Abstract
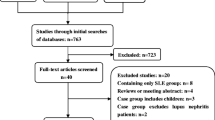
Premature atherosclerosis, the hallmark of cardiovascular diseases, has been found to be a significant cause of late deaths in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients. Therefore, early identification of atherosclerosis before the overt disease is curial for the management program of SLE. Flow-mediated dilatation (FMD%) is a reliable, noninvasive, easy to use, reproducible, and pathogenically relevant index for early atherosclerosis. In recent years, a number of studies have been performed to compare the mean FMD% difference between patients with SLE and healthy controls. However, these studies have shown inconclusive or even contradictory findings. In this study, to derive a more precise comparison of FMD% difference between SLE patients and healthy controls, a meta-analysis was performed. Databases were searched to identify all available studies comparing FMD% between SLE patients and healthy controls. The study eligibility criteria were cohort or case–control studies with data on both patients diagnosed with SLE and healthy controls, and use of high-resolution ultrasonography to detect FMD. Random effect meta-analysis was conducted to evaluate the overall mean FMD% difference between the two groups. Publication bias was detected by funnel plot and Egger’s test. Meta-regression analysis was performed to investigate the potential influencing factors on FMD% difference. Of the 434 articles initially identified, 22 were finally included in the meta-analysis. Compared to healthy controls, SLE patients had significantly lower FMD% (standardized mean difference, −1.19; 95 % CI, −1.63, −0.74; P < 0.001). There was significant heterogeneity among these studies (I 2 = 94.3 %, P < 0.001), which was mainly due to variations in disease duration of SLE patients. The funnel plot showed a skewed shape, indicating a marked publication bias, which was further supported by the Egger’s test (P = 0.006). However, after the correction for potential publication bias by using the trim-and-fill method, the main results for all studies combined were still significant (P < 0.001). Taken together, these findings support the current evidence on a higher cardiovascular burden in SLE and support using FMD% as a surrogate for premature atherosclerosis in SLE patients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Au, K., M.K. Singh, V. Bodukam, et al. 2011. Atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 63: 2078–2090.
Telles, R.W., C.C. Lanna, A.J. Sousa, et al. 2013. Progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Rheumatology 32: 1293–1300.
Frieri, M. 2012. Accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: role of proinflammatory cytokines and therapeutic approaches. Current Allergy and Asthma Reports 12: 25–32.
Kiani, A.N., W.S. Post, L.S. Magder, et al. 2011. Predictors of progression in atherosclerosis over 2 years in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50: 2071–2079.
Deo, S.S., A.R. Chogle, K.J. Mistry, et al. 2012. Increased prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis patients of Indian descent. Experimental and Clinical Cardiology 17: 20–25.
Kobayashi, H., J.T. Giles, J.F. Polak, et al. 2010. Increased prevalence of carotid artery atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis is artery-specific. Journal of Rheumatology 37: 730–739.
Avalos, I., Y.H. Rho, C.P. Chung, et al. 2008. Atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 26: S5–S13.
Wolfe, F., B. Freundlich, and W.L. Straus. 2003. Increase in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease prevalence in rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Rheumatology 30: 36–40.
Hettema, M.E., D. Zhang, K. de Leeuw, et al. 2008. Early atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis and its relation to disease or traditional risk factors. Arthritis Research and Therapy 10: R49.
Khurma, V., C. Meyer, G.S. Park, et al. 2008. A pilot study of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis: coronary artery calcification in cases and controls. Arthritis and Rheumatism 59: 591–597.
Hettema, M.E., H. Bootsma, and C.G. Kallenberg. 2008. Macrovascular disease and atherosclerosis in SSc. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47: 578–583.
Szucs, G., O. Timar, Z. Szekanecz, et al. 2007. Endothelial dysfunction precedes atherosclerosis in systemic sclerosis—relevance for prevention of vascular complications. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46: 759–762.
Hansson, G.K. 2005. Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. New England Journal of Medicine 352: 1685–1695.
Rho, Y.H., C.P. Chung, A. Oeser, et al. 2009. Inflammatory mediators and premature coronary atherosclerosis in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 61: 1580–1585.
