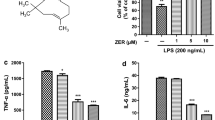
Abstract
Microglia are considered as a major target in the prevention of neuroinflammation by modulating the production of pro-inflammatory mediators. Artesunate, a water-soluble artemisinin derivative, exerts an anti-inflammatory effect. In the present study, we showed artesunate dose-dependently suppressed the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and interleukin-1beta (IL-1β) in BV2 microglial cells. In addition, artesunate inhibited LPS-induced expression of Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4), myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88), and activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) by blockade of inhibitor of NF-κB (IκB) degradation. This data indicate that artesunate attenuates the generation of proinflammatory mediators on LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglial cells. And this effect may be associated with the suppression of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathways. Therefore, artesunate may be a potential anti-neuroinflammatory agent.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ransohoff, R.M., and V.H. Perry. 2009. Microglial physiology: unique stimuli, specialized responses. Annual Review of Immunology 27: 119–145.
Brown, G.C., and J.J. Neher. 2010. Inflammatory neurodegeneration and mechanisms of microglial killing of neurons. Molecular Neurobiology 41: 242–247.
Nelson, P.T., L.A. Soma, and E. Lavi. 2002. Microglia in diseases of the central nervous system. Annals of Medicine 34: 491–500.
Meshnick, S.R., T.E. Taylor, and S. Kamchonwongpaisan. 1996. Artemisinin and the antimalarial endoperoxides: from herbal remedy to targeted chemotherapy. Microbiological Reviews 60: 301–315.
Xu, H., Y. He, X. Yang, L. Liang, Z. Zhan, Y. Ye, X. Yang, F. Lian, and L. Sun. 2007. Anti-malarial agent artesunate inhibits TNF-alpha-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines via inhibition of NF-kappaB and PI3 kinase/Akt signal pathway in human rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 46: 920–926.
Chen, H.H., H.J. Zhou, G.D. Wu, and X.E. Lou. 2004. Inhibitory effects of artesunate on angiogenesis and on expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and VEGF receptor KDR/flk-1. Pharmacology 71: 1–9.
Efferth, T., H. Dunstan, A. Sauerbrey, H. Miyachi, and C.R. Chitambar. 2001. The anti-malarial artesunate is also active against cancer. International Journal of Oncology 18: 767–773.
Li, B., R. Zhang, J. Li, L. Zhang, G. Ding, P. Luo, S. He, Y. Dong, W. Jiang, Y. Lu, H. Cao, J. Zheng, and H. Zhou. 2008. Antimalarial artesunate protects sepsis model mice against heat-killed Escherichia coli challenge by decreasing TLR4, TLR9 mRNA expressions and transcription factor NF-kappa B activation. International Immunopharmacology 8: 379–389.
Wang, X., L. Stridh, W. Li, J. Dean, A. Elmgren, L. Gan, K. Eriksson, H. Hagberg, and C. Mallard. 2009. Lipopolysaccharide sensitizes neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in a MyD88-dependent manner. The Journal of Immunology: Official Journal of the American Association of Immunologists 183: 7471–7477.
Okorji, U.P., and O.A. Olajide. 2014. A semi-synthetic derivative of artemisinin, artesunate inhibits prostaglandin E2 production in LPS/IFNgamma-activated BV2 microglia. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 22: 4726–4734.
Zhu, C., Z. Xiong, X. Chen, F. Peng, X. Hu, Y. Chen, and Q. Wang. 2012. Artemisinin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-stimulated proinflammatory responses by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway in microglia cells. PLoS ONE 7: e35125.
Lee, I.S., D.K. Ryu, J. Lim, S. Cho, B.Y. Kang, and H.J. Choi. 2012. Artesunate activates Nrf2 pathway-driven anti-inflammatory potential through ERK signaling in microglial BV2 cells. Neuroscience Letters 509: 17–21.
Gonzalez, H., D. Elgueta, A. Montoya, and R. Pacheco. 2014. Neuroimmune regulation of microglial activity involved in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Journal of Neuroimmunology 274: 1–13.
Pais, T.F., E.M. Szego, O. Marques, L. Miller-Fleming, P. Antas, P. Guerreiro, R.M. de Oliveira, B. Kasapoglu, and T.F. Outeiro. 2013. The NAD-dependent deacetylase sirtuin 2 is a suppressor of microglial activation and brain inflammation. The EMBO Journal 32: 2603–2616.
