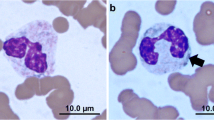
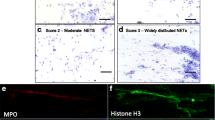
Abstract
Asthma is a common and debilitating chronic airway disease that affects people and horses of all ages worldwide. While asthma in humans most commonly involves an excessive type 2 immune response and eosinophilic inflammation, neutrophils have also been recognized as key players in the pathophysiology of asthma, including in the severe asthma phenotype where neutrophilic inflammation predominates. Severe equine asthma syndrome (sEAS) features prominent neutrophilic inflammation and has been increasingly used as a naturally occurring animal model for the study of human neutrophilic asthma. This comparative review examines the recent literature in order to explore the role of neutrophil inflammatory functions in the pathophysiology and immunology of asthma in humans and horses.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Network, G.A., The global asthma report 2018. 2018.
Hotchkiss, J.W., S.W. Reid, and R.M. Christley. 2007. A survey of horse owners in Great Britain regarding horses in their care. Part 2: risk factors for recurrent airway obstruction. Equine Veterinary Journal 39 (4): 301–308.
Kuruvilla, M.E., F.E. Lee, and G.B. Lee. 2019. Understanding asthma phenotypes, endotypes, and mechanisms of disease. Clinical Reviews in Allergy and Immunology 56 (2): 219–233.
Couëtil, L.L., J.M. Cardwell, V. Gerber, J.P. Lavoie, R. Léguillette, and E.A. Richard. 2016. Inflammatory airway disease of horses--revised consensus statement. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 30 (2): 503–515.
Sheats, M.K., K.U. Davis, and J.A. Poole. 2019. Comparative review of asthma in farmers and horses. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports 19 (11): 50.
Bond, S., R. Léguillette, E.A. Richard, L. Couetil, J.P. Lavoie, J.G. Martin, and R.S. Pirie. 2018. Equine asthma: integrative biologic relevance of a recently proposed nomenclature. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 32 (6): 2088–2098.
Loza, M.J., et al. 2016. Validated and longitudinally stable asthma phenotypes based on cluster analysis of the ADEPT study. Respiratory Research 17 (1): 165.
Lefaudeux, D., B. de Meulder, M.J. Loza, N. Peffer, A. Rowe, F. Baribaud, A.T. Bansal, R. Lutter, A.R. Sousa, J. Corfield, I. Pandis, P.S. Bakke, M. Caruso, P. Chanez, S.E. Dahlén, L.J. Fleming, S.J. Fowler, I. Horvath, N. Krug, P. Montuschi, M. Sanak, T. Sandstrom, D.E. Shaw, F. Singer, P.J. Sterk, G. Roberts, I.M. Adcock, R. Djukanovic, C. Auffray, K.F. Chung, N. Adriaens, H. Ahmed, A. Aliprantis, K. Alving, P. Badorek, D. Balgoma, C. Barber, A. Bautmans, A.F. Behndig, E. Bel, J. Beleta, A. Berglind, A. Berton, J. Bigler, H. Bisgaard, G. Bochenek, M.J. Boedigheimer, K. Bøonnelykke, J. Brandsma, A. Braun, P. Brinkman, D. Burg, D. Campagna, L. Carayannopoulos, J.P. Carvalho da Purfição Rocha, A. Chaiboonchoe, R. Chaleckis, C. Coleman, C. Compton, A. D'Amico, B. Dahlén, J. de Alba, P. de Boer, I. de Lepeleire, T. Dekker, I. Delin, P. Dennison, A. Dijkhuis, A. Draper, J. Edwards, R. Emma, M. Ericsson, V. Erpenbeck, D. Erzen, C. Faulenbach, K. Fichtner, N. Fitch, B. Flood, U. Frey, M. Gahlemann, G. Galffy, H. Gallart, T. Garret, T. Geiser, J. Gent, M. Gerhardsson de Verdier, D. Gibeon, C. Gomez, K. Gove, N. Gozzard, Y.K. Guo, S. Hashimoto, J. Haughney, G. Hedlin, P.P. Hekking, E. Henriksson, L. Hewitt, T. Higgenbottam, U. Hoda, J. Hohlfeld, C. Holweg, P. Howarth, R. Hu, S. Hu, X. Hu, V. Hudson, A.J. James, J. Kamphuis, E.J. Kennington, D. Kerry, M. Klüglich, H. Knobel, R. Knowles, A. Knox, J. Kolmert, J. Konradsen, M. Kots, L. Krueger, S. Kuo, M. Kupczyk, B. Lambrecht, A.S. Lantz, L. Larsson, N. Lazarinis, S. Lone-Satif, L. Marouzet, J. Martin, S. Masefield, C. Mathon, J.G. Matthews, A. Mazein, S. Meah, A. Maiser, A. Menzies-Gow, L. Metcalf, R. Middelveld, M. Mikus, M. Miralpeix, P. Monk, N. Mores, C.S. Murray, J. Musial, D. Myles, S. Naz, K. Nething, B. Nicholas, U. Nihlen, P. Nilsson, B. Nordlund, J. Östling, A. Pacino, L. Pahus, S. Palkonnen, S. Pavlidis, G. Pennazza, A. Petrén, S. Pink, A. Postle, P. Powel, M. Rahman-Amin, N. Rao, L. Ravanetti, E. Ray, S. Reinke, L. Reynolds, K. Riemann, J. Riley, M. Robberechts, A. Roberts, C. Rossios, K. Russell, M. Rutgers, G. Santini, M. Sentoninco, C. Schoelch, J.P.R. Schofield, W. Seibold, R. Sigmund, M. Sjödin, P.J. Skipp, B. Smids, C. Smith, J. Smith, K.M. Smith, P. Söderman, A. Sogbesan, D. Staykova, K. Strandberg, K. Sun, D. Supple, M. Szentkereszty, L. Tamasi, K. Tariq, J.O. Thörngren, B. Thornton, J. Thorsen, S. Valente, W. van Aalderenm, M. van de Pol, K. van Drunen, M. van Geest, J. Versnel, J. Vestbo, A. Vink, N. Vissing, C. von Garnier, A. Wagerner, S. Wagers, F. Wald, S. Walker, J. Ward, Z. Weiszhart, K. Wetzel, C.E. Wheelock, C. Wiegman, S. Williams, S.J. Wilson, A. Woosdcock, X. Yang, E. Yeyashingham, W. Yu, W. Zetterquist, and K. Zwinderman. 2017. U-BIOPRED clinical adult asthma clusters linked to a subset of sputum omics. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 139 (6): 1797–1807.
