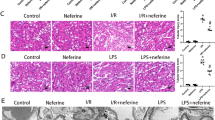
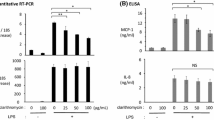
Abstract
Sepsis is often initiated by invasive infection, characterized by overwhelming induction of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The incidence and mortality of sepsis and the associated development of acute kidney injury (AKI) remain high, and lines of research into potential treatments are needed. This study was conducted to investigate effects of alpha-lipoic acid (ALA) on septic AKI in vitro. ALA of 200 or 400 μM was used to pretreat rat HBZY-1 mesangial cells before commencement of 1 μg/mL lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Our data indicated that ALA pretreatment reduced LPS-stimulated release of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), interleukin (IL)-1 beta (IL-1β), as well as IL-6, in HBZY-1 cell supernatant. Moreover, LPS-induced expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) was inhibited by ALA pretreatment, and consequently, the secretion levels of their respective enzymatic products prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and nitric oxide (NO) were significantly decreased. LPS-enhanced phosphorylation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) inhibitor alpha (IκBα) and IκB kinase alpha/beta (IKKα/β) and nuclear translocation of NF-κB subunit p65 in HBZY-1 cells were inhibited by ALA pretreatment. Additionally, the NF-κB inhibitor N-acetylcysteine (NAC) exerted similar inhibitory effects as ALA on COX-2 and iNOS expression. In summary, our study demonstrates that ALA mitigates LPS-induced inflammatory responses in rat mesangial cells probably via inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway, suggesting a therapeutic potential of ALA in AKI related to sepsis.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buras, J.A., B. Holzmann, and M. Sitkovsky. 2005. Animal models of sepsis: Setting the stage. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 4(10): 854–865. doi:10.1038/nrd1854.
Fry, D.E. 2012. Sepsis, systemic inflammatory response, and multiple organ dysfunction: The mystery continues. American Surgeon 78(1): 1–8.
Bagshaw, S.M., C. George, and R. Bellomo. 2008. Early acute kidney injury and sepsis: A multicentre evaluation. Critical Care 12(2): R47. doi:10.1186/cc6863.
Honore, P.M., R. Jacobs, O. Joannes-Boyau, J. De Regt, W. Boer, E. De Waele, V. Collin, and H.D. Spapen. 2011. Septic AKI in ICU patients. diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment type, dosing, and timing: A comprehensive review of recent and future developments. Annals of Intensive Care 1(1): 32.
Waikar, S.S., and J.V. Bonventre. 2009. Creatinine kinetics and the definition of acute kidney injury. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 20(3): 672–679. doi:10.1681/ASN.2008070669.
Chvojka, J., R. Sykora, T. Karvunidis, J. Radej, A. Krouzecky, I. Novak, and M. Matejovic. 2010. New developments in septic acute kidney injury. Physiological Research 59(6): 859–869.
Reed, L.J., B.B. De, I.C. Gunsalus, and C.S. Hornberger Jr. 1951. Crystalline alpha-lipoic acid; a catalytic agent associated with pyruvate dehydrogenase. Science 114(2952): 93–94.
Goraca, A., H. Huk-Kolega, A. Piechota, P. Kleniewska, E. Ciejka, and B. Skibska. 2011. Lipoic acid—biological activity and therapeutic potential. Pharmacological Reports 63(4): 849–858.
Golbidi, S., M. Badran, and I. Laher. 2011. Diabetes and alpha lipoic acid. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2: 69. doi:10.3389/fphar.2011.00069.
Wollin, S.D., and P.J. Jones. 2003. Alpha-lipoic acid and cardiovascular disease. Journal of Nutrition 133(11): 3327–3330.
Feuerecker, B., S. Pirsig, C. Seidl, M. Aichler, A. Feuchtinger, G. Bruchelt, and R. Senekowitsch-Schmidtke. 2012. Lipoic acid inhibits cell proliferation of tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biology and Therapy 13(14): 1425–1435. doi:10.4161/cbt.22003.
Packer, L., E.H. Witt, and H.J. Tritschler. 1995. alpha-Lipoic acid as a biological antioxidant. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 19(2): 227–250.
Evans, J.L., and I.D. Goldfine. 2000. Alpha-lipoic acid: A multifunctional antioxidant that improves insulin sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics 2(3): 401–413.
