Abstract
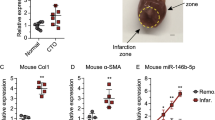
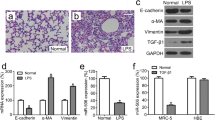
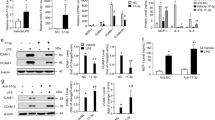
Emerging evidence indicates that acute rejection mainly associated with the inflammatory response is an independent risk factor for chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Monocytes are the main pro-inflammatory leukocytes infiltrating around the lesions and play vital roles in triggering the acute rejection. In the rat lung transplantation model, lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced severe acute rejection was strongly associated with advanced chronic rejection. The exact regulatory mechanism of pro-inflammation in monocytes is not yet clear. In this study, we identified a novel anti-inflammatory effect of miR-199b-5p (miR-199b) through the GSK3β and NF-κB pathways. THP-1 monocytes treated with LPS showed a significant decrease in miR-199b that is inversely correlated to GSK3β expression and NF-κB activation. Furthermore, the NF-κB-associated inflammatory response was reduced due to the overexpression of miR-199b targeting GSK3β, which was rescued by the inhibition of miR-199b. These results indicated that miR-199b attenuated the inflammatory response at least partly through the GSK3β/NF-κB signaling pathways in monocytes. Our data point toward a potentially important role for miR-199b in the inhibition of rejection after lung transplantation.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sayegh, M.H., and C.B. Carpenter. 2004. Transplantation 50 years later—progress, challenges, and promises. The New England Journal of Medicine 351 (26): 2761–2766. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMon043418.
Yusen, R.D., L.B. Edwards, A.Y. Kucheryavaya, C. Benden, A.I. Dipchand, F. Dobbels, S.B. Goldfarb, et al. 2014. The registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: thirty-first adult lung and heart-lung transplant report—2014; focus theme: retransplantation. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 33 (10): 1009–1024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2014.08.004.
Verleden, G.M., R. Vos, B. Vanaudenaerde, L. Dupont, J. Yserbyt, D. Van Raemdonck, and S. Verleden. 2015. Current views on chronic rejection after lung transplantation. Transplant International 28 (10): 1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12579.
Hachem, R.R., A.P. Khalifah, M.M. Chakinala, R.D. Yusen, A.A. Aloush, T. Mohanakumar, G.A. Patterson, E.P. Trulock, and M.J. Walter. 2005. The significance of a single episode of minimal acute rejection after lung transplantation. Transplantation 80 (10): 1406–1413.
Stewart, S., M.C. Fishbein, G.I. Snell, G.J. Berry, A. Boehler, M.M. Burke, A. Glanville, et al. 2007. Revision of the 1996 working formulation for the standardization of nomenclature in the diagnosis of lung rejection. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 26 (12): 1229–1242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2007.10.017.
Zhou, X., X. He, and Y. Ren. 2014. Function of microglia and macrophages in secondary damage after spinal cord injury. Neural Regeneration Research 9 (20): 1787–1795. https://doi.org/10.4103/1673-5374.143423.
Atanasova, S., M. Hirschburger, D. Jonigk, M. Obert, K. Petri, A. Evers, A. Hecker, et al. 2013. A relevant experimental model for human bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 32 (11): 1131–1139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.healun.2013.07.016.
Janeway, Charles A., Jr., and Ruslan Medzhitov. 2002. Innate Immune Recognition. Annual Review of Immunology 20 (1): 197–216. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.20.083001.084359.
Su, G.L., R.L. Simmons, and S.C. Wang. 1995. Lipopolysaccharide binding protein participation in cellular activation by LPS. Critical Reviews in Immunology 15 (3–4): 201–214.
Lai, E.C. 2002. Micro RNAs are complementary to 3′ UTR sequence motifs that mediate negative post-transcriptional regulation. Nature Genetics 30 (4): 363–364. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng865.
Woodbury, M.E., R.W. Freilich, C.J. Cheng, H. Asai, S. Ikezu, J.D. Boucher, F. Slack, and T. Ikezu. 2015. miR-155 is essential for inflammation-induced hippocampal neurogenic dysfunction. The Journal of Neuroscience 35 (26): 9764–9781. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.4790-14.2015.