Chung, K.F., S.E. Wenzel, J.L. Brozek, A. Bush, M. Castro, P.J. Sterk, I.M. Adcock, E.D. Bateman, E.H. Bel, E.R. Bleecker, L.P. Boulet, C. Brightling, P. Chanez, S.E. Dahlen, R. Djukanovic, U. Frey, M. Gaga, P. Gibson, Q. Hamid, N.N. Jajour, T. Mauad, R.L. Sorkness, and W.G. Teague. 2014. International ERS/ATS guidelines on definition, evaluation and treatment of severe asthma. The European Respiratory Journal 43 (2): 343–373.
Svenningsen, S., and P. Nair. 2017. Asthma endotypes and an overview of targeted therapy for asthma. Frontiers of Medicine (Lausanne) 4: 158.
McBrien, C.N., and A. Menzies-Gow. 2017. The biology of eosinophils and their role in asthma. Frontiers of Medicine (Lausanne) 4: 93.
Grünig, G., et al. 1998. Requirement for IL-13 independently of IL-4 in experimental asthma. Science 282 (5397): 2261–2263.
Frigas, E., and G.J. Gleich. 1986. The eosinophil and the pathophysiology of asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 77 (4): 527–537.
van Dalen, C.J., and A.J. Kettle. 2001. Substrates and products of eosinophil peroxidase. The Biochemical Journal 358 (Pt 1): 233–239.
Ohno, I., Y. Nitta, K. Yamauchi, H. Hoshi, M. Honma, K. Woolley, P. O'Byrne, G. Tamura, M. Jordana, and K. Shirato. 1996. Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF beta 1) gene expression by eosinophils in asthmatic airway inflammation. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 15 (3): 404–409.
Douwes, J., P. Gibson, J. Pekkanen, and N. Pearce. 2002. Non-eosinophilic asthma: importance and possible mechanisms. Thorax 57 (7): 643–648.
Carr, T.F., A.A. Zeki, and M. Kraft. 2018. Eosinophilic and noneosinophilic asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 197 (1): 22–37.
Telenga, E.D., S.W. Tideman, H.A.M. Kerstjens, N.H.T.. Hacken, W. Timens, D.S. Postma, and M. van den Berge. 2012. Obesity in asthma: more neutrophilic inflammation as a possible explanation for a reduced treatment response. Allergy 67 (8): 1060–1068.
Gibson, P.G., J.L. Simpson, and N. Saltos. 2001. Heterogeneity of airway inflammation in persistent asthma : evidence of neutrophilic inflammation and increased sputum interleukin-8. Chest 119 (5): 1329–1336.
Mahmutovic Persson, I., M. Menzel, S. Ramu, S. Cerps, H. Akbarshahi, and L. Uller. 2018. IL-1β mediates lung neutrophilia and IL-33 expression in a mouse model of viral-induced asthma exacerbation. Respiratory Research 19 (1): 16.
Ricciardolo, F.L.M., V. Sorbello, A. Folino, F. Gallo, G.M. Massaglia, G. Favatà, S. Conticello, D. Vallese, F. Gani, M. Malerba, G. Folkerts, G. Rolla, M. Profita, T. Mauad, A. di Stefano, and G. Ciprandi. 2017. Identification of IL-17F/frequent exacerbator endotype in asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 140 (2): 395–406.
Magnan, A., A. Bourdin, C.M. Prazma, F.C. Albers, R.G. Price, S.W. Yancey, and H. Ortega. 2016. Treatment response with mepolizumab in severe eosinophilic asthma patients with previous omalizumab treatment. Allergy 71 (9): 1335–1344.
Busse, W., et al. 2019. Anti-IL-5 treatments in patients with severe asthma by blood eosinophil thresholds: Indirect treatment comparison. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 143 (1): 190–200.e20.
Kubes, P. 2018. The enigmatic neutrophil: what we do not know. Cell and Tissue Research 371 (3): 399–406.
Kolaczkowska, E., and P. Kubes. 2013. Neutrophil recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nature Reviews. Immunology 13 (3): 159–175.
Phillipson, M., and P. Kubes. 2011. The neutrophil in vascular inflammation. Nature Medicine 17 (11): 1381–1390.
Jorch, S.K., and P. Kubes. 2017. An emerging role for neutrophil extracellular traps in noninfectious disease. Nature Medicine 23 (3): 279–287.
Ciepiela, O., M. Ostafin, and U. Demkow. 2015. Neutrophils in asthma--a review. Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology 209: 13–16.
Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of asthma (EPR-3). 2007. National Heart. Lung, and Blood Institute.
Sato, E., S. Koyama, A. Takamizawa, T. Masubuchi, K. Kubo, R.A. Robbins, S. Nagai, and T. Izumi. 1999. Smoke extract stimulates lung fibroblasts to release neutrophil and monocyte chemotactic activities. The American Journal of Physiology 277 (6): L1149–L1157.
Cox, G. 1995. Glucocorticoid treatment inhibits apoptosis in human neutrophils. Separation of survival and activation outcomes. Journal of Immunology 154 (9): 4719–4725.
Pham, D.L., G.Y. Ban, S.H. Kim, Y.S. Shin, Y.M. Ye, Y.J. Chwae, and H.S. Park. 2017. Neutrophil autophagy and extracellular DNA traps contribute to airway inflammation in severe asthma. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 47 (1): 57–70.
Wu, W., E. Bleecker, W. Moore, W.W. Busse, M. Castro, K.F. Chung, W.J. Calhoun, S. Erzurum, B. Gaston, E. Israel, D. Curran-Everett, and S.E. Wenzel. 2014. Unsupervised phenotyping of Severe Asthma Research Program participants using expanded lung data. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 133 (5): 1280–1288.
