Abstract
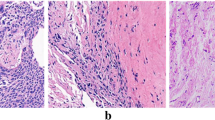
Based on tissues from 34 patients, we investigated the performance of terahertz (THz) time-domain spectroscopy (TDS) to diagnose gastric tissues in surgical resected specimens. The results indicated that THz absorption spectra not only can clearly distinguish cancer tissues from normal tissues without hematoxylin-eosin staining (H&E staining) but also can identify carcinoma in situ and cancer tissues. Using THz-TDS to directly diagnose gastric cancer was also demonstrated with another 40 samples. Comparison of the data with the results of pathological examination indicated that the sensitivity and specificity were both 100%. Due to the ability to perform quantitative analysis and enable follow-up staining and traditional histopathological analysis, our study indicated considerable potential of THz-TDS for future automation, which is critical for the rapid and thorough prescreening of gastric cancer pathological examinations.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Yang, R. Zheng, N. Wang, Y. Yuan, S. Liu, H. Li, S. Zhang, H. Zeng, and W. Chen, “Incidence and mortality of stomach cancer in China, 2014,” Chinese J. Cancer Res. 30(3), 291–298 (2018).
W. Chen, R. Zheng, P. D. Baade, S. Zhang, H. Zeng, F. Bray, A. Jemal, X. Q. Yu, and J. He, “Cancer statistics in China, 2015,” CA. Cancer J. Clin. 66(2), 115–132 (2016).
S. Luo, C. Chen, H. Mao, and S. Jin, “Discrimination of premalignant lesions and cancer tissues from normal gastric tissues using Raman spectroscopy,” J. Biomed. Opt. 18(6), 067004:1-8 (2013).
S. K. Teh, W. Zheng, K. Y. Ho, M. Teh, K. G. Yeoh, and Z. Huang, “Diagnostic potential of near-infrared Raman spectroscopy in the stomach: Differentiating dysplasia from normal tissue,” Brit. J. Cancer 98(2), 457–465 (2008).
Q. Li, W. Wang, X. Ling, and J. G. Wu, “Detection of gastric cancer with fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and support vector machine classification,” Biomed Res. Int. 2013(9), 4–7 (2013).
W. S. Yi, D. S. Cui, Z. Li, L. L. Wu, A. G. Shen, and J. M. Hu, “Gastric cancer differentiation using Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy with unsupervised pattern recognition,” Spectrochim. Acta. A. 101, 127–131 (2013).
Y. Bin Ji, C. H. Park, H. Kim, S.-H. Kim, G. M. Lee, S. K. Noh, T.-I. Jeon, J.-H. Son, Y.-M. Huh, S. Haam, S. J. Oh, S. K. Lee, and J.-S. Suh, “Feasibility of terahertz reflectometry for discrimination of human early gastric cancers,” Biomed. Opt. Express 6(4), 1398–1406 (2015).
D. Hou, X. Li, J. Cai, Y. Ma, X. Kang, P. Huang, and G. Zhang, “Terahertz spectroscopic investigation of human gastric normal and tumor tissues,” Phys. Med. Biol. 59(18), 5423–5440 (2014).
H. A. Kashanian, H. B. Ghaffary, and N. C. Bagherzadeh, “Gastric cancer diagnosis using terahertz imaging,” Majlesi J. Multimed. Process. 4(4), 1–7 (2015).
Y. Cao, P. Huang, X. Li, W. Ge, D. Hou and G. Zhang, “Terahertz spectral unmixing based method for identifying gastric cancer,” Phys. Med. Biol. 63(3), 035016 (2018)
F. Wahaia, I. Kasalynas, D. Seliuta, G. Molis, A. Urbanowicz, C. D. Carvalho Silva, F. Carneiro, G. Valusis, and P. L. Granja, “Terahertz spectroscopy for the study of paraffin-embedded gastric cancer samples,” Journal of Molecular Structure, 1079, 391–395 (2015).
E. Berry, G. C. Walker, A. J. Fitzgerald, N. N. Zinov’ev, M. Chamberlain, S. W. Smye, R. E. Miles, and M. A. Smith, “Do in vivo terahertz imaging systems comply with safety guidelines?” J. Laser Appl. 15(3), 192–198 (2003).
K. H. Ng, “Non-ionizing radiations - sources, biological effects, emissions and exposures,” in Proceedings of the International Conference on Non-Ionizing Radiation at UNITEN (ICNIR2003) Electromagnetic Fields and Our Health (Selangor, Malaysia, 2003), pp. 1–16.
M. Yamaguchi, F. Miyamaru, K. Yamamoto, M. Tani, and M. Hangyo, “Terahertz absorption spectra of L-, D-, and DL-alanine and their application to determination of enantiometric composition,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 86(5), 1–3 (2005).
