Abstract
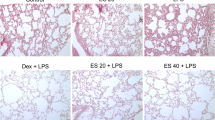
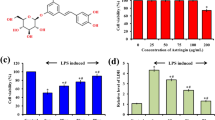
Sweroside, as one of the main components of Swertia L. in Gentianaceae, has the effect of clearing heat and detoxifying. In previous studies, sweroside has been reported to have anti-inflammatory effect on LPS-induced inflammation by alleviating NF-κB signaling pathway. In this paper, we investigate the anti-inflammatory effects of sweroside by establishing LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) model in mice. Experimental results showed that sweroside could reduce the wet-to-dry ratio of the lung and inhibit MPO activity. In addition, it turned out that sweroside reduced pathological changes in lung tissue and the numbers of inflammatory cells. Moreover, sweroside significantly reduced the levels of inflammatory cytokines and down-regulated the NF-κB signaling pathway. And the results demonstrated that sweroside could increase the expression of SIRT1, and the protective effects of sweroside on LPS-induced ALI were reversed by SIRT1 inhibitor EX-527. In conclusion, sweroside can protect LPS-induced ALI mice through inhibiting inflammation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Ferguson, N.D., F. Frutos-Vivar, A. Esteban, P. Fernandez-Segoviano, J.A. Aramburu, L. Najera, and T.E. Stewart. 2005. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: underrecognition by clinicians and diagnostic accuracy of three clinical definitions. Crit Care Med 33: 2228–2234.
Goodman, R.B., J. Pugin, J.S. Lee, and M.A. Matthay. 2003. Cytokine-mediated inflammation in acute lung injury. Cytokine & Growth Factor Reviews 14: 523–535.
Murray, J.F., M.A. Matthay, J.M. Luce, and M.R. Flick. 1988. An expanded definition of the adult respiratory-distress syndrome. American Review of Respiratory Disease 138: 720–723.
Ruffini, E., A. Parola, E. Papalia, P.L. Filosso, M. Mancuso, A. Oliaro, G. Actis-Dato, and G. Maggi. 2001. Frequency and mortality of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome after pulmonary resection for bronchogenic carcinoma. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 20: 30–37.
Blank, R., and L.M. Napolitano. 2011. Epidemiology of ARDS and ALI. Crit Care Clin 27: 439–458.
Fitzgerald, K.A., D.C. Rowe, and D.T. Golenbock. 2004. Endotoxin recognition and signal transduction by the TLR4/MD2-complex. Microbes Infect 6: 1361–1367.
Lu, Y.C., W.C. Yeh, and P.S. Ohashi. 2008. LPS/TLR4 signal transduction pathway. Cytokine 42: 145–151.
Wang, R., Z.Y. Dong, X.Z. Lan, Z.H. Liao, and M. Chen. 2019. Sweroside Alleviated LPS-induced inflammation via SIRT1 mediating NF-kappa B and FOXO1 signaling pathways in RAW264.7 Cells. Molecules 24.
Zhang, R., C.M. Wang, H.J. Jiang, X.G. Tian, W.J. Li, W. Liang, J.H. Yang, C.L. Zhong, Y.H. Chen, and T. Li. 2019. Protective effects of sweroside on IL-1-induced inflammation in rat articular chondrocytes through suppression of NF-B and mTORC1 signaling pathway. Inflammation 42: 496–505.
Yang, Q.L., F. Yang, J.T. Gong, X.W. Tang, G.Y. Wang, Z.T. Wang, and L. Yang. 2016. Sweroside ameliorates alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced cholestatic liver injury in mice by regulating bile acids and suppressing pro-inflammatory responses. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 37: 1218–1228.
Spragg, R.G., G.R. Bernard, W. Checkley, J.R. Curtis, O. Gajic, G. Guyatt, J. Hall, E. Israel, M. Jain, D.M. Needham, A.G. Randolph, G.D. Rubenfeld, D. Schoenfeld, B.T. Thompson, L.B. Ware, D. Young, and A.L. Harabin. 2010. Beyond mortality future clinical research in acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 181: 1121–1127.
Parker, J.C. 2011. Acute lung injury and pulmonary vascular permeability: use of transgenic models. Comprehensive Physiology 1: 835–882.
De Luca, D., M. Piastra, F. Tosi, S. Pulitano, A. Mancino, O. Genovese, D. Pietrini, and G. Conti. 2012. Pharmacological Therapies for pediatric and neonatal ALI/ARDS: an evidence-based review. Current Drug Targets 13: 906–916.
Zhong, W.T., Y.W. Cui, Q.L. Yu, X.X. Xie, Y. Liu, M.M. Wei, X.X. Ci, and L.P. Peng. 2014. Modulation of LPS-Stimulated pulmonary inflammation by borneol in murine acute lung injury model. Inflammation 37: 1148–1157.
Chen, H., C. Bai, and X. Wang. 2010. The value of the lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory medicine. Expert Rev Respir Med 4: 773–783.
Chignard, M., and V. Balloy. 2000. Neutrophil recruitment and increased permeability during acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 279: L1083–L1090.
Kawai, T., and S. Akira. 2007. Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13: 460–469.
Maruyama, K., Y. Takada, N. Ray, Y. Kishimoto, J.M. Penninger, H. Yasuda, and K. Matsuo. 2006. Receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand and osteoprotegerin regulate proinflammatory cytokine production in mice. Journal of Immunology 177: 3799–3805.
Rahman, A., and F. Fazal. 2011. Blocking NF-kappaB: an inflammatory issue. Proc Am Thorac Soc 8: 497–503.
Xie, J., X.M. Zhang, and L. Zhang. 2013. Negative regulation of inflammation by SIRT1. Pharmacological Research 67: 60–67.
Hwang, J.W., H.W. Yao, S. Caito, I.K. Sundar, and I. Rahman. 2013. Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular senescence. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 61: 95–110.
Yang, H.Y., W. Zhang, H. Pan, H.G. Feldser, E. Lainez, C. Miller, S. Leung, Z. Zhong, H.Z. Zhao, S. Sweitzer, et al. 2012. SIRT1 activators suppress inflammatory responses through promotion of p65 Deacetylation and inhibition of NF-kappa B activity. Plos One 7.
Tian, Y.L., J.T. Ma, W.D. Wang, L.J. Zhang, J. Xu, K. Wang, and D.F. Li. 2016. Resveratrol supplement inhibited the NF-kappa B inflammation pathway through activating AMPK alpha-SIRT1 pathway in mice with fatty liver. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 422: 75–84.
Yuan, Q., D.Q. Zhang, C.Q. Liu, C.C. Zhang, and D. Yuan. 2018. Chikusetsusaponin V inhibits LPS-activated inflammatory responses via SIRT1/NF-B signaling pathway in RAW264.7 cells. Inflammation 41: 2149–2159.
Funding
This work was supported by the grant for Key Research and Development Project of Shandong Province (2019GSF108265).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Juan Wang and Fengshan Wang designed the experiment; Juan Wang, Xiaolan Cai, Rui Ma, and Dapeng Lei did the experiment; Xinliang Pan analyzed the data; Juan Wang and Xiaolan Cai revised the paper; Juan Wang wrote the paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
All the experimental protocols in this study were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Shandong University. All authors consent to participate this research.
Consent for Publication
All authors consent to publish this article.
Competing Interests
All authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Cai, X., Ma, R. et al. Anti-inflammatory Effects of Sweroside on LPS-Induced ALI in Mice Via Activating SIRT1. Inflammation 44, 1961–1968 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01473-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-021-01473-4