Zhang, W.J., H. Wei, T. Hagen, and B. Frei. 2007. Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates LPS-induced inflammatory responses by activating the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104(10): 4077–4082. doi:10.1073/pnas.0700305104.
Li, L., K.K. Steinauer, A.J. Dirks, B. Husbeck, I. Gibbs, and S.J. Knox. 2003. Radiation-induced cyclooxygenase 2 up-regulation is dependent on redox status in prostate cancer cells. Radiation Research 160(6): 617–621.
Ha, H., J.H. Lee, H.N. Kim, H.M. Kim, H.B. Kwak, S. Lee, H.H. Kim, and Z.H. Lee. 2006. alpha-Lipoic acid inhibits inflammatory bone resorption by suppressing prostaglandin E2 synthesis. Journal of Immunology 176(1): 111–117.
Koriyama, Y., Y. Nakayama, S. Matsugo, K. Sugitani, K. Ogai, T. Takadera, and S. Kato. 2013. Anti-inflammatory effects of lipoic acid through inhibition of GSK-3beta in lipopolysaccharide-induced BV-2 microglial cells. Neuroscience Research 77(1–2): 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.neures.2013.07.001.
Wongmekiat, O., D. Leelarungrayub, and K. Thamprasert. 2013. Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates renal injury in rats with obstructive nephropathy. BioMed Research International 2013: 138719. doi:10.1155/2013/138719.
Li, G., L. Gao, J. Jia, X. Gong, B. Zang, and W. Chen. 2014. Alpha-lipoic acid prolongs survival and attenuates acute kidney injury in a rat model of sepsis. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology. doi:10.1111/1440-1681.12244.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4): 402–408. doi:10.1006/meth.2001.1262.
Wu, F., W. Zhang, L. Li, F. Zheng, X. Shao, J. Zhou, and H. Li. 2011. Inhibitory effects of honokiol on lipopolysaccharide-induced cellular responses and signaling events in human renal mesangial cells. European Journal of Pharmacology 654(1): 117–121. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.11.022.
Pfeilschifter, J. 2002. Nitric oxide triggers the expression of proinflammatory and protective gene products in mesangial cells and the inflamed glomerulus. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation 17(3): 347–348.
Gu, G., Z. Zhang, G. Wang, F. Han, L. Han, K. Wang, J. Liu, and W. Li. 2011. Effects of electroacupuncture pretreatment on inflammatory response and acute kidney injury in endotoxaemic rats. Journal of International Medical Research 39(5): 1783–1797.
Dinchuk, J.E., B.D. Car, R.J. Focht, J.J. Johnston, B.D. Jaffee, M.B. Covington, N.R. Contel, V.M. Eng, R.J. Collins, P.M. Czerniak, et al. 1995. Renal abnormalities and an altered inflammatory response in mice lacking cyclooxygenase II. Nature 378(6555): 406–409. doi:10.1038/378406a0.
Abraham, E. 2003. Nuclear factor-kappaB and its role in sepsis-associated organ failure. Journal of Infectious Diseases 187(Suppl 2): S364–369. doi:10.1086/374750.
Liu, S.F., and A.B.. Malik. 2006. NF-kappa B activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. American Journal of Physiology - Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 290(4): L622–L645. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00477.2005.
Munford, R.S. 2008. Sensing gram-negative bacterial lipopolysaccharides: A human disease determinant? Infection and Immunity 76(2): 454–465. doi:10.1128/IAI.00939-07.
Davis MR, Jr., Goldberg JB. 2012. Purification and visualization of lipopolysaccharide from Gram-negative bacteria by hot aqueous-phenol extraction. Journal of Visualized Experiments (63). doi:10.3791/3916
Wang, W., S. Bansal, S. Falk, D. Ljubanovic, and R. Schrier. 2009. Ghrelin protects mice against endotoxemia-induced acute kidney injury. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 297(4): F1032–1037. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00044.2009.
Lamping, N., R. Dettmer, N.W. Schroder, D. Pfeil, W. Hallatschek, R. Burger, and R.R. Schumann. 1998. LPS-binding protein protects mice from septic shock caused by LPS or gram-negative bacteria. Journal of Clinical Investigation 101(10): 2065–2071. doi:10.1172/JCI2338.
Esposito, V., F. Grosjean, J. Tan, L. Huang, L. Zhu, J. Chen, H. Xiong, G.E. Striker, and F. Zheng. 2013. CHOP deficiency results in elevated lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and kidney injury. American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology 304(4): F440–450. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00487.2011.
