Abstract
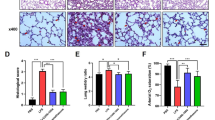
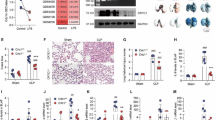
Acute lung injury (ALI) is one of the most important complications after cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) and the complex pathophysiology remains to be resolved incomplete. SDF-1/CXCR4 chemokine axis can chemotactically accumulate inflammatory cell to local tissue and regulate the release of inflammatory factors, and SDF-1 has a strong chemotaxis effect on neutrophils with CXCR4. Since CPB animal model was difficult to establish, there was still no report about the effect of SDF-1/CXCR4 on neutrophil chemotaxis in ALI after CPB. Here, a stable CPB rat model was constructed to clarify the role of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in the CPB-induced ALI. Real-time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), Western blot analysis, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) were used to detect the changes of SDF-1 and CXCR4 in lung tissues, blood, bronchoalveolar lavage (BALF), and/or isolated neutrophils. SDF-1/CXCR4 was increased after CPB, both of that were increased in blood; CXCR4 was increased in neutrophils; SDF-1/CXCR4 was also increased in BALF of CPB model. Results indicated that SDF-1/CXCR4 axis played a key role in the process of early ALI after CPB, also showed that lung injury was significantly reduce after blocking SDF-1/CXCR4 axis, suggest that CXCR4 might be a new target for ALI treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perl, M., J. Lomas-Neira, F. Venet, C.S. Chung, and A. Ayala. 2011. Pathogenesis of indirect (secondary) acute lung injury. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine 5: 115–126.
Koch, C., L. Li, P. Figueroa, T. Mihaljevic, L. Svensson, and E.H. Blackstone. 2009. Transfusion and pulmonary morbidity after cardiac surgery. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 88: 1410–1418.
Vlaar, A.P., J.J. Hofstra, R.M. Determann, D.P. Veelo, F. Paulus, W. Kulik, J. Korevaar, B.A. de Mol, M.M. Koopman, L. Porcelijn, J.M. Binnekade, M.B. Vroom, M.J. Schultz, and N.P. Juffermans. 2011. The incidence, risk factors, and outcome of transfusion-related acute lung injury in a cohort of cardiac surgery patients: a prospective nested case-control study. Blood 117: 4218–4225.
Luehr, M., J. Bachet, F.W. Mohr, and C.D. Etz. 2014. Modern temperature management in aortic arch surgery: the dilemma of moderate hypothermia. European Journal of Cardio-Thoracic Surgery 45: 27–39.
Ng, C.S., S. Wan, A.P. Yim, and A.A. Arifi. 2002. Pulmonary dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Chest 121: 1269–1277.
Bhatia, M., R.L. Zemans, and S. Jeyaseelan. 2012. Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 46: 566–572.
Xiang, M., and J. Fan. 2010. Pattern recognition receptor-dependent mechanisms of acute lung injury. Molecular Medicine 16: 69–82.
Kallet, R.H., and M.A. Matthay. 2013. Hyperoxic acute lung injury. Respiratory Care 58: 123–141.
Raghavendran, K., G.S. Pryhuber, P.R. Chess, B.A. Davidson, P.R. Knight, and R.H. Notter. 2008. Pharmacotherapy of acute lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome. Current Medicinal Chemistry 15: 1911–1924.
Martin, C., P.C. Burdon, G. Bridger, J.C. Gutierrez-Ramos, T.J. Williams, and S.M. Rankin. 2003. Chemokines acting via CXCR2 and CXCR4 control the release of neutrophils from the bone marrow and their return following senescence. Immunity 19: 583–593.
Furze, R.C., and S.M. Rankin. 2008. Neutrophil mobilization and clearance in the bone marrow. Immunology 125: 281–288.
Petty, J.M., V. Sueblinvong, C.C. Lenox, C.C. Jones, G.P. Cosgrove, C.D. Cool, P.R. Rai, K.K. Brown, D.J. Weiss, M.E. Poynter, and B.T. Suratt. 2007. Pulmonary stromal-derived factor-1 expression and effect on neutrophil recruitment during acute lung injury. Journal of Immunology 178: 8148–8157.
Delano, M.J., K.M. Kelly-Scumpia, T.C. Thayer, R.D. Winfield, P.O. Scumpia, A.G. Cuenca, P.B. Harrington, K.A. O’Malley, E. Warner, S. Gabrilovich, C.E. Mathews, D. Laface, P.G. Heyworth, R. Ramphal, R.M. Strieter, L.L. Moldawer, and P.A. Efron. 2011. Neutrophil mobilization from the bone marrow during polymicrobial sepsis is dependent on CXCL12 signaling. Journal of Immunology 187: 911–918.