Moore, W.C., et al. 2014. Sputum neutrophil counts are associated with more severe asthma phenotypes using cluster analysis. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 133 (6): 1557–63.e5.
Ordoñez, C.L., et al. 2000. Increased neutrophil numbers and IL-8 levels in airway secretions in acute severe asthma: Clinical and biologic significance. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 161 (4 Pt 1): 1185–1190.
Shaw, D.E., M.A. Berry, B. Hargadon, S. McKenna, M.J. Shelley, R.H. Green, C.E. Brightling, A.J. Wardlaw, and I.D. Pavord. 2007. Association between neutrophilic airway inflammation and airflow limitation in adults with asthma. Chest 132 (6): 1871–1875.
Nabe, T. 2020. Steroid-resistant asthma and neutrophils. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 43 (1): 31–35.
Kianmeher, M., V. Ghorani, and M.H. Boskabady. 2016. Animal model of asthma, various methods and measured parameters: a methodological review. Iranian Journal of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology 15 (6): 445–465.
Nials, A.T., and S. Uddin. 2008. Mouse models of allergic asthma: acute and chronic allergen challenge. Disease Models & Mechanisms 1 (4-5): 213–220.
Kalidhindi, R.S.R., et al. 2019. Role of estrogen receptors α and β in a murine model of asthma: exacerbated airway hyperresponsiveness and remodeling in ERβ knockout mice. Frontiers in Pharmacology 10: 1499.
Vandamme, T.F. 2014. Use of rodents as models of human diseases. Journal of Pharmacy & Bioallied Sciences 6 (1): 2–9.
Jucker, M. 2010. The benefits and limitations of animal models for translational research in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature Medicine 16 (11): 1210–1214.
Marqués-García, F., and E. Marcos-Vadillo. 2016. Review of mouse models applied to the study of asthma. Methods in Molecular Biology 1434: 213–222.
Wenzel, S., and S.T. Holgate. 2006. The mouse trap: it still yields few answers in asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 174 (11): 1173–1176 discussion 1176-8.
Kumar, R.K., and P.S. Foster. 2002. Modeling allergic asthma in mice: pitfalls and opportunities. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 27 (3): 267–272.
Kumar, R.K., and P.S. Foster. 2012. Are mouse models of asthma appropriate for investigating the pathogenesis of airway hyper-responsiveness? Frontiers in Physiology 3: 312.
Leclere, M., A. Lavoie-Lamoureux, and J.P. Lavoie. 2011. Heaves, an asthma-like disease of horses. Respirology 16 (7): 1027–1046.
Davis, K.U., and M.K. Sheats. 2019. Bronchoalveolar lavage cytology characteristics and seasonal changes in a herd of pastured teaching horses. Frontiers in Veterinary Science 6: 74.
Ewart, S.L., and N.E. Robinson. 2007. Genes and respiratory disease: a first step on a long journey. Equine Veterinary Journal 39 (3): 270–274.
McGorum, B.C., P.M. Dixon, and R.E. Halliwell. 1993. Responses of horses affected with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease to inhalation challenges with mould antigens. Equine Veterinary Journal 25 (4): 261–267.
Jose-Cunilleras, E., C.W. Kohn, A. Hillier, W.J.A. Saville, and G. Lorch. 2001. Intradermal testing in healthy horses and horses with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, recurrent urticaria, or allergic dermatitis. Journal of the American Veterinary Medical Association 219 (8): 1115–1121.
Gorman, B.K., and M. Chu. 2009. Racial and ethnic differences in adult asthma prevalence, problems, and medical care. Ethnicity & Health 14 (5): 527–552.
Shah, R., and D.C. Newcomb. 2018. Sex bias in asthma prevalence and pathogenesis. Frontiers in Immunology 9: 2997.
Marti, E., et al. 1991. The genetic basis of equine allergic diseases. 1. Chronic hypersensitivity bronchitis. Equine Veterinary Journal 23 (6): 457–460.
Ramseyer, A., C. Gaillard, D. Burger, R. Straub, U. Jost, C. Boog, E. Marti, and V. Gerber. 2007. Effects of genetic and environmental factors on chronic lower airway disease in horses. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 21 (1): 149–156.
McPherson, E.A., G.H.K. Lawson, J.R. Murphy, J.M. Nicholson, R.G. BREEZE, and H.M. PIRIE. 1979. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD): factors influencing the occurrence. Equine Veterinary Journal 11 (3): 167–171.
Lavoie, J.P., et al. 2001. Neutrophilic airway inflammation in horses with heaves is characterized by a Th2-type cytokine profile. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 164 (8 Pt 1): 1410–1413.
Padoan, E., S. Ferraresso, S. Pegolo, M. Castagnaro, C. Barnini, and L. Bargelloni. 2013. Real time RT-PCR analysis of inflammatory mediator expression in recurrent airway obstruction-affected horses. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 156 (3-4): 190–199.
Ainsworth, D.M., G. Grünig, M.B. Matychak, J. Young, B. Wagner, H.N. Erb, and D.F. Antczak. 2003. Recurrent airway obstruction (RAO) in horses is characterized by IFN-gamma and IL-8 production in bronchoalveolar lavage cells. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 96 (1-2): 83–91.
Ainsworth, D.M., B. Wagner, M. Franchini, G. Grünig, H.N. Erb, and J.Y. Tan. 2006. Time-dependent alterations in gene expression of interleukin-8 in the bronchial epithelium of horses with recurrent airway obstruction. American Journal of Veterinary Research 67 (4): 669–677.
Hastie, A.T., et al. 2010. Analyses of asthma severity phenotypes and inflammatory proteins in subjects stratified by sputum granulocytes. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 125 (5): 1028–1036.e13.
Durrant, D.M., and D.W. Metzger. 2010. Emerging roles of T helper subsets in the pathogenesis of asthma. Immunological Investigations 39 (4-5): 526–549.