N. Li, J. L. Shen, J. H. Sun, L. S. Liang, X. Y. Xu, M. H. Lu, and Y. Jia, “Study on the THz spectrum of methamphetamine,” Opt. Express 13(18), 6750–6755 (2005).
T. Ikeda, A. Matsushita, M. Tatsuno, Y. Minami, M. Yamaguchi, K. Yamamoto, M. Tani, and M. Hangyo, “Investigation of inflammable liquids by terahertz spectroscopy,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 87(3), 034105:1-3 (2005).
K. Yamamoto, M. Yamaguchi, M. Tani, M. Hangyo, S. Teramura, T. Isu, and N. Tomita, “Degradation diagnosis of ultrahigh-molecular weight polyethylene with terahertz-time-domain spectroscopy,” Appl. Phys. Lett. 85(22), 5194–5196 (2004).
P. C. Ashworth, E. Pickwell-MacPherson, E. Provenzano, S. E. Pinder, A. D. Purushotham, M. Pepper, and V. P. Wallace, “Terahertz pulsed spectroscopy of freshly excised human breast cancer,” Opt. Express 17(15), 12444-12454 (2009).
H. Chen, T. H. Chen, T. F. Tseng, J. T. Lu, C. C. Kuo, S. C. Fu, W. J. Lee, Y. F. Tsai, Y. Y. Huang, E. Y. Chuang, Y. J. Hwang, and C. K. Sun, “High-sensitivity in vivo THz transmission imaging of early human breast cancer in a subcutaneous xenograft mouse model,” Opt. Express 19(22), 21552-21562 (2011).
H. Chen, S. H. Ma, W. X. Yan, X. M. Wu, and X. Z. Wang, “The diagnosis of human liver cancer by using THz fiber-scanning near-field imaging,” Chin. Phys. Lett. 30(3), 030702:1–3 (2013).
P. Huang, Y. Cao, J. Chen, W. Ge, D. Hou, and G. Zhang, “Analysis and inspection techniques for mouse liver injury based on terahertz spectroscopy,” Opt. Express 27(18), 26014-26026 (2019).
R. M. Woodward, V. P. Wallace, D. D. Arnone, E. H. Linfield, and M. Pepper, “Terahertz pulsed imaging of skin cancer in the time and frequency domain,” J. Biol. Phys. 29(2–3), 257–259 (2003).
R. M. Woodward, B. E. Cole, V. P. Wallace, R. J. Pye, D. D. Arnone, E. H. Linfield, and M. Pepper, “Terahertz pulse imaging in reflection geometry of human skin cancer and skin tissue,” Phys. Med. Biol. 47(21), 3853–3863 (2002).
G. M. Png, J. W. Choi, B. W. H. Ng, S. P. Mickan, D. Abbott, and X. C. Zhang, “The impact of hydration changes in fresh bio-tissue on THz spectroscopic measurements,” Phys. Med. Biol. 53(13), 3501–3517 (2008).
W. Withayachumnankul and M. Naftaly, “Fundamentals of measurement in terahertz time-domain spectroscopy,” J. Infrared Millim. Te. 35(8), 610–637 (2014).
I. Pupeza, R. Wilk, and M. Koch, “Highly accurate optical material parameter determination with THz time-domain spectroscopy,” Opt. Express 15(7), 4335-4350 (2007).
L. I. Jiusheng, “Optical parameters of vegetable oil studied by terahertz time-domain spectroscopy,” Appl. Spectrosc. 64(2), 231–234 (2010).
S. Sy, S. Huang, Y. X. J. Wang, J. Yu, A. T. Ahuja, Y. T. Zhang, and E. Pickwell-MacPherson, “Terahertz spectroscopy of liver cirrhosis: Investigating the origin of contrast,” Phys. Med. Biol. 55(24), 7587–7596 (2010).
A. K. Akobeng, “Understanding diagnostic tests 1: Sensitivity, specificity and predictive values,” Acta Paediatr. 96(3), 338–341 (2007).
D. G. Altman and J. M. Bland, “Statistics Notes: Diagnostic tests 1: Sensitivity and specificity,” Br. Med. J. 308(6943), 1552 (1994).
Funding
This study was supported by a Joint Research Project between Southeast University and Nanjing Medical University (No. 3207027381).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Han, J., Wang, D. et al. Application of THz Time-Domain Spectroscopy to Diagnose Gastric Cancer Tissues in Surgical Resected Specimens. J Infrared Milli Terahz Waves 42, 802–812 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-021-00805-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10762-021-00805-7