 (1968)
Lichnerowicz, A.: C.R. Acad. Sci. 273, 528 (1971)
Taub, A.H.: J. Math. Phys. 21, 1423 (1980)
Israel, W.: Nuovo Cim., B 44, 1 (1966)
Israel, W.: Nuovo Cim., B 48, 463 (1967)
Poisson, E.: A Relativist’S Toolkit: The Mathematics of Black-Hole Mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Richterek, L., Novotný, J., Horský, J.: Czechoslov. J. Phys. 50, 925 (2000)
Richterek, L., Horský, J.: Czechoslov. J. Phys. 54, 1451 (2004)
Arfken, G.B., Weber, H.J.: Mathematical Methods for Physicists, 5th ed. Academic Press, San Diego (2001)
Morse, P.M., Feshbach, H.: Methods of Theoretical Physics, International Series in Pure and Applied Physics. McGraw-Hill, New York (1953)
González, G.A., Reina, J.I.: Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 371, 1873 (2006)
Semerák, O.: Class. Quantum Gravity 18, 3589 (2001)
Nakahara, M., Brewer, D.F.: Geometry, Topology and Physics;, 2nd edn. IOP, Bristol (2003)
Acknowledgements
A.C. G.-P. wants to acknowledge financial support from COLCIENCIAS, Colombia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
We pass on to the definition of the Hodge ⋆ (star) operation. Let’s us M a m-dimensional manifold endowed with a metric g. The Hodge ⋆ (star) operation is a map: Ω r(M)→Ω r−m(M) whose action, on the basis of the vector Ω r(M), is defined by [54]
For a r-form
we have
where the totally anti-symmetric tensor ε is
and “∧” is the usual exterior product or wedge product.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gutiérrez-Piñeres, A.C., González, G.A. An Infinite Family of Magnetized Morgan-Morgan Relativistic Thin Disks. Int J Theor Phys 51, 1737–1752 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-011-1051-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10773-011-1051-0