Zernecke, A., I. Bot, Y. Djalali-Talab, E. Shagdarsuren, K. Bidzhekov, S. Meiler, R. Krohn, A. Schober, M. Sperandio, O. Soehnlein, J. Bornemann, F. Tacke, E.A. Biessen, and C. Weber. 2008. Protective role of CXC receptor 4/CXC ligand 12 unveils the importance of neutrophils in atherosclerosis. Circulation Research 102: 209–217.
Hartl, D., S. Krauss-Etschmann, B. Koller, P.L. Hordijk, T.W. Kuijpers, F. Hoffmann, A. Hector, E. Eber, V. Marcos, I. Bittmann, O. Eickelberg, M. Griese, and D. Roos. 2008. Infiltrated neutrophils acquire novel chemokine receptor expression and chemokine responsiveness in chronic inflammatory lung diseases. Journal of Immunology 181: 8053–8067.
Liu, K., L. Shen, J. Wang, G. Dong, H. Wu, H. Shao, and H. Jing. 2012. The preventative role of curcumin on the lung inflammatory response induced by cardiopulmonary bypass in rats. Journal of Surgical Research 174: 73–82.
Liu, K., H.L. Chen, H. Huang, H. Jing, G.H. Dong, H.W. Wu, and Q.S. You. 2012. Curcumin attenuates cardiopulmonary bypass-induced lung oxidative damage in rats. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics 17: 395–402.
Lukacs, N.W., A. Berlin, D. Schols, R.T. Skerlj, and G.J. Bridger. 2002. AMD3100, a CxCR4 antagonist, attenuates allergic lung inflammation and airway hyperreactivity. American Journal of Pathology 160: 1353–1360.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Heikkinen, L.O., and K.V. Alakulju. 2009. Abdominal complications following cardiopulmonary bypass in open-heart surgery. Scandinavian Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery 95: 1–7.
Dhein, S., M. Grassl, M. Gerdom, M. Vollroth, F. Bakhtiary, S. von Salisch, K. Krämer, A. Sobiraj, M. Kostelka, F.W. Mohr, and A. Salameh. 2015. Organ-protective effects on the liver and kidney by minocycline in small piglets undergoing cardiopulonary bypass. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology 388: 663–676.
Du, S., J. Ai, X. Zeng, J. Wan, X. Wu, and J. He. 2016. Plasma level of advanced oxidation protein products as a novel biomarker of acute lung injury following cardiac surgery. Springerplus 5: 231.
Senay, S., F. Toraman, S. Gunaydin, M. Kilercik, H. Karabulut, and C. Alhan. 2009. The impact of allogenic red cell transfusion and coated bypass circuit on the inflammatory response during cardiopulmonary bypass: a randomized study. Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery 8: 93–99.
Melley, D.D., T.W. Evans, and G.J. Quinlan. 2005. Redox regulation of neutrophil apoptosis and the systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Clinical Science (London) 108: 413–424.
Fujishima, S., H. Morisaki, A. Ishizaka, Y. Kotake, M. Miyaki, K. Yoh, K. Sekine, J. Sasaki, S. Tasaka, N. Hasegawa, Y. Kawai, J. Takeda, and N. Aikawa. 2008. Neutrophil elastase and systemic inflammatory response syndrome in the initiation and development of acute lung injury among critically ill patients. Biomedicine and Pharmacotherapy 62: 333–338.
Yamada, M., H. Kubo, S. Kobayashi, K. Ishizawa, M. He, T. Suzuki, N. Fujino, H. Kunishima, M. Hatta, K. Nishimaki, T. Aoyagi, K. Tokuda, M. Kitagawa, H. Yano, H. Tamamura, N. Fujii, and M. Kaku. 2011. The increase in surface CXCR4 expression on lung extravascular neutrophils and its effects on neutrophils during endotoxin-induced lung injury. Cellular and Molecular Immunology 8: 305–314.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from Six Talent Peaks Project in Jiangsu Province, China (no. 2014-YY-006), the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of China (no. 2013M541705), the Postdoctoral Research Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (no. 1301072C), and the Science Foundation of Nantong City, Jiangsu Province, China (nos. HS2012025 and MS32015016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
All procedures of animal treatments were in accordance with the guidelines for experimental animals approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Nantong University (China).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Hai Shi and Rujian Lu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, H., Lu, R., Wang, S. et al. Effects of SDF-1/CXCR4 on Acute Lung Injury Induced by Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Inflammation 40, 937–945 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0538-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-017-0538-0