Abstract
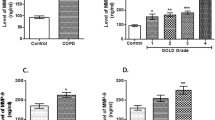
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is associated with abnormal inflammation and high oxidative stress. Studies suggest that reactive oxygen species modulator 1 (Romo1) involve in diseases associated with oxidative stress and inflammation. However, the relationship between COPD and Romo1 is still not clear. In this study, we compared serum Romo1 in 49 COPD patients and 34 health controls, and their correlation with lung function, systematic inflammation, and oxidative stress. In addition, serum levels of Romo1, C-reactive protein (CRP), and oxidative stress (measured by reactive oxygen species, ROS) were analyzed using commercial kits. Serum Romo1 was significantly higher in COPD patients than that of control (132.24 ± 10.34 vs. 93.26 ± 7.75 pg/ml, P < 0.05). Serum CRP and ROS were also significantly higher in COPD patients. Serum Romo1 was correlated inversely with FEV1% predicted in COPD patients (푟 = − 0.347, 푃 = 0.016), while it was correlated positively with CRP and ROS levels, respectively. These results suggest that serum Romo1 increase in COPD patients and that these levels are associated with lung function, inflammation, and oxidative stress in COPD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Decramer, M., W. Janssens, and M. Miravitlles. 2012. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Lancet 379 (9823): 1341–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(11)60968-9.
Vogelmeier, C.F., G.J. Criner, F.J. Martinez, A. Anzueto, P.J. Barnes, J. Bourbeau, B.R. Celli, R. Chen, M. Decramer, L.M. Fabbri, P. Frith, D.M.G. Halpin, M.V. López Varela, M. Nishimura, N. Roche, R. Rodriguez-Roisin, D.D. Sin, D. Singh, R. Stockley, J. Vestbo, J.A. Wedzicha, and A. Agustí. 2017. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive lung disease 2017 report. GOLD executive summary. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 195 (5): 557–582. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201701-0218PP.
Apperley, S., H.Y. Park, D.T. Holmes, S.F.P. Man, D. Tashkin, R.A. Wise, J.E. Connett, and D.D. Sin. 2015. Serum bilirubin and disease progression in mild COPD. Chest 148 (1): 169–175. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.14-2150.
Vaitkus, M., S. Lavinskiene, D. Barkauskiene, K. Bieksiene, J. Jeroch, and R. Sakalauskas. 2013. Reactive oxygen species in peripheral blood and sputum neutrophils during bacterial and nonbacterial acute exacerbation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Inflammation 36 (6): 1485–1493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9690-3.
Can, U., F.H. Yerlikaya, and S. Yosunkaya. 2015. Role of oxidative stress and serum lipid levels in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Journal of the Chinese Medical Association 78 (12): 702–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcma.2015.08.004.
Miller, J., L.D. Edwards, A. Agusti, P. Bakke, P.M. Calverley, B. Celli, H.O. Coxson, et al. 2013. Comorbidity, systemic inflammation and outcomes in the ECLIPSE cohort. Respiratory Medicine 107 (9): 1376–1384. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2013.05.001.
Boeck, L., J. Mandal, L. Costa, M. Roth, M. Tamm, and D. Stolz. 2015. Longitudinal measurement of serum vascular endothelial growth factor in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respiration 90 (2): 97–104. https://doi.org/10.1159/000430993.
Boots, A.W., G.R. Haenen, and A. Bast. 2003. Oxidant metabolism in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The European Respiratory Journal. Supplement 46: 14s–27s.
de Boer, W.I., H. Yao, and I. Rahman. 2007. Future therapeutic treatment of COPD: struggle between oxidants and cytokines. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2 (3): 205–228.
Fischer, B.M., J.A. Voynow, and A.J. Ghio. 2015. COPD: balancing oxidants and antioxidants. International Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 10: 261–276. https://doi.org/10.2147/copd.s42414.
Rahman, I., and I.M. Adcock. 2006. Oxidative stress and redox regulation of lung inflammation in COPD. The European Respiratory Journal 28 (1): 219–242. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.06.00053805.
Yao, H., and I. Rahman. 2011. Current concepts on oxidative/carbonyl stress, inflammation and epigenetics in pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 254 (2): 72–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2009.10.022.
