Abstract
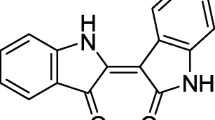
Magnolol is a traditional Chinese medicine from the root and bark of Magnolia officinalis. It has long been used to treat anxiety, cough, headache and allergies, as well as a variety of inflammations. Lung inflammation is a key event in the pathogenesis of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The present study sought to examine the effects of magnolol on tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced upregulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1), activation of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway in cultured human pulmonary epithelial cells, and adhesion of human macrophage-like U937 cells to A549 cells. A549 cells were incubated with magnolol at 25 and 50 μmol/l. Then, 20 ng/ml TNF-α was used to activate the cells. Magnolol inhibited the growth of human pulmonary epithelial A549 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. Magnolol suppressed the adhesion of U937 cells to TNF-α-induced A549 cells. In cultured human pulmonary epithelial A549 cells, magnolol decreased TNF-α-induced upregulation of ICAM-1. Magnolol repressed TNF-α-induced activation of NF-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways in A549 cells by inhibiting phosphorylation of NF-κB, p38, extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2, and stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK)/c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). These findings support the hypothesis that magnolol inhibits the inflammatory process in lung epithelial A549 cells by suppressing the ICAM-1 and NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Taken together, these results indicate that magnolol offers significant potential as a therapeutic treatment for inflammatory diseases of the lungs including asthma, sepsis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lin, C.C., C.W. Lee, T.H. Chu, C.Y. Cheng, S.F. Luo, L.D. Hsiao, and C.M. Yang. 2007. Transactivation of Src, PDGF receptor, and Akt is involved in IL-1β-induced ICAM-1 expression in A549 cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology 211: 771–780.
Lee, I.T., C.C. Lin, C.Y. Lee, P.W. Hsieh, and C.M. Yang. 2013. Protective effects of (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate against TNF-α-induced lung inflammation via ROS-dependent ICAM-1 inhibition. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 24: 124–136.
Armstrong, E.J., D.A. Morrow, and M.S. Sabatine. 2006. Inflammatory biomarkers in acute coronary syndromes. Part II: Acute-phase reactants and biomarkers of endothelial cell activation. Circulation 113: e152–e155.
Yang, C.M., S.F. Luo, H.L. Hsieh, P.L. Chi, C.C. Lin, C.C. Wu, and L.D. Hsiao. 2010. Interleukin-1beta induces ICAM-1 expression enhancing leukocyte adhesion in human rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts: Involvement of ERK, JNK, AP-1, and NF-kappaB. Journal of Cellular Physiology 224: 516–526.
Ang, L.T., L.Y. Tan, V.T. Chow, and M.K. Sim. 2012. Des-aspartate-angiotensin I exerts antiviral effects and attenuates ICAM-1 formation in rhinovirus-infected epithelial cells. European Journal of Pharmacology 683: 310–315.
Sumagin, R., J.M. Kuebel, and I.H. Sarelius. 2011. Leukocyte rolling and adhesion both contribute to regulation of microvascular permeability to albumin via ligation of ICAM-1. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology 301: C804–C813.
Pina-Canseco Mdel, S., A. Páez-Arenas, F. Massó, E. Pérez-Campos, R. Martínez-Cruz, P. Hernández-Cruz, A. Majluf-Cruz, M. Martínez-Cruz, L. Pérez-Campos Mayoral, A.D. Pérez-Santiago, and E. Zenteno. 2012. Protein C activation peptide inhibits the expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, and interleukin-8 induced by TNF-α in human dermal microvascular endothelial cells. Folia Histochemica et Cytobiologica 50: 407–413.
Ying, B., T. Yang, X. Song, X. Hu, H. Fan, X. Lu, L. Chen, D. Cheng, T. Wang, D. Liu, D. Xu, Y. Wei, and F. Wen. 2009. Quercetin inhibits IL-1 beta-induced ICAM-1 expression in pulmonary epithelial cell line A549 through the MAPK pathways. Molecular Biology Reports 36: 1825–1832.
