Abstract
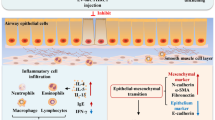
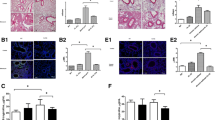
The aim of our study was to elucidate the function and signaling pathway of found in inflammatory zone 1 (FIZZ1) in airway remodeling in asthma. We used a mice model sensitized and challenged by ovalbumin (OVA) to evaluate the expression of FIZZ1, type I collagen, and fibronectin-1 in the airway in asthma. To investigate the signaling pathway regulated by FIZZ1, we treated a cultured murine lung epithelium cell-12 (MLE-12) with FIZZ1 recombination protein, silenced the expression of FIZZ1 with FIZZ1-shRNA in vitro, and then detected phosphorylated phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) and expression of type I collagen and fibronectin-1 (FN-1) by Western blotting. In addition, we increased the expression of PTEN by PTEN plasmid transfection then detected the expression of type I collagen and fibronectin-1 in MLE-12 by Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence cytochemistry technology, respectively. First, the expression of FIZZ1, type I collagen, and fibronectin-1 was significantly elevated in the lungs of OVA-challenged mice compared with saline-treated control animals. Secondly, the phosphorylation of PTEN was decreased in MLE-12 treated with FIZZ1 recombination protein in vitro. On the contrary, the phosphorylation of PTEN was increased in MLE-12 cells transfected with FIZZ1-shRNA. Thirdly, results of the Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence cytochemistry showed that expression of type I collagen and fibronectin-1 was increased in cells treated with FIZZ1 recombination protein, while the levels of type I collagen and fibronectin-1 were significantly decreased in cells transfected with PTEN plasmid. FIZZ1 may be a critical cytokine in airway remodeling in asthma. This study indicates that targeting FIZZ1 and/or PTEN may be a new therapeutic strategy for asthma.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holgate, S.T. 2008. Pathogenesis of asthma. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 38(6): 872–897.
Seow, C.Y., R.R. Schellenberg, and P.D. Pare. 1998. Structural and functional changes in the airway smooth muscle of asthmatic subjects. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 158(5): 179–186.
Kaminska, M., S. Foley, K. Maghni, et al. 2009. Airway remodeling in subjects with severe asthma with or without chronic persistent airflow obstruction. Journal of Allergy Clinical Immunology 124(1): 45–51.
Wu J, Liu F, Zhao J, Wei Y, Lv J, Dong F, et al. 2012. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin promotes asthmatic airway remodeling in human lung fibroblast cells through STAT3 signalling pathway. Cell biochemistry and function.
Guo, Z., J. Wu, J. Zhao, et al. 2014. IL-33 promotes airway remodeling and is a marker of asthma disease severity. The Journal of Asthma 5: 1–7.
Holgate, S.T., D.E. Davies, P.M. Lackie, et al. 2000. Epithelial mesenchymal interactions in the pathogenesis of asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 105: 193–204.
Richter, A., S.M. Puddicombe, J.L. Lordan, et al. 2001. The contribution of interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 to the epithelial-mesenchymal trophic unit in asthma. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 25(3): 385–391.
Homer, R.J., and J.A. Elias. 2005. Airway remodeling in asthma: therapeutic implications of mechanisms. Physiology 20: 28–35.
Shifren A, Witt C, Christie C, Castro M. 2012. Mechanisms of remodeling in asthmatic airways. Journal of Allergy.
Holcomb, I.N., R.C. Kabakoff, and B. Chan. 2000. FIZZ1, a novel cysteine-rich secreted protein associated with pulmonary inflammation, defines a new gene family. The EMBO Journal 19: 4046–4055.
Liu, T.J., and Saravana M. Dhanasekaran. 2004. FIZZ1 stimulation of myofibroblast differentiation. The American Journal of Pathology 164: 1315–1326.
Ma, W.L., H. Ye, X.N. Tao, and J.B. Xin. 2005. Dynamic changes of found in inflammatory zone 1 protein and mRNA expression in the lung with experimental pulmonary fibrosis of the rat. Sheng Li Xue Bao 57: 493–497.
Shujuan, W., C.M. Blanca, L. Hongjia, et al. 2008. FIZZ1 plays a crucial role in early stage airway remodeling of OVA-induced asthma. Journal of Asthma 45: 648–653.
Chung, M.J., T. Liu, M. Ullenbruch, and S.H. Phan. 2007. Antiapoptotic effect of found in inflammatory zone (FIZZ) 1 on mouse lung fibroblasts. The Journal of Pathology 2: 180–187.