Lange-Consiglio, A., L. Stucchi, E. Zucca, J.P. Lavoie, F. Cremonesi, and F. Ferrucci. 2019. Insights into animal models for cell-based therapies in translational studies of lung diseases: is the horse with naturally occurring asthma the right choice? Cytotherapy 21 (5): 525–534.
Venner, M., S. Schmidbauer, W. Drommer, and E. Deegen. 2006. Percutaneous lung biopsy in the horse: comparison of two instruments and repeated biopsy in horses with induced acute interstitial pneumopathy. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 20 (4): 968–973.
Clements, J.M., and R.S. Pirie. 2007. Respirable dust concentrations in equine stables. Part 1: validation of equipment and effect of various management systems. Research in Veterinary Science 83 (2): 256–262.
Berndt, A., F.J. Derksen, and N. Edward Robinson. 2010. Endotoxin concentrations within the breathing zone of horses are higher in stables than on pasture. Veterinary Journal 183 (1): 54–57.
Wålinder, R., M. Riihimäki, S. Bohlin, C. Hogstedt, T. Nordquist, A. Raine, J. Pringle, and L. Elfman. 2011. Installation of mechanical ventilation in a horse stable: effects on air quality and human and equine airways. Environmental Health and Preventive Medicine 16 (4): 264–272.
Ivester, K.M., L.L. Couëtil, G.E. Moore, N.J. Zimmerman, and R.E. Raskin. 2014. Environmental exposures and airway inflammation in young thoroughbred horses. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 28 (3): 918–924.
Poole, J.A., and D.J. Romberger. 2012. Immunological and inflammatory responses to organic dust in agriculture. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology 12 (2): 126–132.
Pirie, R.S., P.M. Dixon, D.D. Collie, and B. McGorum. 2001. Pulmonary and systemic effects of inhaled endotoxin in control and heaves horses. Equine Veterinary Journal 33 (3): 311–318.
Michel, O., J. Kips, J. Duchateau, F. Vertongen, L. Robert, H. Collet, R. Pauwels, and R. Sergysels. 1996. Severity of asthma is related to endotoxin in house dust. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 154 (6 Pt 1): 1641–1646.
Dauvillier, J., F. Ter Woort, and E. van Erck-Westergren. 2019. Fungi in respiratory samples of horses with inflammatory airway disease. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine 33 (2): 968–975.
Fairs, A., J. Agbetile, B. Hargadon, M. Bourne, W.R. Monteiro, C.E. Brightling, P. Bradding, R.H. Green, K. Mutalithas, D. Desai, I.D. Pavord, A.J. Wardlaw, and C.H. Pashley. 2010. IgE sensitization to Aspergillus fumigatus is associated with reduced lung function in asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 182 (11): 1362–1368.
Lien, E., and R.R. Ingalls. 2002. Toll-like receptors. Critical Care Medicine 30 (1 Supp): S1–S11.
Wyatt, T.A., R.E. Slager, A.J. Heires, J.M. DeVasure, S.G. VonEssen, J.A. Poole, and D.J. Romberger. 2010. Sequential activation of protein kinase C isoforms by organic dust is mediated by tumor necrosis factor. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 42 (6): 706–715.
Palmberg, L., B.M. Larsson, P. Malmberg, and K. Larsson. 1998. Induction of IL-8 production in human alveolar macrophages and human bronchial epithelial cells in vitro by swine dust. Thorax 53 (4): 260–264.
Pirie, R.S., P.M. Dixon, and B.C. McGorum. 2002. Evaluation of nebulised hay dust suspensions (HDS) for the diagnosis and investigation of heaves. 3: Effect of fractionation of HDS. Equine Veterinary Journal 34 (4): 343–347.
Sundblad, B.M., I. von Scheele, L. Palmberg, M. Olsson, and K. Larsson. 2009. Repeated exposure to organic material alters inflammatory and physiological airway responses. The European Respiratory Journal 34 (1): 80–88.
Hadebe, S., F. Kirstein, K. Fierens, K. Chen, R.A. Drummond, S. Vautier, S. Sajaniemi, G. Murray, D.L. Williams, P. Redelinghuys, T.A. Reinhart, B.A. Fallert Junecko, J.K. Kolls, B.N. Lambrecht, F. Brombacher, and G.D. Brown. 2015. Microbial ligand costimulation drives neutrophilic steroid-refractory asthma. PLoS One 10 (8): e0134219.
Pirie, R.S., D.D.S. Collie, P.M. Dixon, and B.C. McGorum. 2003. Inhaled endotoxin and organic dust particulates have synergistic proinflammatory effects in equine heaves (organic dust-induced asthma). Clinical and Experimental Allergy 33 (5): 676–683.
Nocker, R.E., et al. 1996. Interleukin-8 in airway inflammation in patients with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 109 (2): 183–191.
Medoff, B.D., A. Sauty, A.M. Tager, J.A. Maclean, R.N. Smith, A. Mathew, J.H. Dufour, and A.D. Luster. 2002. IFN-gamma-inducible protein 10 (CXCL10) contributes to airway hyperreactivity and airway inflammation in a mouse model of asthma. Journal of Immunology 168 (10): 5278–5286.
Singh, S.R., A. Sutcliffe, D. Kaur, S. Gupta, D. Desai, R. Saunders, and C.E. Brightling. 2014. CCL2 release by airway smooth muscle is increased in asthma and promotes fibrocyte migration. Allergy 69 (9): 1189–1197.
Molet, S., Q. Hamid, F. Davoineb, E. Nutku, R. Tahaa, N. Pagé, R. Olivenstein, J. Elias, and J. Chakir. 2001. IL-17 is increased in asthmatic airways and induces human bronchial fibroblasts to produce cytokines. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 108 (3): 430–438.
Itakura, E., C. Kishi-Itakura, and N. Mizushima. 2012. The hairpin-type tail-anchored SNARE syntaxin 17 targets to autophagosomes for fusion with endosomes/lysosomes. Cell 151 (6): 1256–1269.
Korn, T., E. Bettelli, M. Oukka, and V.K. Kuchroo. 2009. IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annual Review of Immunology 27: 485–517.
