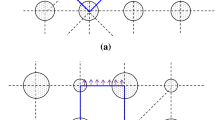
Based on the microstructure features of xonotlite-type micro-pore calcium silicate, two unit cell models, the point-contact hollow spherical model and the surface-contact hollow cubic model, are developed. As one of several excellent insulation materials, xonotlite is represented as porous media with hollow spherical agglomerates. By one-dimensional heat conduction analysis using theunit cell, the effective thermal conductivity of xonotlite is determined. The results show that both of the models are in agreement with experimental data. The algebraic expressions based on the unit cell models can be used to calculate the effective thermal conductivity of porous media that have similar structure features as xonotlite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
White S., and Rask D. (1999). Mater. Technol 14:13
Li M.Q., Chen Y.F., Xia S.Q., Li J.H., and Ling H.X. (2000). J. Chinese Ceramic Soc 28:401 [in Chinese]
Zheng Q.J., and Wang W. (2000). New Build. Mater 10:25 [in Chinese]
Wang Z.Y., Huang Y.M., Wu M.M., and Xue G.Q. (1997). Naihuo Cailiao 31:134 [in Chinese]
Ni W., and Liu F.M. (2000). New Build Mater 1:36 [in Chinese]
Burns P.J., and Tien C.L. (1979). Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 22:929
Xi T.G. (1981). A Study on Thermophysical Properties of Inorganic Material. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai [in Chinese]
Zehnder P., and Schlunder E.U. (1970). Chem. Ingr.-Tech 42:933 [in German]
Zimmerman R.W. (1989). J. Petrol. Sci. Eng 3:219
Verma L.S., Shrotriya A.K., Singh R., and Chaudhary D.R. (1991). J. Phys. D 24:1729
Hsu C.T., Cheng P., and Wong K.W. (1995). J. Heat Transfer 177:264
Yu B.M., and Cheng P. (2002). J. Thermophys. Heat Transfer 16:22
Ma Y.T., Yu B.M., Zhang D.M., and Zou M.Q. (2003). J. Phys. D 36:2157
Feng Y.J., Yu B.M., Zou M.Q., and Zhang D.M. (2004). J. Phys. D 37:3030
Loeb A.L. (1954). J. Am. Ceram. Soc 37:96
Mo L.J., Wang Z.H., and Liu X.H. (1997). A Handbook of Insulating Engineering and Technology. Chinese Petrochemical Press, Beijing [in Chinese]
Saez A.E., Perfetto J.C., and Rusinek L. (1991). Trans. Porous Media 6:143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Paper presented at the Seventh Asian Thermophysical Properties Conference, August 23–28, 2004, Hefei and Huangshan, Anhui, P. R. China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, F., Wei, G., Zhang, X. et al. Two Effective Thermal Conductivity Models for Porous Media with Hollow Spherical Agglomerates. Int J Thermophys 27, 293–303 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-006-0032-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-006-0032-7