Liu, X., F. He, R. Pang, D. Zhao, W. Qiu, K. Shan, J. Zhang, Y. Lu, Y. Li, and Y. Wang. 2014. Interleukin-17 (IL-17)-induced microRNA 873 (miR-873) contributes to the pathogenesis of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by targeting A20 ubiquitin-editing enzyme. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 289 (42): 28971–28986. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.577429.
Kong, R., J. Gao, Y. Si, and D. Zhao. 2017. Combination of circulating miR-19b-3p, miR-122-5p and miR-486-5p expressions correlates with risk and disease severity of knee osteoarthritis. American Journal of Translational Research 9 (6): 2852–2864.
Zhou, H.J., L.Q. Wang, Q.S. Xu, Z.X. Fan, Y. Zhu, H. Jiang, X.J. Zheng, Y.H. Ma, and R.Y. Zhan. 2016. Downregulation of miR-199b promotes the acute spinal cord injury through IKKbeta-NF-kappaB signaling pathway activating microglial cells. Experimental Cell Research 349 (1): 60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.09.020.
Schmittgen, T.D., and K.J. Livak. 2008. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nature Protocols 3 (6): 1101–1108.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25 (4): 402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Szklarczyk, D., A. Franceschini, S. Wyder, K. Forslund, D. Heller, J. Huerta-Cepas, M. Simonovic, et al. 2015. STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Research 43 (Database issue): D447–D452. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003.
Hayden, M.S., A.P. West, and S. Ghosh. 2006. SnapShot: NF-kappaB signaling pathways. Cell 127 (6): 1286–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.12.005.
Napetschnig, Johanna, and Hao Wu. 2013. Molecular basis of NF-κB signaling. Annual Review of Biophysics 42 (1): 443–468. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biophys-083012-130338.
Hoeflich, K.P., J. Luo, E.A. Rubie, M.S. Tsao, O. Jin, and J.R. Woodgett. 2000. Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in cell survival and NF-kappaB activation. Nature 406 (6791): 86–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/35017574.
Martin, M., K. Rehani, R.S. Jope, and S.M. Michalek. 2005. Toll-like receptor-mediated cytokine production is differentially regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3. Nature Immunology 6 (8): 777–784. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1221.
Wang, C., B. Song, W. Song, J. Liu, A. Sun, D. Wu, H. Yu, J. Lian, L. Chen, and J. Han. 2011. Underexpressed microRNA-199b-5p targets hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in hepatocellular carcinoma and predicts prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 26 (11): 1630–1637. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.06758.x.
Du, P., F. Dai, Y. Chang, C. Wei, J. Yan, J. Li, and X. Liu. 2016. Role of miR-199b-5p in regulating angiogenesis in mouse myocardial microvascular endothelial cells through HSF1/VEGF pathway. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 47: 142–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2016.09.007.
Costa, J., L.J. Benvenuto, and J.R. Sonett. 2017. Long-term outcomes and management of lung transplant recipients. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Anaesthesiology 31 (2): 285–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpa.2017.05.006.
Sharples, L.D., K. McNeil, S. Stewart, and J. Wallwork. 2002. Risk factors for bronchiolitis obliterans: a systematic review of recent publications. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation 21 (2): 271–281.
Vallabhapurapu, Sivakumar, and Michael Karin. 2009. Regulation and function of NF-κB transcription factors in the immune system. Annual Review of Immunology 27 (1): 693–733. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.021908.132641.
Beurel, E., and R.S. Jope. 2009. Lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 production is controlled by glycogen synthase kinase-3 and STAT3 in the brain. Journal of Neuroinflammation 6: 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-6-9.
Beurel, E. 2011. Regulation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 of inflammation and T cells in CNS diseases. Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience 4: 18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnmol.2011.00018.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project 81373161) and two awards from the Health Department of Zhejiang Province, China (Project 2012ZDA017, 2012KYA081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Xu, H., Lv, W. et al. miR-199b-5p Regulates Immune-Mediated Allograft Rejection after Lung Transplantation Through the GSK3β and NF-κB Pathways. Inflammation 41, 1524–1535 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0799-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0799-2