Murcia, R.Y., A. Vargas, and J.P. Lavoie. 2016. The interleukin-17 induced activation and increased survival of equine neutrophils is insensitive to glucocorticoids. PLoS One 11 (5): e0154755.
Debrue, M., E. Hamilton, P. Joubert, S. Lajoie-Kadoch, and J.P. Lavoie. 2005. Chronic exacerbation of equine heaves is associated with an increased expression of interleukin-17 mRNA in bronchoalveolar lavage cells. Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology 105 (1-2): 25–31.
Wolf, L., S. Sapich, A. Honecker, C. Jungnickel, F. Seiler, M. Bischoff, B. Wonnenberg, C. Herr, N. Schneider-Daum, C.M. Lehr, R. Bals, and C. Beisswenger. 2016. IL-17A-mediated expression of epithelial IL-17C promotes inflammation during acute Pseudomonas aeruginosa pneumonia. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 311 (5): L1015–L1022.
Ramirez-Carrozzi, V., A. Sambandam, E. Luis, Z. Lin, S. Jeet, J. Lesch, J. Hackney, J. Kim, M. Zhou, J. Lai, Z. Modrusan, T. Sai, W. Lee, M. Xu, P. Caplazi, L. Diehl, J. de Voss, M. Balazs, L. Gonzalez Jr., H. Singh, W. Ouyang, and R. Pappu. 2011. IL-17C regulates the innate immune function of epithelial cells in an autocrine manner. Nature Immunology 12 (12): 1159–1166.
Honda, K., H. Wada, M. Nakamura, K. Nakamoto, T. Inui, M. Sada, T. Koide, S. Takata, T. Yokoyama, T. Saraya, D. Kurai, H. Ishii, H. Goto, and H. Takizawa. 2016. IL-17A synergistically stimulates TNF-α-induced IL-8 production in human airway epithelial cells: a potential role in amplifying airway inflammation. Experimental Lung Research 42 (4): 205–216.
Morishima, Y., et al. 2013. Th17-associated cytokines as a therapeutic target for steroid-insensitive asthma. Clinical & Developmental Immunology 2013: 609395.
Qiu, Y.Y., X.Y. Zhou, X.F. Qian, Y.X. Wu, C. Qin, and T. Bian. 2017. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 reduces mouse airway inflammation of neutrophilic asthma by transcriptional modulation of interleukin-17A. American Journal of Translational Research 9 (12): 5411–5421.
Al-Harbi, N.O., et al. 2019. Sulforaphane treatment reverses corticosteroid resistance in a mixed granulocytic mouse model of asthma by upregulation of antioxidants and attenuation of Th17 immune responses in the airways. European Journal of Pharmacology 855: 276–284.
Liang, L., J. Hur, J.Y. Kang, C.K. Rhee, Y.K. Kim, and S.Y. Lee. 2018. Effect of the anti-IL-17 antibody on allergic inflammation in an obesity-related asthma model. The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine 33 (6): 1210–1223.
Dos Santos, T.M., et al. 2018. Effect of anti-IL17 antibody treatment alone and in combination with Rho-kinase inhibitor in a murine model of asthma. Frontiers in Physiology 9: 1183.
Camargo, L.D.N., et al. 2017. Effects of anti-IL-17 on inflammation, remodeling, and oxidative stress in an experimental model of asthma exacerbated by LPS. Frontiers in Immunology 8: 1835.
Fei, X., P.Y. Zhang, X. Zhang, G.Q. Zhang, W.P. Bao, Y.Y. Zhang, M. Zhang, and X. Zhou. 2017. IL-17A monoclonal antibody partly reverses the glucocorticoids insensitivity in mice exposed to ozonec. Inflammation 40 (3): 788–797.
Busse, W.W., S. Holgate, E. Kerwin, Y. Chon, J.Y. Feng, J. Lin, and S.L. Lin. 2013. Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of brodalumab, a human anti-IL-17 receptor monoclonal antibody, in moderate to severe asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 188 (11): 1294–1302.
O'Byrne, P.M., H. Metev, M. Puu, K. Richter, C. Keen, M. Uddin, B. Larsson, M. Cullberg, and P. Nair. 2016. Efficacy and safety of a CXCR2 antagonist, AZD5069, in patients with uncontrolled persistent asthma: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 4 (10): 797–806.
Nathan, C., and A. Cunningham-Bussel. 2013. Beyond oxidative stress: an immunologist's guide to reactive oxygen species. Nature Reviews. Immunology 13 (5): 349–361.
Nguyen, G.T., E.R. Green, and J. Mecsas. 2017. Neutrophils to the ROScue: mechanisms of NADPH oxidase activation and bacterial resistance. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology 7: 373.
Zuo, L., T. Zhou, B.K. Pannell, A.C. Ziegler, and T.M. Best. 2015. Biological and physiological role of reactive oxygen species--the good, the bad and the ugly. Acta Physiologica (Oxford, England) 214 (3): 329–348.
Kleniewska, P., and R. Pawliczak. 2017. The participation of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 94: 100–108.
Bishopp, A., R. Sathyamurthy, S. Manney, C. Webbster, M.T. Krishna, and A.H. Mansur. 2017. Biomarkers of oxidative stress and antioxidants in severe asthma: a prospective case-control study. Annals of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology 118 (4): 445–451.
Erzurum, S.C. 2016. New insights in oxidant biology in asthma. Annals of the American Thoracic Society 13 (Suppl 1): S35–S39.
Robinson, J.M. 2008. Reactive oxygen species in phagocytic leukocytes. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 130 (2): 281–297.
Fukunaga, M., Y. Gon, S. Nunomura, T. Inoue, M. Yoshioka, S. Hashimoto, and C. Ra. 2011. Protease-mediated house dust mite allergen-induced reactive oxygen species production by neutrophils. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 155 (Suppl 1): 104–109.
Natarajan, K., K.R. Gottipati, K. Berhane, B. Samten, U. Pendurthi, and V. Boggaram. 2016. Proteases and oxidant stress control organic dust induction of inflammatory gene expression in lung epithelial cells. Respiratory Research 17 (1): 137.