Hill, R., and H. Wu. 2009. PTEN, stem cells, and cancer stem cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 284(18): 11755–11759.
Lee, Y.C. 2004. The role of PTEN in allergic inflammation. Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis 52: 250–254.
Lee, K.S., S.R. Kim, S.J. Park, et al. 2006. Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) reduces vascular endothelial growth factor expression in allergen-induced airway inflammation. Molecular Pharmacology 69(6): 1829–1839.
Kim, S.R., K.S. Lee, S.J. Park, et al. 2007. PTEN down-regulates IL-17 expression in a murine model of toluene diisocyanate-induced airway disease. Journal of Immunology 179(10): 6820–6829.
Smit, J.J., H. Van Loveren, and M.O. Hoekstra. 2003. Therapeutic treatment with heat-killed Mycobacterium vaccae (SRL172) in a mild and severe mouse model for allergic asthma. European Journal of Pharmacology 470: 193–199.
Davies, D.E., J. Wicks, R.M. Powell, et al. 2003. Airway remodeling in asthma: new insights. Journal of Allery Clinical Immunology 111(2): 215–225.
Hackett, T.L., and D.A. Knight. 2007. The role of epithelial injury and repair in the origins of asthma. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology 7: 63–68.
Vignola, A.M., R. Gagliardo, and A. Siena. 2001. Airway remodeling in the pathogenesis of asthma. Current Opinion in Allergy and Clinical Immunology 1: 85–93.
Pilewski, J.M., and S.M. Albelda. 1995. Cell adhesion molecules in asthma: homing, activation, and airway remodeling. Journal of Respiration Cell Molecular Biology 12: 1–3.
Wagner, K.F., A.K. Hellberg, and S. Balenger. 2004. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor has antiapoptotic action and is upregulated in the developing lung: coexpression with hypoxia-inducible factor-2alpha. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 31: 276–282.
Patel, S.D., M.W. Rajala, and L. Rossetti. 2004. Disulfide-dependent multimeric assembly of resistin family hormones. Science 304(5674): 1154–1158.
Katsuma, S., K. Nishi, K. Tanigawara, et al. 2001. Molecular monitoring of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis by cDNA microarray-based gene expression profiling. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 288: 747–751.
Shen, W.H., A.S. Balajee, J. Wang, et al. 2007. Essential role for nuclear PTEN in maintaining chromosomal integrity. Cell 128(1): 157–170.
Cai, X.M., B.B. Tao, L.Y. Wang, et al. 2005. Protein phosphatase activity of PTEN inhibited the invasion of glioma cells with epidermal growth factor receptor mutation type 3 expression. International Journal of Cancer 117(6): 905–912.
Jiang, B.H., and L.Z. Liu. 2008. PI3K/PTEN signaling in tumorigenesis and angiogenesis. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1784(1): 150–158.
Downes, C.P., N. Perera, S. Ross, et al. 2007. Substrate specificity and acute regulation of the tumor suppressor phosphatase PTEN. Biochemical Society Symposium 74(1): 69–80.
Lan, H., H. Zhong, Y. Gao, et al. 2010. The PTEN tumor suppressor inhibits human airway smooth muscle cell migration. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 26(6): 893–899.
Koul, D., R. Shen, S. Shishodia, et al. 2007. PTEN downregulates AP-1 and targets c-fos in human glioma cells via PI3-kinase/ Akt pathway. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 300: 77–87.
Tiddens, H., M. Silverman, and A. Bush. 2000. The role of inflammation in airway disease: remodeling. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 162: 7–10.
Yamaji-Kegan, K., Q. Su, D.J. Angelini, A.C. Myers, C. Cheadle, and R.A. Johns. 2010. Hypoxia-induced mitogenic factor (HIMF/FIZZ1/RELMalpha) increases lung inflammation and activates pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells via an IL-4-dependent mechanism. Journal of Immunology 185: 5539–5548.
Ito, T., M. Schaller, T. Raymond, et al. 2009. Toll-like receptor 9 activation is a key mechanism for the maintenance of chronic lung inflammation. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 180: 1227–1238.
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Wenxiang Bi (Institute of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, School of Medicine, Shandong University) for the excellent technical assistance and Yan Wang for providing us with the histochemistry staining apparatus and technical guidance. This work was supported by grants from the Natural and Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81070016, 81270072).
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest. The authors alone are responsible for the content and writing of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jiping Zhao and Xingai Jiao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, J., Jiao, X., Wu, J. et al. FIZZ1 Promotes Airway Remodeling in Asthma Through the PTEN Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 38, 1464–1472 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0121-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-015-0121-5