Ciencewicki, J., S. Trivedi, and S.R. Kleeberger. 2008. Oxidants and the pathogenesis of lung diseases. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 122 (3): 456–468; quiz 469-470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.08.004.
Sosa, V., T. Moline, R. Somoza, R. Paciucci, H. Kondoh, and M.E. Leonart. 2013. Oxidative stress and cancer: an overview. Ageing Res Rev 12 (1): 376–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2012.10.004.
Veskoukis, A.S., A.M. Tsatsakis, and D. Kouretas. 2012. Dietary oxidative stress and antioxidant defense with an emphasis on plant extract administration. Cell Stress & Chaperones 17 (1): 11–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-011-0293-3.
Chung, Y.M., J.S. Kim, and Y.D. Yoo. 2006. A novel protein, Romo1, induces ROS production in the mitochondria. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 347 (3): 649–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.06.140.
Lee, S.H., J.S. Lee, E.J. Lee, K.H. Min, G.Y. Hur, S.H. Lee, S.Y. Lee, J.H. Kim, S.Y. Lee, C. Shin, J.J. Shim, K.H. Kang, and K.H. in. 2014. Serum reactive oxygen species modulator 1 (Romo1) as a potential diagnostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 85 (2): 175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.05.023.
Shin, J.A., J.S. Chung, S.H. Cho, H.J. Kim, and Y.D. Yoo. 2013. Romo1 expression contributes to oxidative stress-induced death of lung epithelial cells. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 439 (2): 315–320. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.07.012.
Vestbo, J., S.S. Hurd, A.G. Agusti, P.W. Jones, C. Vogelmeier, A. Anzueto, P.J. Barnes, et al. 2013. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 187 (4): 347–365. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201204-0596PP.
Kowluru, R.A., V. Kowluru, Y. Xiong, and Y.S. Ho. 2006. Overexpression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase in mice protects the retina from diabetes-induced oxidative stress. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 41 (8): 1191–1196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.012.
Lee, S.B., J.J. Kim, T.W. Kim, B.S. Kim, M.S. Lee, and Y.D. Yoo. 2010. Serum deprivation-induced reactive oxygen species production is mediated by Romo1. Apoptosis 15 (2): 204–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-009-0411-1.
Chung, J.S., S.B. Lee, S.H. Park, S.T. Kang, A.R. Na, T.S. Chang, H.J. Kim, and Y.D. Yoo. 2009. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species originating from Romo1 exert an important role in normal cell cycle progression by regulating p27(Kip1) expression. Free Radical Research 43 (8): 729–737. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715760903038432.
Wiegman, C.H., C. Michaeloudes, G. Haji, P. Narang, C.J. Clarke, K.E. Russell, W. Bao, S. Pavlidis, P.J. Barnes, J. Kanerva, A. Bittner, N. Rao, M.P. Murphy, P.A. Kirkham, K.F. Chung, I.M. Adcock, C.E. Brightling, D.E. Davies, D.K. Finch, A.J. Fisher, A. Gaw, A.J. Knox, R.J. Mayer, M. Polkey, M. Salmon, and D. Singh. 2015. Oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction drives inflammation and airway smooth muscle remodeling in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 136 (3): 769–780. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.01.046.
Lee, I.T., and C.M. Yang. 2012. Role of NADPH oxidase/ROS in pro-inflammatory mediators-induced airway and pulmonary diseases. Biochemical Pharmacology 84 (5): 581–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.05.005.
Goldkorn, T., S. Filosto, and S. Chung. 2014. Lung injury and lung cancer caused by cigarette smoke-induced oxidative stress: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities involving the ceramide-generating machinery and epidermal growth factor receptor. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 21 (15): 2149–2174. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2013.5469.
Funding
This study was supported by the Intelligent Medical Scientific and Technology Program, Nanjing Scientific and Technology Fund (No. 201727003), and the Nanjing Scientific and Technology Fund (No. 201803007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ye, L., Mao, S., Fang, S. et al. Increased Serum Romo1 Was Correlated with Lung Function, Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Inflammation 42, 1555–1560 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01017-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01017-x