To, M., et al. 2018. Obesity-related systemic oxidative stress: an important factor of poor asthma control. Allergology International 67 (1): 147–149.
Suzuki, S., S. Matsukura, H. Takeuchi, M. Kawaguchi, K. Ieki, M. Odaka, S. Watanabe, T. Homma, K. Dohi, T. Aruga, M. Sato, M. Kurokawa, F. Kokubu, and M. Adachi. 2008. Increase in reactive oxygen metabolite level in acute exacerbations of asthma. International Archives of Allergy and Immunology 146 (Suppl 1): 67–72.
Nakamoto, K., M. Watanabe, M. Sada, T. Inui, M. Nakamura, K. Honda, H. Wada, Y. Mikami, H. Matsuzaki, M. Horie, S. Noguchi, Y. Yamauchi, H. Koyama, T. Kogane, T. Kohyama, and H. Takizawa. 2016. Serum reactive oxygen metabolite levels predict severe exacerbations of asthma. PLoS One 11 (10): e0164948.
Kelly, C., C. Ward, C.S. Stenton, G. Bird, D.J. Hendrick, and E.H. Walters. 1988. Number and activity of inflammatory cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid in asthma and their relation to airway responsiveness. Thorax 43 (9): 684–692.
Vachier, I., P. Chanez, C. le Doucen, M. Damon, B. Descomps, and P. Godard. 1994. Enhancement of reactive oxygen species formation in stable and unstable asthmatic patients. The European Respiratory Journal 7 (9): 1585–1592.
Lacy, P., D.A. Latif, M. Steward, S. Musat-Marcu, S.F.P. Man, and R. Moqbel. 2003. Divergence of mechanisms regulating respiratory burst in blood and sputum eosinophils and neutrophils from atopic subjects. Journal of Immunology 170 (5): 2670–2679.
Bucchieri, F., S.M. Puddicombe, J.L. Lordan, A. Richter, D. Buchanan, S.J. Wilson, J. Ward, G. Zummo, P.H. Howarth, R. Djukanović, S.T. Holgate, and D.E. Davies. 2002. Asthmatic bronchial epithelium is more susceptible to oxidant-induced apoptosis. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 27 (2): 179–185.
Zeng, H., Y. Wang, Y. Gu, J. Wang, H. Zhang, H. Gao, Q. Jin, and L. Zhao. 2019. Polydatin attenuates reactive oxygen species-induced airway remodeling by promoting Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling in asthma mouse model. Life Sciences 218: 25–30.
Ravasi, S., S. Citro, B. Viviani, V. Capra, and G.E. Rovati. 2006. CysLT1 receptor-induced human airway smooth muscle cells proliferation requires ROS generation, EGF receptor transactivation and ERK1/2 phosphorylation. Respiratory Research 7: 42.
Tuo, Q.R., Y.F. Ma, W. Chen, X.J. Luo, J. Shen, D. Guo, Y.M. Zheng, Y.X. Wang, G. Ji, and Q.H. Liu. 2013. Reactive oxygen species induce a Ca(2+)-spark increase in sensitized murine airway smooth muscle cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 434 (3): 498–502.
Qu, J., Y. Li, W. Zhong, P. Gao, and C. Hu. 2017. Recent developments in the role of reactive oxygen species in allergic asthma. Journal of Thoracic Disease 9 (1): E32–E43.
Jesenak, M., M. Zelieskova, and E. Babusikova. 2017. Oxidative stress and bronchial asthma in children-causes or consequences? Frontiers in Pediatrics 5: 162.
Venugopal, C., et al. 2013. Effect of potential therapeutic agents in reducing oxidative stress in pulmonary tissues of recurrent airway obstruction-affected and clinically healthy horses. Equine Veterinary Journal 45 (1): 80–84.
Marr, K.A., A.P. Foster, P. Lees, F.M. Cunningham, and C.P. Page. 1997. Effect of antigen challenge on the activation of peripheral blood neutrophils from horses with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Research in Veterinary Science 62 (3): 253–260.
Bowler, R.P. 2004. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of asthma. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports 4 (2): 116–122.
Psarras, S., G. Caramori, M. Contoli, N. Papadopoulos, and A. Papi. 2005. Oxidants in asthma and in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Current Pharmaceutical Design 11 (16): 2053–2062.
Liao, M.F., C.C. Chen, and M.H. Hsu. 2004. Evaluation of the serum antioxidant status in asthmatic children. Acta Paediatrica Taiwanica 45 (4): 213–217.
Sagdic, A., O. Sener, F. Bulucu, N. Karadurmus, H.E. Özel, L. Yamanel, C. Tasci, I. Naharci, R. Ocal, and A. Aydin. 2011. Oxidative stress status and plasma trace elements in patients with asthma or allergic rhinitis. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 39 (4): 200–205.
Niedzwiedz, A., H. Borowicz, L. Januszewska, I. Markiewicz-Gorka, and Z. Jaworski. 2016. Serum 8-hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine as a marker of DNA oxidative damage in horses with recurrent airway obstruction. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica 58 (1): 38.
Deaton, C.M., et al. 2005. Antioxidant and inflammatory responses of healthy horses and horses affected by recurrent airway obstruction to inhaled ozone. Equine Veterinary Journal 37 (3): 243–249.
Deaton, C.M., D.J. Marlin, L. Deaton, N.C. Smith, P.A. Harris, R.C. Schroter, and F.J. Kelly. 2006. Comparison of the antioxidant status in tracheal and bronchoalveolar epithelial lining fluids in recurrent airway obstruction. Equine Veterinary Journal 38 (5): 417–422.
Tecklenburg, S.L., T.D. Mickleborough, A.D. Fly, Y. Bai, and J.M. Stager. 2007. Ascorbic acid supplementation attenuates exercise-induced bronchoconstriction in patients with asthma. Respiratory Medicine 101 (8): 1770–1778.
Burbank, A.J., et al. 2018. Gamma tocopherol-enriched supplement reduces sputum eosinophilia and endotoxin-induced sputum neutrophilia in volunteers with asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 141 (4): 1231–1238.e1.
