Abstract
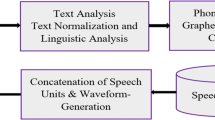
Speech Synthesis deals with artificial production of speech and a text-to-speech system (TTS) in this aspect converts natural language text into a spoken waveform or speech. There are a number of TTS systems available today for different languages, still Indian languages are lacking behind in providing high quality synthesized speech. Even though almost all Indian languages share a common phonetic base, till now a generic model for all official Indian languages is not available. Also, the existing speech synthesis techniques are found to be less effective in the scripting format of Indian languages. Considering the intelligibility of speech production and increasing memory requirement in concatenative speech synthesis technique, in this paper, we have proposed an efficient technique for text-to-speech synthesis in Indian languages. The model uses a pronunciation rule based waveform concatenation approach, to produce intelligible speech minimizing the memory requirement. To show the effectiveness of the technique, at an initial step of implementation the Odia (formerly Oriya), Bengali and Hindi languages are considered. The model is being compared with the existing technique and the results of our experiments show our technique outperforms the existing technique.


























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alías, F., Sevillano, X., Socoró, J. C., & Gonzalvo, X. (2008). Towards high-quality next-generation text-to-speech synthesis: A multidomain approach by automatic domain classification. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 16, 1340–1354.
Alwan, A., Narayanan, S., Strope, B., & Shen, A. (1995). Speech production and perception models and their applications to synthesis, recognition, and coding. In ISSSE ’95, Proceedings of URSI International Symposium on Signals, Systems, and Electronics (pp. 367–372).
Bates, M. (1975). The use of syntax in a speech understanding system. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 23, 112–117.
Bhakat, R. K., Narendra, N. P., & Rao, K. S. (2013). Corpus based emotional speech synthesis in hindi, pattern recognition and machine intelligence. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 8251, 390–395.
Buza, O., Toderean, G., Nica, A., Caruntu, A. (2006). Voice signal processing for speech synthesis. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Automation, Quality and Testing, Robotics (Vol. 2, pp. 360–364).
Feng, J., Ramabhadran, B., Hansel, J., & Williams, J. D. (2012). Trends in speech and language processing. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 29, 177–179.
http://dhvani.sourceforge.net. Accessed 7 August 2014.
http://www.unicode.org/. Accessed 7 August 2014.
http://tdil.mit.gov.in/. Accessed 7 August 2014.
https://ccrma.stanford.edu/courses/422/projects/WaveFormat/. Accessed 7th August 2014.
Liang, M.S., Yang, R.C., Chiang, Y.C., Lyu, D.C., & Lyu, R.Y. (2004). A Taiwanese text-to-speech system with applications to language learning. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Advanced Learning Technologies (pp. 91–95).
Manning, A., & Amare, N. (2007). A simpler approach to grammar: (Re)engineering parts-of-speech instruction to assist EFL/ESP students. In Proceedings of IEEE International Professional Communication Conference (pp. 1–9).
Narendra, N. P., & Rao, K. S. (2013). Optimal weight tuning method for unit selection cost functions in syllable based text-to-speech synthesis. Applied Soft Computing, 13, 773–781.
Narendra, N. P., Rao, K. S., Ghosh, K., Vempada, R. R., & Maity, S. (2011). Development of syllable-based text to speech synthesis system in Bengali. International Journal of Speech Technology, 14, 167–181.
Nebbia, L., Quazza, S., & Luigi Salza, P. (1998). A specialised speech synthesis technique for application to automatic reverse directory service. In 4th Workshop Interactive Voice Technology for Telecommunications (pp. 223–228).
Nukaga, N., Kamoshida, R., Nagamatsu, K., & Kitahara, Y. (2006). Scalable implementation of unit selection based text-to-speech system for embedded solutions. In ICASSP, IEEE.
Rafieee, M.S., Jafari, S., Ahmadi, H.S., & Jafari, M. (2011). Considerations to spoken language recognition for text-to-speech applications. In ICCMS’13th Proceedings (pp. 330–309).
Raghavendra, E.V., Desai, S., Yegnanarayana, B., Black, A.W., & Prahallad, K. (2008). Global syllable set for building speech synthesis in Indian languages. In IEEE Workshop on Spoken Language Technology (pp. 49–52).
Raj, A. K., Sarkar, T., Pammi, S.C., Yuvaraj, S., Bansal, M., Prahallad, K., & Black, A.W. (2007). Text processing for text-to-speech systems in Indian languages. In ISCA’ 6th Workshop on Speech Synthesis.
Rama, J., Ramakrishnan, A. G., Muralishankar, R., & Prathibha, R. (2002). A complete text-to-speech synthesis system in Tamil. In WSS’ Proceedings (pp. 191–194).
Ramani, B., Actlin Jeeva, M.P., Vijayalakshmi, P., & Nagarajan, T. (2013). Voice conversion-based multilingual to polyglot speech synthesizer for Indian languages. In TENCON’s 10th Proceedings (pp. 1–4).
Sak, H., Saraclar, M., & Guungoor, T. (2010). Morphology-based and sub-word language modeling for Turkish speech recognition. In ICASSP Proceedings (pp. 5402–5405).
Tabet, Y., & Boughazi, M. (2011) Speech synthesis techniques. A survey. In Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Workshop on System, Signal Processing and their Applications (pp. 67–70).
Talesara, S., Patil, H.A., Patel, T., Sailor, H., & Shah, N.A. (2013). Novel Gaussian filter-based automatic labeling of speech data for TTS system in Gujarati language. In ICALP Proceedings (pp. 139–142).
Tiomkin, S., Malah, D., Shechtman, S., & Kons, Z. (2011). A hybrid text-to-speech system that combines concatenative and statistical synthesis units. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing, 19, 1278–1288.
Vinodh, M.V., Bellur, A, Narayan, K.B., Thakare, D.M., Susan, A., Suthakar, N.M., & Murthy, H.A. (2010). Using polysyllabic units for text to speech synthesis in Indian languages. In Proceedings NCC (pp. 1–5).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panda, S.P., Nayak, A.K. An efficient model for text-to-speech synthesis in Indian languages. Int J Speech Technol 18, 305–315 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-015-9271-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10772-015-9271-y