Abstract
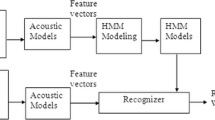
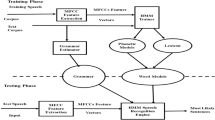
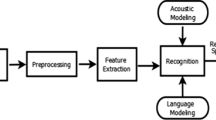
The speech recognition system basically extracts the textual information present in the speech. In the present work, speaker independent isolated word recognition system for one of the south Indian language—Kannada has been developed. For European languages such as English, large amount of research has been carried out in the context of speech recognition. But, speech recognition in Indian languages such as Kannada reported significantly less amount of work and there are no standard speech corpus readily available. In the present study, speech database has been developed by recording the speech utterances of regional Kannada news corpus of different speakers. The speech recognition system has been implemented using the Hidden Markov Tool Kit. Two separate pronunciation dictionaries namely phone based and syllable based dictionaries are built in-order to design and evaluate the performances of phone-level and syllable-level sub-word acoustical models. Experiments have been carried out and results are analyzed by varying the number of Gaussian mixtures in each state of monophone Hidden Markov Model (HMM). Also, context dependent triphone HMM models have been built for the same Kannada speech corpus and the recognition accuracies are comparatively analyzed. Mel frequency cepstral coefficients along with their first and second derivative coefficients are used as feature vectors and are computed in acoustic front-end processing. The overall word recognition accuracy of 60.2 and 74.35 % respectively for monophone and triphone models have been obtained. The study shows a good improvement in the accuracy of isolated-word Kannada speech recognition system using triphone HMM models compared to that of monophone HMM models.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal, R., & Dave, M. (2011). Using gaussian mixtures for Hindi speech recognition system. International Journal of Signal Processing, Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, 4(4), 157–170.
Aggarwal, R., & Dave, M. (2012). Integration of multiple acoustic and language models for improved Hindi speech recognition system. International Journal of Speech Technology, 15(2), 165–180.
Ananthakrishna, T., Maithri, M., & Shama, K. (2015). Kannada word recognition system using HTK. In: 2015 annual IEEE India conference (INDICON) (pp. 1–5). IEEE.
Bharali, S. S., & Kalita, S. K. (2015). A comparative study of different features for isolated spoken word recognition using HMM with reference to assamese language. International Journal of Speech Technology, 18(4), 673–684.
Bhaskar, P. V., Rao, S., & Gopi, A. (2012). HTK based Telugu speech recognition. International Journal of Advanced Research In Computer Science and Software Engineering, 2(12), 307–314.
Davis, S. B., & Mermelstein, P. (1980). Comparison of parametric representations for monosyllabic word recognition in continuously spoken sentences. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 28(4), 357–366.
Deller, J. R, Jr., Proakis, J. G., & Hansen, J. H. (1993). Discrete time processing of speech signals. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall PTR.
Hassan, F., Kotwal, M. R. A., Muhammad, G., & Huda, M. N. (2011). MLN-based bangla ASR using context sensitive triphone HMM. International Journal of Speech Technology, 14(3), 183–191.
Hegde, S., Achary, K., & Shetty, S. (2012). Isolated word recognition for kannada language using support vector machine. In: Wireless networks and computational intelligence (pp. 262–269). Berlin: Springer.
Hegde, S., Achary, K., & Shetty, S. (2015). Statistical analysis of features and classification of alphasyllabary sounds in Kannada language. International Journal of Speech Technology, 18(1), 65–75.
Hemakumar, G., & Punitha, P. (2014b). Speaker dependent continuous Kannada speech recognition using HMM. In: 2014 international conference on intelligent computing applications (ICICA) (pp. 402–405). IEEE.
Hemakumar, G., & Punitha, P. (2014a). Automatic segmentation of Kannada speech signal into syllables and sub-words: Noised and noiseless signals. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research, 5(1), 1707–1711.
Johnson, R. A., Wichern, D. W., et al. (1992). Applied multivariate statistical analysis (Vol. 4). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Kumar, K., & Aggarwal, R. K. (2012). A Hindi speech recognition system for connected words using HTK. International Journal of Computational Systems Engineering, 1(1), 25–32.
Lakshmi, A., & Murthy, H. A. (2006). A syllable based continuous speech recognizer for Tamil. In: INTERSPEECH.
Mannepalli, K., Sastry, P. N., & Suman, M. (2016). MFCC-GMM based accent recognition system for Telugu speech signals. International Journal of Speech Technology, 19(1), 1–7.
Mishra, A., Chandra, M., Biswas, A., & Sharan, S. (2011). Robust features for connected Hindi digits recognition. International Journal of Signal Processing, Image Processing and Pattern Recognition, 4(2), 79–90.
Muralikrishna, H., Ananthakrishna, T., Shama, K. (2013). HMM based isolated Kannada digit recognition system using MFCC. In: 2013 international conference on advances in computing, communications and informatics (ICACCI) (pp. 730–733). IEEE.
Neti, C., Rajput, N., Verma, A. (2002). A large vocabulary continuous speech recognition system for Hindi. In Proceeding of works multimedia signal processing (pp. 475–481).
Nilsson, M. (2005). First order hidden markov model: Theory and implementation issues. Research Report, February 2005, Department of Signal Processing, Blekinge Institute of Technology.
OShaughnessy, D. (2008). Invited paper: Automatic speech recognition: History, methods and challenges. Pattern Recognition, 41(10), 2965–2979.
Panda, S. P., & Nayak, A. K. (2015). Automatic speech segmentation in syllable centric speech recognition system. International Journal of Speech Technology, 19(1), 1–10.
Rabiner, L. R. (1989). A tutorial on hidden markov models and selected applications in speech recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 77(2), 257–286.
Rabiner, L., & Juang, B. H. (2012). Fundamentals of speech recognition. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall.
Radha, V., et al. (2012). Speaker independent isolated speech recognition system for Tamil language using HMM. Procedia Engineering, 30, 1097–1102.
Saini, P., Kaur, P., & Dua, M. (2013). Hindi automatic speech recognition using htk. International Journal of Engineering Trends And Technology, 4(6), 2223–2229.
Shridhara, M., Banahatti, B. K., Narthan, L., Karjigi, V., & Kumaraswamy, R. (2013). Development of Kannada speech corpus for prosodically guided phonetic search engine. In 2013 international conference oriental COCOSDA held jointly with 2013 conference on Asian spoken language research and evaluation (O-COCOSDA/CASLRE) (pp. 1–6). IEEE.
Steever, S. B. (2015). The Dravidian languages. London: Routledge Publications.
Sunitha, K., Kalyani, N., et al. (2012). Isolated word recognition using morph-knowledge for Telugu language. International Journal of Computer Applications, 38(12), 47–54.
Thangarajan, R., Natarajan, A., & Selvam, M. (2009). Syllable modeling in continuous speech recognition for Tamil language. International Journal of Speech Technology, 12(1), 47–57.
Young, S., Evermann, G., Gales, M., Hain, T., Kershaw, D., Liu, X., et al. (1997). The HTK book (Vol. 2). Cambridge: Entropic Cambridge Research Laboratory.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thalengala, A., Shama, K. Study of sub-word acoustical models for Kannada isolated word recognition system. Int J Speech Technol 19, 817–826 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9374-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-016-9374-0