Wu, C., D. Feng, H. Ma, H. Xie, H. Wang, and J. Wang. 2009. Effect of Pinus massoniana bark extract on IFN-gamma-induced ICAM-1 expression in HaCaT human keratinocytes. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122: 48–53.
Krunkosky, T.M., B.M. Fischer, L.D. Martin, N. Jones, N.J. Akley, and K.B. Adler. 2000. Effects of TNF-alpha on expression of ICAM-1 in human airway epithelial cells in vitro. Signaling pathways controlling surface and gene expression. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 22: 685–692.
Park, J.B., M.S. Lee, E.Y. Cha, J.S. Lee, J.Y. Sul, I.S. Song, and J.Y. Kim. 2012. Magnolol-induced apoptosis in HCT-116 colon cancer cells is associated with the AMP-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 35: 1614–1620.
Fu, Y., B. Liu, N. Zhang, Z. Liu, D. Liang, F. Li, Y. Cao, X. Feng, X. Zhang, and Z. Yang. 2013. Magnolol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response by interfering with TLR4 mediated NF-κB and MAPKs signaling pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 145: 193–199.
Jada, S., M.R. Doma, P.P. Singh, S. Kumar, F. Malik, A. Sharma, I.A. Khan, G.N. Qazi, and H.M. Kumar. 2012. Design and synthesis of novel magnolol derivatives as potential antimicrobial and antiproliferative compounds. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 51: 35–41.
Shih, C.Y., and T.C. Chou. 2012. The antiplatelet activity of magnolol is mediated by PPAR-β/γ. Biochemical Pharmacology 84: 793–803.
Choi, S.S., B.Y. Cha, Y.S. Lee, T. Yonezawa, T. Teruya, K. Nagai, and J.T. Woo. 2009. Magnolol enhances adipocyte differentiation and glucose uptake in 3 T3-L1 cells. Life Sciences 84: 908–914.
Lu, Y.C., H.H. Chen, C.H. Ko, Y.R. Lin, and M.H. Chan. 2003. The mechanism of honokiol-induced and magnolol-induced inhibition on muscle contraction and Ca2+ mobilization in rat uterus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology 368: 262–269.
Chen, S.C., Y.L. Chang, D.L. Wang, and J.J. Cheng. 2006. Herbal remedy magnolol suppresses IL-6-induced STAT3 activation and gene expression in endothelial cells. British Journal of Pharmacology 148: 226–232.
Chen, Y.H., S.J. Lin, J.W. Chen, H.H. Ku, and Y.L. Chen. 2002. Magnolol attenuates VCAM-1 expression in vitro in TNF-α-treated human aortic endothelial cells and in vivo in the aorta of cholesterol-fed rabbits. British Journal of Pharmacology 135: 37–47.
Lai, C.S., Y.S. Lai, D.H. Kuo, C.H. Wu, C.T. Ho, and M.H. Pan. 2011. Magnolol potently suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced iNOS and COX-2 expression via downregulating MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Journal of Functional Foods 3: 198–206.
Li, M.H., G. Kothandan, S.J. Cho, T.T.H. Pham, Y.H. Nan, K.Y. Lee, S.Y. Shin, S.S. Yea, and Y.J. Jeon. 2010. Magnolol inhibits LPS-induced NF-κB/Rel activation by blocking p38 kinase in murine macrophages. Korean Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 14: 353–358.
Tse, A.K., C.K. Wan, G.Y. Zhu, X.L. Shen, H.Y. Cheung, M. Yang, and W.F. Fong. 2007. Magnolol suppresses NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB regulated gene expression through inhibition of IkappaB kinase activation. Molecular Immunology 44: 2647–2658.
Hardie, W.D., T.D. Le Cras, K. Jiang, J.W. Tichelaar, M. Azhar, and T.R. Korfhagen. 2004. Conditional expression of transforming growth factor-alpha in adult mouse lung causes pulmonary fibrosis. American Journal of Physiology 286: L741–L749.
Gong, X., L. Zhang, R. Jiang, M. Ye, X. Yin, and J. Wan. 2013. Anti-inflammatory effects of mangiferin on sepsis-induced lung injury in mice via up-regulation of heme oxygenase-1. Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry 24: 1173–1181.