McMahon, M., J. Grossman, J. FitzGerald, et al. 2006. Proinflammatory high-density lipoprotein as a biomarker for atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 54: 2541–2549.
O'Neill, S.G., I. Giles, A. Lambrianides, et al. 2010. Antibodies to apolipoprotein A-I, high-density lipoprotein, and C-reactive protein are associated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 62: 845–854.
Piper, M.K., K. Raza, S.L. Nuttall, et al. 2007. Impaired endothelial function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 16: 84–88.
Tyrrell, P.N., J. Beyene, B.M. Feldman, et al. 2010. Rheumatic disease and carotid intima-media thickness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 30: 1014–1026.
Yeboah, J., J.R. Crouse, F.C. Hsu, et al. 2007. Brachial flow-mediated dilation predicts incident cardiovascular events in older adults: the Cardiovascular Health Study. Circulation 115: 2390–2397.
Hochberg, M.C. 1997. Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis and Rheumatism 40: 1725.
Whitlock, R.P., S. Chan, P.J. Devereaux, et al. 2008. Clinical benefit of steroid use in patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. European Heart Journal 29: 2592–2600.
DerSimonian, R., and N. Laird. 1986. Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Controlled Clinical Trials 7: 177–188.
Higgins, J.P., and S.G. Thompson. 2002. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Statistics in Medicine 21: 1539–1558.
Higgins, J.P., S.G. Thompson, J.J. Deeks, et al. 2003. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327: 557–560.
Sterne, J.A., and M. Egger. 2001. Funnel plots for detecting bias in meta-analysis: guidelines on choice of axis. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 54: 1046–1055.
Egger, M., G. Davey Smith, M. Schneider, et al. 1997. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 315: 629–634.
Peters, J.L., A.J. Sutton, D.R. Jones, et al. 2007. Performance of the trim and fill method in the presence of publication bias and between-study heterogeneity. Statistics in Medicine 26: 4544–4562.
Lima, D.S., E.I. Sato, V.C. Lima, et al. 2002. Brachial endothelial function is impaired in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of Rheumatology 29: 292–297.
El-Magadmi, M., H. Bodill, Y. Ahmad, et al. 2004. Systemic lupus erythematosus: an independent risk factor for endothelial dysfunction in women. Circulation 110: 399–404.
Rajagopalan, S., E.C. Somers, R.D. Brook, et al. 2004. Endothelial cell apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a common pathway for abnormal vascular function and thrombosis propensity. Blood 103: 3677–3683.
Wright, S.A., F.M. O'Prey, D.J. Rea, et al. 2006. Microcirculatory hemodynamics and endothelial dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 26: 2281–2287.
Karadag, O., M. Calguneri, E. Atalar, et al. 2007. Novel cardiovascular risk factors and cardiac event predictors in female inactive systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clinical Rheumatology 26: 695–699.
Svenungsson, E., A. Cederholm, K. Jensen-Urstad, et al. 2008. Endothelial function and markers of endothelial activation in relation to cardiovascular disease in systemic lupus erythematosus. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 37: 352–359.
Valdivielso, P., J.J. Gomez-Doblas, M. Macias, et al. 2008. Lupus-associated endothelial dysfunction, disease activity and arteriosclerosis. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 26: 827–833.
Aizer, J., E.W. Karlson, L.B. Chibnik, et al. 2009. A controlled comparison of brachial artery flow mediated dilation (FMD) and digital pulse amplitude tonometry (PAT) in the assessment of endothelial function in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 18: 235–242.
Cypiene, A., M. Kovaite, A. Venalis, et al. 2009. Arterial wall dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 18: 522–529.
Ghosh, P., A. Kumar, S. Kumar, et al. 2009. Subclinical atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction in young South-Asian patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical Rheumatology 28: 1259–1265.
Soltesz, P., H. Der, G. Kerekes, et al. 2009. A comparative study of arterial stiffness, flow-mediated vasodilation of the brachial artery, and the thickness of the carotid artery intima-media in patients with systemic autoimmune diseases. Clinical Rheumatology 28: 655–662.