Perez, B., C. Henriquez, J. Sarmiento, N. Morales, H. Folch, J.S. Galesio, B. Uberti, and G. Morán. 2016. Tamoxifen as a new therapeutic tool for neutrophilic lung inflammation. Respirology 21 (1): 112–118.
Borlone, C., N. Morales, C. Henriquez, H. Folch, C. Olave, J. Sarmiento, B. Uberti, and G. Moran. 2017. In vitro effects of tamoxifen on equine neutrophils. Research in Veterinary Science 110: 60–64.
Olave, C., P. Alvarez, B. Uberti, N. Morales, C. Henriquez, H. Folch, J. Sarmiento, and G. Moran. 2019. Tamoxifen induces apoptosis and inhibits respiratory burst in equine neutrophils independently of estrogen receptors. Journal of Veterinary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 42 (2): 248–254.
Twaddell, S.H., K.J. Baines, C. Grainge, and P.G. Gibson. 2019. The emerging role of neutrophil extracellular traps in respiratory disease. Chest 156 (4): 774–782.
Saffarzadeh, M., C. Juenemann, M.A. Queisser, G. Lochnit, G. Barreto, S.P. Galuska, J. Lohmeyer, and K.T. Preissner. 2012. Neutrophil extracellular traps directly induce epithelial and endothelial cell death: a predominant role of histones. PLoS One 7 (2): e32366.
Narasaraju, T., E. Yang, R.P. Samy, H.H. Ng, W.P. Poh, A.A. Liew, M.C. Phoon, N. van Rooijen, and V.T. Chow. 2011. Excessive neutrophils and neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to acute lung injury of influenza pneumonitis. The American Journal of Pathology 179 (1): 199–210.
Kaplan, M.J., and M. Radic. 2012. Neutrophil extracellular traps: double-edged swords of innate immunity. Journal of Immunology 189 (6): 2689–2695.
Wright, T.K., P.G. Gibson, J.L. Simpson, V.M. McDonald, L.G. Wood, and K.J. Baines. 2016. Neutrophil extracellular traps are associated with inflammation in chronic airway disease. Respirology 21 (3): 467–475.
Dworski, R., H.U. Simon, A. Hoskins, and S. Yousefi. 2011. Eosinophil and neutrophil extracellular DNA traps in human allergic asthmatic airways. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 127 (5): 1260–1266.
Vargas, A., R. Boivin, P. Cano, Y. Murcia, I. Bazin, and J.P. Lavoie. 2017. Neutrophil extracellular traps are downregulated by glucocorticosteroids in lungs in an equine model of asthma. Respiratory Research 18 (1): 207.
Toussaint, M., D.J. Jackson, D. Swieboda, A. Guedán, T.D. Tsourouktsoglou, Y.M. Ching, C. Radermecker, H. Makrinioti, J. Aniscenko, N.W. Bartlett, M.R. Edwards, R. Solari, F. Farnir, V. Papayannopoulos, F. Bureau, T. Marichal, and S.L. Johnston. 2017. Host DNA released by NETosis promotes rhinovirus-induced type-2 allergic asthma exacerbation. Nature Medicine 23 (6): 681–691.
Lapponi, M.J., A. Carestia, V.I. Landoni, L. Rivadeneyra, J. Etulain, S. Negrotto, R.G. Pozner, and M. Schattner. 2013. Regulation of neutrophil extracellular trap formation by anti-inflammatory drugs. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 345 (3): 430–437.
Geng, X., X. Wang, M. Luo, M. Xing, Y. Wu, W. Li, Z. Chen, H. Shen, and S. Ying. 2018. Induction of neutrophil apoptosis by a Bcl-2 inhibitor reduces particulate matter-induced lung inflammation. Aging (Albany NY) 10 (6): 1415–1423.
Tian, B.P., L.X. Xia, Z.Q. Bao, H. Zhang, Z.W. Xu, Y.Y. Mao, C. Cao, L.Q. Che, J.K. Liu, W. Li, Z.H. Chen, S. Ying, and H.H. Shen. 2017. Bcl-2 inhibitors reduce steroid-insensitive airway inflammation. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 140 (2): 418–430.
Lee, N.R., S.Y. Baek, A. Gu, D.H. Kim, S.Y. Kim, J.S. Lee, and I.S. Kim. 2016. House dust mite allergen suppresses neutrophil apoptosis by cytokine release via PAR2 in normal and allergic lymphocytes. Immunologic Research 64 (1): 123–132.
Breuer, J., U. Müller, L. Locher, A. Spallek, S. Recknagel, A. Uhlig, and G.F. Schusser. 2011. Differentiation of viable, apoptotic and necrotic cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of normal horses and horses with recurrent airway obstruction. Berliner und Münchener Tierärztliche Wochenschrift 124 (3-4): 154–160.
Niedzwiedz, A., Z. Jaworski, B. Tykalowski, and M. Smialek. 2014. Neutrophil and macrophage apoptosis in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from healthy horses and horses with recurrent airway obstruction (RAO). BMC Veterinary Research 10: 29.
Olave, C., N. Morales, B. Uberti, C. Henriquez, J. Sarmiento, A. Ortloff, H. Folch, and G. Moran. 2018. Tamoxifen induces apoptotic neutrophil efferocytosis in horses. Veterinary Research Communications 42 (1): 57–63.
Lawrence, S.M., R. Corriden, and V. Nizet. 2018. The ontogeny of a neutrophil: mechanisms of granulopoiesis and homeostasis. Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews: 82(1).
Pillay, J., I. den Braber, N. Vrisekoop, L.M. Kwast, R.J. de Boer, J.A.M. Borghans, K. Tesselaar, and L. Koenderman. 2010. In vivo labeling with 2H2O reveals a human neutrophil lifespan of 5.4 days. Blood 116 (4): 625–627.
Tak, T., K. Tesselaar, J. Pillay, J.A.M. Borghans, and L. Koenderman. 2013. What's your age again? Determination of human neutrophil half-lives revisited. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 94 (4): 595–601.