Wang, Z.Y., S.N. Wu, Z.Z. Zhu, B.X. Yang, and X. Zhu. 2013. Inhaled unfractionated heparin improves abnormalities of alveolar coagulation, fibrinolysis and inflammation in endotoxemia-induced lung injury rats. Chinese Medical Journal (English) 126: 318–324.
Lee, I.T., S.F. Luo, C.W. Lee, S.W. Wang, C.C. Lin, C.C. Chang, Y.L. Chen, L.Y. Chau, and C.M. Yang. 2009. Overexpression of HO-1 protects against TNF-α-mediated airway inflammation by down-regulation of TNFR1-dependent oxidative stress. American Journal of Pathology 175: 519–532.
Lin, C.C., H.W. Tseng, H.L. Hsieh, C.W. Lee, C.Y. Wu, C.Y. Cheng, and C.M. Yang. 2008. Tumor necrosis factor-α induces MMP-9 expression via p42/p44 MAPK, JNK, and nuclear factor-κB in A549 cells. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 229: 386–398.
Lin, F.S., C.C. Lin, C.S. Chien, S.F. Luo, and C.M. Yang. 2005. Involvement of p42/p44 MAPK, JNK, and NF-κB in IL-1β-induced ICAM-1 expression in human pulmonary epithelial cells. Journal of Cellular Physiology 202: 464–473.
Lee, K.H., M.H. Yeh, S.T. Kao, C.M. Hung, B.C. Chen, C.J. Liu, and C.C. Yeh. 2009. Xia-bai-san inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced activation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and nuclear factor-kappa B in human lung cells. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 124: 530–538.
Zhong, X., X. Li, F. Liu, H. Tan, and D. Shang. 2012. Omentin inhibits TNF-α-induced expression of adhesion molecules in endothelial cells via ERK/NF-κB pathway. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 425: 401–406.
Hayden, M.S., and S. Ghosh. 2004. Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes & Development 18: 2195–2224.
Suzuki, J., M. Ogawa, S. Muto, A. Itai, M. Isobe, Y. Hirata, and R. Nagai. 2011. Novel IkB kinase inhibitors for treatment of nuclear factor-kB-related diseases. Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs 20: 395–405.
Ren, Z.H., J.H. Cui, Z.R. Huo, J.R. Xue, H. Cui, B. Luo, L.J. Jiang, and R.R. Yang. 2012. Cordycepin suppresses TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation by reducing p65 transcriptional activity, inhibiting IκBα phosphorylation, and blocking IKKγ ubiquitination. International Immunopharmacology 14: 698–703.
Catley, M.C., J.E. Chivers, N.S. Holden, P.J. Barnes, and R. Newton. 2005. Validation of IKK beta as therapeutic target in airway inflammatory disease by adenoviral-mediated delivery of dominant-negative IKK beta to pulmonary epithelial cells. British Journal of Pharmacology 145: 114–122.
Jiang, J.X., Y. Zhang, S.H. Ji, P. Zhu, and Z.G. Wang. 2002. Kinetics of mitogen-activated protein kinase family in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated mouse Kupffer cells and their role in cytokine production. Shock 18: 336–341.
Rao, K.M. 2001. MAP kinase activation in macrophages. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 69: 3–10.
Choi, K., M. Kim, J. Ryu, and C. Choi. 2007. Ginsenosides compound K and Rh(2) inhibit tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced activation of the NF-kappaB and JNK pathways in human astroglial cells. Neuroscience Letters 421: 37–41.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81272433) and grant from the Tongji University 985 Project (No. 129182), major training project of Sichuan Provincial Department of Education (13CZ0029), State Key Laboratory Breeding Base of Eco-Environments and Bio-Resources of the Three Gorges Reservoir Region (SKL-2011-05), and China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013 M540391).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wu Chunlian and Wang Heyong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chunlian, W., Heyong, W., Jia, X. et al. Magnolol Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-α-Induced ICAM-1 Expression via Suppressing NF-κB And MAPK Signaling Pathways in Human Lung Epithelial Cells. Inflammation 37, 1957–1967 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9928-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9928-8