Zhang, C.Y., L.J. Lu, F.H. Li, et al. 2009. Evaluation of risk factors that contribute to high prevalence of premature atherosclerosis in Chinese premenopausal systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Journal of Clinical Rheumatology 15: 111–116.
Cypiene, A., J. Dadoniene, R. Rugiene, et al. 2010. The influence of mean blood pressure on arterial stiffening and endothelial dysfunction in women with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicina (Kaunas, Lithuania) 46: 522–530.
Mak, A., P.A. Robless, L. Gong, et al. 2010. Endothelial reactivity predicts bone mineral density (BMD) in patients with systmeic lupus erythematosus (SLE). International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases 13: 124–125.
Ahmadi, B., Z.S. Bonakdar, S.M. Hashemi, et al. 2011. Endothelial dysfunction in Iranian lupus patients. Rheumatology International 31: 27–31.
Mak, A., L.H. Ling, R.C.M. Ho, et al. 2011. Lumbar spine bone mineral density predicts endothelial reactivity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 29: 261–268.
Stalc, M., M. Tomsic, M.K. Jezovnik, et al. 2011. Endothelium-dependent and independent dilation capability of peripheral arteries in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome. Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 29: 616–623.
Gaber, R., N. Kotb, E. Kassem, et al. 2011. Association of circulating endothelial cells with flow mediated vasodilation and disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging 12: ii158.
El-Banawy, H.S., E.W. Gaber, D.A. Maharem, et al. 2012. Angiopoietin-2, endothelial dysfunction and renal involvement in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Journal of Nephrology 25: 541–550.
Somers, E.C., W. Zhao, E.E. Lewis, et al. 2012. Type I interferons are associated with subclinical markers of cardiovascular disease in a cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus patients. PLoS One 7: e37000.
Parker, B., A. Al-Husain, P. Pemberton, et al. 2013. Suppression of inflammation reduces endothelial microparticles in active systemic lupus erythematosus. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 73: 1144–1150.
Valer, P., B. Paul, B. Eugenia, et al. 2013. Annexin A5 as independent predictive biomarker for subclinical atherosclerosis and endothelial dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clinical Laboratory 59: 359–367.
Manzi, S., E.N. Meilahn, J.E. Rairie, et al. 1997. Age-specific incidence rates of myocardial infarction and angina in women with systemic lupus erythematosus: comparison with the Framingham Study. American Journal of Epidemiology 145: 408–415.
Roman, M.J., B.A. Shanker, A. Davis, et al. 2003. Prevalence and correlates of accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. New England Journal of Medicine 349: 2399–2406.
Masoura, C., C. Pitsavos, K. Aznaouridis, et al. 2011. Arterial endothelial function and wall thickness in familial hypercholesterolemia and familial combined hyperlipidemia and the effect of statins. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 214: 129–138.
Inaba, Y., J.A. Chen, and S.R. Bergmann. 2010. Prediction of future cardiovascular outcomes by flow-mediated vasodilatation of brachial artery: a meta-analysis. International Journal of Cardiovascular Imaging 26: 631–640.
Nikpour, M., D. Gladman, and M. Urowitz. 2013. Premature coronary heart disease in systemic lupus erythematosus: what risk factors do we understand? Lupus 22: 1243–1250.
Hopkins, N.D., G. Stratton, T.M. Tinken, et al. 2009. Relationships between measures of fitness, physical activity, body composition and vascular function in children. Atherosclerosis 204: 244–249.
Reis-Neto, E.T., A.E. Silva, C.M. Monteiro, et al. 2013. Supervised physical exercise improves endothelial function in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52: 2187–2195.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81102192, 81373073), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education of China (20113420120008), as well as the Grants for Scientific Research of BSKY (No. XJ201014) from Anhui Medical University.
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors has any potential financial conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
De-Guang Wang, Xiao-Wu Tang, and Ye Fan contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, DG., Tang, XW., Fan, Y. et al. Decreased Flow-Mediated Dilatation in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: a Meta-analysis. Inflammation 37, 2067–2075 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9940-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9940-z