Abstract
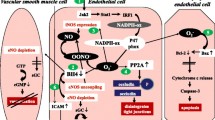
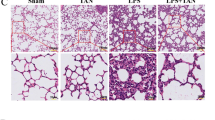
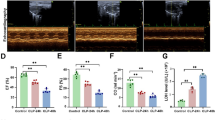
Experimental studies indicate that sepsis causes remote organ injury although the molecular mechanism has not been clearly defined. In this report, the role of oxidative damage, and inflammation on lung injury, following sepsis model by cecal ligation and puncture, and the effects of quercetin, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory flavonoid, in the lung tissue were investigated. In the present study, we found that administration of single-dose quercetin before cecal ligation and puncture procedure, while markedly diminishing the levels of YKL-40 and oxidant molecules (xanthine oxidase (XO), nitric oxide (NO), and malondialdehyde (MDA)), increases the antioxidant enzymes levels. Quercetin is beneficial to acute lung injury by decreasing the levels of oxidative stress markers and increasing the antioxidant enzyme activities. Quercetin also causes a decrease in the serum levels of YKL-40 and periostin in the oxidative lung injury induced by the experimental sepsis model.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin, G.S. 2012. Sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock: changes in incidence, pathogens and outcomes. Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy 10(6): 701–6.
Wang, L., J. Chen, B. Wang, D. Wu, and H. Li. 2014. Protective effect of quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice by inhibiting inflammatory cell influx. Experimental Biology and Medicine 239(12): 1653–1662.
Huang, R., T. Zhong, and H. Wu. 2015. Quercetin protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats through suppression of inflammation and oxidative stress. Archives of Medical Science 11(2): 427–432.
Grommes, J., and O. Soehnlein. 2011. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Molecular Medicine 17: 293–307.
Osuchowski, M.F., J. Connett, K. Welch, J. Granger, and D.G. Remick. 2009. Stratification is the key: inflammatory biomarkers accurately direct immunomodulatory therapy in experimental sepsis. Critical Care Medicine 37(5): 1567–1573.
Hattori, N., S. Oda, T. Sadahiro, M. Nakamura, and R. Abe. 2009. YKL-40 identified by proteomic analysis as a biomarker of sepsis. Shock 32(4): 393–400.
DeCoux, A., Y. Tian, K.Y. DeLeon-Pennell, N.T. Nguyen, L.E. de Castro Brás, E.R. Flynn, et al. 2015. Plasma glycoproteomics reveals sepsis outcomes linked to distinct proteins in common pathways. Critical Care Medicine 43(10): 2049–2058.
Luangaram, S., U. Kukongviriyapan, P. Pakdeechote, V. Kukongviriyapan, and P. Pannangpetch. 2007. Protective effects of quercetin against phenylhydrazine-induced vascular dysfunction and oxidative stress in rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology 45(3): 448–455.
Ganesan, S., A.N. Faris, A.T. Comstock, S.S. Chattoraj, and A. Chattoraj. 2010. Quercetin prevents progression of disease in elastase/LPS-exposed mice by negatively regulating MMP expression. Respiratory Research 11(131): 1–15.
Conway, S.J., K. Izuhara, Y. Kudo, J. Litvin, and R. Markwald. 2014. The role of periostin in tissue remodeling across health and disease. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 71: 1279–1288.
Li, W., P. Gao, Y. Zhi, W. Xu, Y. Wu, J. Yin, et al. 2015. Periostin: its role in asthma and its potential as a diagnostic or therapeutic target. Respiratory Research 16(1): 57.
Dejager, L., I. Pinheiro, E. Dejonckheere, and C. Libert. 2011. Cecal ligation and puncture: the gold standard model for polymicrobial sepsis? Trends in Microbiology 19(4): 198–208.
Wichterman, K.A., A.E. Baue, and I.H. Chaudry. 1980. Sepsis and septic shock—a review of laboratory models and a proposal. Journal of Surgical Research 29: 189–201.
Hubbard, W.J., M. Choudhry, M.G. Schwacha, and J.D. Kerby. 2005. Cecal ligation and puncture. Shock 24: 52–57.
Prajda, N., and G. Weber. 1975. Malign transformation-linked imbalance: decreased XO activity in hepatomas. FEBS Letters 59: 245–249.
Sun, Y., L.W. Oberley, and Y. Li. 1988. A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clinical Chemistry 34: 497–500.
Aebi H. Catalase. Methods Enzym. Anal. New York and London: Academic Press; 1974;673–677.
Lowry, O.H., N.J. Rosebrough, A.L. Farr, and R.J. Randall. 1951. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. Journal of Biological Chemistry 193: 265–275.
Liao, Y.R., and J.Y. Lin. 2015. Quercetin intraperitoneal administration ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced systemic inflammation in mice. Life Sciences 137(15): 89–97.
Chang, Y.C., M.H. Tsai, W.H. Sheu, S.C. Hsieh, and A.N. Chiang. 2013. The therapeutic potential and mechanisms of action of quercetin in relation to lipopolysaccharide-induced sepsis in vitro and in vivo. PloS One 8(11), e80744.
Kukongviriyapan, U., K. Sompamit, P. Pannagpetch, V. Kukongviriyapan, and W. Donpunha. 2012. Preventive and therapeutic effects of quercetin on lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress and vascular dysfunction in mice. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 90(10): 1345–1353.
Czapski, G.A., D. Avram, D.V. Sakharov, K.W. Wirtz, J.B. Strosznajder, and E.H. Pap. 2002. Activated neutrophils oxidize extracellular proteins of endothelial cells in culture: effect of nitric oxide donors. Biochemical Journal 365: 897–902.
Johansen, J.S., K.S. Krabbe, K. Møller, and B.K. Pedersen. 2005. Circulating YKL-40 levels during human endotoxaemia. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 140: 343–348.
Van Bilsen, J.H.M., H. van Dongen, L.R. Lard, E.I.H. van der Voort, D.G. Elferink, A.M. Bakker, et al. 2004. Functional regulatory immune responses against human cartilage glycoprotein-39 in health vs. proinflammatory responses in rheumatoid arthritis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 101: 17180–17185.
Kronborg, G., C. Østergaard, N. Weis, H. Nielsen, and N. Obel. 2002. Serum level of YKL-40 is elevated in patients with Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteremia and is associated with the outcome of the disease. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 34: 323–326.
Huang, Y., W. Liu, H. Xiao, A. Maitikabili, Q. Lin, T. Wu, et al. 2015. Matricellular protein periostin contributes to hepatic inflammation and fibrosis. American Journal of Pathology 185(3): 786–797.
Takayama, G., K. Arima, T. Kanaji, S. Toda, H. Tanaka, S. Shoji, et al. 2006. Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13 signals. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 118: 98–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerin, F., Sener, U., Erman, H. et al. The Effects of Quercetin on Acute Lung Injury and Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in the Rat Model of Sepsis. Inflammation 39, 700–705 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0296-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0296-9