Zhang, L., J. Zhang, L. Yang, Y. Dong, Y. Zhang, and Z. Xie. 2013. Isoflurane and sevoflurane increase interleukin-6 levels through the nuclear factor-kappa B pathway in neuroglioma cells. British Journal of Anaesthesia 110(Suppl 1): i82–91.
Kingwell, K. 2012. Neurodegenerative disease: microglia in early disease stages. Nature Reviews. Neurology 8: 475.
Kang, C.H., R.G. Jayasooriya, M.G. Dilshara, Y.H. Choi, Y.K. Jeong, N.D. Kim, and G.Y. Kim. 2012. Caffeine suppresses lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells by suppressing Akt-mediated NF-kappaB activation and ERK phosphorylation. Food and Chemical Toxicology: an International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 50: 4270–4276.
Zhu, H.T., C. Bian, J.C. Yuan, W.H. Chu, X. Xiang, F. Chen, C.S. Wang, H. Feng, and J.K. Lin. 2014. Curcumin attenuates acute inflammatory injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway in experimental traumatic brain injury. Journal of Neuroinflammation 11: 59.
Zhong, L.M., Y. Zong, L. Sun, J.Z. Guo, W. Zhang, Y. He, R. Song, W.M. Wang, C.J. Xiao, and D. Lu. 2012. Resveratrol inhibits inflammatory responses via the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway in cultured LPS-stimulated microglial cells. PLoS ONE 7: e32195.
de Vries, P.J., and T.K. Dien. 1996. Clinical pharmacology and therapeutic potential of artemisinin and its derivatives in the treatment of malaria. Drugs 52: 818–836.
Kim, H.G., J.H. Yang, E.H. Han, J.H. Choi, T. Khanal, M.H. Jeong, T.C. Jeong, and H.G. Jeong. 2013. Inhibitory effect of dihydroartemisinin against phorbol ester-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in macrophages. Food and Chemical Toxicology: An International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association 56: 93–99.
Wang, Y., Z. Huang, L. Wang, S. Meng, Y. Fan, T. Chen, J. Cao, R. Jiang, and C. Wang. 2011. The anti-malarial artemisinin inhibits pro-inflammatory cytokines via the NF-kappaB canonical signaling pathway in PMA-induced THP-1 monocytes. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 27: 233–241.
Smith, J.A., A. Das, S.K. Ray, and N.L. Banik. 2012. Role of pro-inflammatory cytokines released from microglia in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Research Bulletin 87: 10–20.
Crampton, S.J., L.M. Collins, A. Toulouse, Y.M. Nolan, and G.W. O’Keeffe. 2012. Exposure of foetal neural progenitor cells to IL-1beta impairs their proliferation and alters their differentiation—a role for maternal inflammation. Journal of Neurochemistry 120: 964–973.
Rothwell, N., S. Allan, and S. Toulmond. 1997. The role of interleukin 1 in acute neurodegeneration and stroke: pathophysiological and therapeutic implications. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 100: 2648–2652.
Yao, L., E.M. Kan, J. Lu, A. Hao, S.T. Dheen, C. Kaur, and E.A. Ling. 2013. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates microglial activation and production of inflammatory mediators in neonatal rat brain following hypoxia: role of TLR4 in hypoxic microglia. Journal of Neuroinflammation 10: 23.
Zhang, G., and S. Ghosh. 2001. Toll-like receptor-mediated NF-kappaB activation: a phylogenetically conserved paradigm in innate immunity. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 107: 13–19.
Zhang, P., X.M. Chen, B.D. Luo, Q. Tan, F. Zou, W.R. Wan, and J.Q. Guo. 2006. Effects of artesunate on CD14 and toll-like receptor 4 in peritoneal macrophages of mice with heat stroke endotoxemia. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi = Zhonghua Laodong Weisheng Zhiyebing Zazhi = Chinese Journal of Industrial Hygiene and Occupational Diseases 24: 226–228.
Mankan, A.K., M.W. Lawless, S.G. Gray, D. Kelleher, and R. McManus. 2009. NF-kappaB regulation: the nuclear response. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine 13: 631–643.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the affiliated hospital of Xuzhou Medical College (No. 2013104049). Additional support is provided by the neurobiology laboratory of Xuzhou Medical College.
Conflict of Interest
There is no conflict of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, D., Shi, J., Lv, S. et al. Artesunate Attenuates Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Proinflammatory Responses by Suppressing TLR4, MyD88 Expression, and NF-κB Activation in Microglial Cells. Inflammation 38, 1925–1932 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0172-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0172-7