Casanova-Acebes, M., C. Pitaval, L.A. Weiss, C. Nombela-Arrieta, R. Chèvre, N. A-González, Y. Kunisaki, D. Zhang, N. van Rooijen, L.E. Silberstein, C. Weber, T. Nagasawa, P.S. Frenette, A. Castrillo, and A. Hidalgo. 2013. Rhythmic modulation of the hematopoietic niche through neutrophil clearance. Cell 153 (5): 1025–1035.
Adrover, J.M., C. del Fresno, G. Crainiciuc, M.I. Cuartero, M. Casanova-Acebes, L.A. Weiss, H. Huerga-Encabo, C. Silvestre-Roig, J. Rossaint, I. Cossío, A.V. Lechuga-Vieco, J. García-Prieto, M. Gómez-Parrizas, J.A. Quintana, I. Ballesteros, S. Martin-Salamanca, A. Aroca-Crevillen, S.Z. Chong, M. Evrard, K. Balabanian, J. López, K. Bidzhekov, F. Bachelerie, F. Abad-Santos, C. Muñoz-Calleja, A. Zarbock, O. Soehnlein, C. Weber, L.G. Ng, C. Lopez-Rodriguez, D. Sancho, M.A. Moro, B. Ibáñez, and A. Hidalgo. 2019. A neutrophil timer coordinates immune defense and vascular protection. Immunity 51 (5): 966–967.
Zhang, D., G. Chen, D. Manwani, A. Mortha, C. Xu, J.J. Faith, R.D. Burk, Y. Kunisaki, J.E. Jang, C. Scheiermann, M. Merad, and P.S. Frenette. 2015. Neutrophil ageing is regulated by the microbiome. Nature 525 (7570): 528–532.
Becher, B., A. Schlitzer, J. Chen, F. Mair, H.R. Sumatoh, K.W.W. Teng, D. Low, C. Ruedl, P. Riccardi-Castagnoli, M. Poidinger, M. Greter, F. Ginhoux, and E.W. Newell. 2014. High-dimensional analysis of the murine myeloid cell system. Nature Immunology 15 (12): 1181–1189.
Ng, L.G., R. Ostuni, and A. Hidalgo. 2019. Heterogeneity of neutrophils. Nature Reviews. Immunology 19 (4): 255–265.
Ji, J.J., and J. Fan. 2019. Discovering myeloid cell heterogeneity in the lung by means of next generation sequencing. Military Medical Research 6 (1): 33.
Wang, J., M. Hossain, A. Thanabalasuriar, M. Gunzer, C. Meininger, and P. Kubes. 2017. Visualizing the function and fate of neutrophils in sterile injury and repair. Science 358 (6359): 111–116.
Buckley, C.D., E.A. Ross, H.M. McGettrick, C.E. Osborne, O. Haworth, C. Schmutz, P.C.W. Stone, M. Salmon, N.M. Matharu, R.K. Vohra, G.B. Nash, and G.E. Rainger. 2006. Identification of a phenotypically and functionally distinct population of long-lived neutrophils in a model of reverse endothelial migration. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 79 (2): 303–311.
Denny, M.F., S. Yalavarthi, W. Zhao, S.G. Thacker, M. Anderson, A.R. Sandy, W.J. McCune, and M.J. Kaplan. 2010. A distinct subset of proinflammatory neutrophils isolated from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus induces vascular damage and synthesizes type I IFNs. Journal of Immunology 184 (6): 3284–3297.
Hacbarth, E., and A. Kajdacsy-Balla. 1986. Low density neutrophils in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and acute rheumatic fever. Arthritis and Rheumatism 29 (11): 1334–1342.
Marini, O., C. Spina, E. Mimiola, A. Cassaro, G. Malerba, G. Todeschini, O. Perbellini, M. Scupoli, G. Carli, D. Facchinelli, M. Cassatella, P. Scapini, and C. Tecchio. 2016. Identification of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells (G-MDSCs) in the peripheral blood of Hodgkin and non-Hodgkin lymphoma patients. Oncotarget 7 (19): 27676–27688.
Sagiv, J.Y., J. Michaeli, S. Assi, I. Mishalian, H. Kisos, L. Levy, P. Damti, D. Lumbroso, L. Polyansky, R.V. Sionov, A. Ariel, A.H. Hovav, E. Henke, Z.G. Fridlender, and Z. Granot. 2015. Phenotypic diversity and plasticity in circulating neutrophil subpopulations in cancer. Cell Reports 10 (4): 562–573.
Cloke, T., M. Munder, G. Taylor, I. Müller, and P. Kropf. 2012. Characterization of a novel population of low-density granulocytes associated with disease severity in HIV-1 infection. PLoS One 7 (11): e48939.
Abdel-Salam, B.K., and H. Ebaid. 2014. Expression of CD11b and CD18 on polymorphonuclear neutrophils stimulated with interleukin-2. Central European Journal of Immunology 39 (2): 209–215.
Fortunati, E., K.M. Kazemier, J.C. Grutters, L. Koenderman, and J.M.M. van den Bosch. 2009. Human neutrophils switch to an activated phenotype after homing to the lung irrespective of inflammatory disease. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 155 (3): 559–566.
Fu, J., M.C. Tobin, and L.L. Thomas. 2014. Neutrophil-like low-density granulocytes are elevated in patients with moderate to severe persistent asthma. Annals of Allergy Asthma Immunology 113 (6): 635–640.e2.
Herteman, N., A. Vargas, and J.P. Lavoie. 2017. Characterization of circulating low-density neutrophils intrinsic properties in healthy and asthmatic horses. Scientific Reports 7 (1): 7743.
Nair, P., M. Gaga, E. Zervas, K. Alagha, F.E. Hargreave, P.M. O'Byrne, P. Stryszak, L. Gann, J. Sadeh, P. Chanez, and on behalf of the study investigators. 2012. Safety and efficacy of a CXCR2 antagonist in patients with severe asthma and sputum neutrophils: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 42 (7): 1097–1103.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, K.U., Sheats, M.K. The Role of Neutrophils in the Pathophysiology of Asthma in Humans and Horses. Inflammation 44, 450–465 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01362-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-020-01362-2