Schlondorff, D. 1987. The glomerular mesangial cell: An expanding role for a specialized pericyte. FASEB Journal 1(4): 272–281.
Younes-Ibrahim, M. 2013. Mesangial cells: Renal function protagonists or coadjuvants? Jornal Brasileiro de Nefrologia 35(4): 248–249. doi:10.5935/0101-2800.20130041.
Benes, J., J. Chvojka, R. Sykora, J. Radej, A. Krouzecky, I. Novak, and M. Matejovic. 2011. Searching for mechanisms that matter in early septic acute kidney injury: An experimental study. Critical Care 15(5): R256. doi:10.1186/cc10517.
Simmons, D.L., R.M. Botting, and T. Hla. 2004. Cyclooxygenase isozymes: The biology of prostaglandin synthesis and inhibition. Pharmacological Reviews 56(3): 387–437. doi:10.1124/pr.56.3.3.
Ricciotti, E., and G.A. FitzGerald. 2011. Prostaglandins and inflammation. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 31(5): 986–1000. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.110.207449.
FitzGerald, G.A. 2003. COX-2 and beyond: Approaches to prostaglandin inhibition in human disease. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 2(11): 879–890. doi:10.1038/nrd1225.
Harris, R.C. 2006. COX-2 and the kidney. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 47(Suppl 1): S37–42. doi:10.1097/00005344-200605001-00007.
Chen, Q., N. Shinohara, T. Abe, T. Watanabe, K. Nonomura, and T. Koyanagi. 2004. Significance of COX-2 expression in human renal cell carcinoma cell lines. International Journal of Cancer 108(6): 825–832. doi:10.1002/ijc.11646.
Yamada, M., M. Kaibori, H. Tanaka, K. Habara, T. Hijikawa, Y. Tanaka, M. Oishi, T. Okumura, M. Nishizawa, and A.H. Kwon. 2012. alpha-lipoic acid prevents the induction of iNOS gene expression through destabilization of its mRNA in proinflammatory cytokine-stimulated hepatocytes. Digestive Diseases and Sciences 57(4): 943–951. doi:10.1007/s10620-011-2012-4.
Heemskerk, S., R. Masereeuw, F.G. Russel, and P. Pickkers. 2009. Selective iNOS inhibition for the treatment of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury. Nature Reviews Nephrology 5(11): 629–640. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2009.155.
Tak, P.P., and G.S. Firestein. 2001. NF-kappaB: A key role in inflammatory diseases. Journal of Clinical Investigation 107(1): 7–11. doi:10.1172/JCI11830.
Lawrence, T. 2009. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 1(6): a001651. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a001651.
Sanz, A.B.., M.D. Sanchez-Nino, A.M. Ramos, J.A. Moreno, B. Santamaria, M. Ruiz-Ortega, J. Egido, and A. Ortiz. 2010. NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 21(8): 1254–1262. doi:10.1681/ASN.2010020218.
Ng, Y.Y., C.C. Hou, W. Wang, X.R. Huang, and H.Y. Lan. 2005. Blockade of NFkappaB activation and renal inflammation by ultrasound-mediated gene transfer of Smad7 in rat remnant kidney. Kidney International. Supplement 94: S83–91. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.09421.x.
Zhang, W.J., and B. Frei. 2001. Alpha-lipoic acid inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation and adhesion molecule expression in human aortic endothelial cells. FASEB Journal 15(13): 2423–2432. doi:10.1096/fj.01-0260com.
Lee, K.M., B.S. Kang, H.L. Lee, S.J. Son, S.H. Hwang, D.S. Kim, J.S. Park, and H.J. Cho. 2004. Spinal NF-kB activation induces COX-2 upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity. European Journal of Neuroscience 19(12): 3375–3381. doi:10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03441.x.
Jia, J., Y. Liu, X. Zhang, X. Liu, and J. Qi. 2013. Regulation of iNOS expression by NF-kappaB in human lens epithelial cells treated with high levels of glucose. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 54(7): 5070–5077. doi:10.1167/iovs.13-11796.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Science and Technology Research Project of Department of Science and Technology of Liaoning Province (Grant No.: 2010225034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, G., Fu, J., Zhao, Y. et al. Alpha-Lipoic Acid Exerts Anti-Inflammatory Effects on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated Rat Mesangial Cells via Inhibition of Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Signaling Pathway. Inflammation 38, 510–519 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9957-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9957-3