Abstract
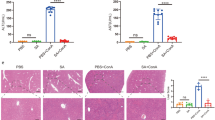
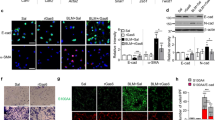
FTY720 is a novel immunosuppressant that modulates sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptors for the treatment of several diseases. Several hallmarks of liver fibrosis are influenced by S1P, and the interference of S1P signaling by treatment with FTY720 results in beneficial effects in various animal models of fibrosis. However, whether these treatment strategies suppress liver fibrosis progression is incompletely understood. Here, we investigated the effects and mechanisms by which FTY720 improves liver fibrosis in the carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced mouse model. FTY720 treatment significantly attenuated the expression of fibrotic markers in the injured liver of both wild-type and SCID-beige mice. The migration of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) to circulation, and subsequently the injured liver, was suppressed by FTY720. Furthermore, in vitro, phosphorylated-FTY720 blocked the migration of BMSCs mediated by S1P. Thus, FTY720 is an effective therapy for liver fibrosis via the suppression of BMSC migration in the CCl4-induced mouse model.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brinkmann, V., A. Billich, T. Baumruker, P. Heining, R. Schmouder, G. Francis, et al. 2010. Fingolimod (FTY720): discovery and development of an oral drug to treat multiple sclerosis. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 9(11): 883–897.
Aktas, O., P. Kury, B. Kieseier, and H.P. Hartung. 2010. Fingolimod is a potential novel therapy for multiple sclerosis. Nature Reviews Neurology 6(7): 373–382.
Zemann, B., B. Kinzel, M. Muller, R. Reuschel, D. Mechtcheriakova, N. Urtz, et al. 2006. Sphingosine kinase type 2 is essential for lymphopenia induced by the immunomodulatory drug FTY720. Blood 107(4): 1454–1458.
Mandala, S., R. Hajdu, J. Bergstrom, E. Quackenbush, J. Xie, J. Milligan, et al. 2002. Alteration of lymphocyte trafficking by sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor agonists. Science 296(5566): 346–349.
Brinkmann, V., M.D. Davis, C.E. Heise, R. Albert, S. Cottens, R. Hof, et al. 2002. The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277(24): 21453–21457.
Matloubian, M., C.G. Lo, G. Cinamon, M.J. Lesneski, Y. Xu, V. Brinkmann, et al. 2004. Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature 427(6972): 355–360.
Graeler, M., G. Shankar, and E.J. Goetzl. 2002. Cutting edge: suppression of T cell chemotaxis by sphingosine 1-phosphate. Journal of Immunology 169(8): 4084–4087.
Pappu, R., S.R. Schwab, I. Cornelissen, J.P. Pereira, J.B. Regard, Y. Xu, et al. 2007. Promotion of lymphocyte egress into blood and lymph by distinct sources of sphingosine-1-phosphate. Science 316(5822): 295–298.
Schwab, S.R., J.P. Pereira, M. Matloubian, Y. Xu, Y. Huang, and J.G. Cyster. 2005. Lymphocyte sequestration through S1P lyase inhibition and disruption of S1P gradients. Science 309(5741): 1735–1739.
Liu, W., M. Zi, H. Tsui, S.K. Chowdhury, L. Zeef, Q.J. Meng, et al. 2013. A novel immunomodulator, FTY-720 reverses existing cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis from pressure overload by targeting NFAT (nuclear factor of activated T-cells) signaling and periostin. Circulation Heart Failure 6(4): 833–844.
Ni, H.F., J.F. Chen, M.H. Zhang, M.M. Pan, J.D. Zhang, H. Liu, et al. 2013. FTY720 attenuates tubulointerstitial inflammation and fibrosis in subtotally nephrectomized rats. Renal Failure 35(7): 996–1004.
Ni, H., J. Chen, M. Pan, M. Zhang, J. Zhang, P. Chen, et al. 2013. FTY720 prevents progression of renal fibrosis by inhibiting renal microvasculature endothelial dysfunction in a rat model of chronic kidney disease. Journal of Molecular Histology 44(6): 693–703.
Friedman, S.L. 2000. Molecular regulation of hepatic fibrosis, an integrated cellular response to tissue injury. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275(4): 2247–2250.
Friedman, S.L. 2008. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 134(6): 1655–1669.
Bataller, R., and D.A. Brenner. 2005. Liver fibrosis. Journal of Clinical Investigation 115(2): 209–218.
Russo, F.P., M.R. Alison, B.W. Bigger, E. Amofah, A. Florou, F. Amin, et al. 2006. The bone marrow functionally contributes to liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 130(6): 1807–1821.
Watterson, K.R., D.A. Lanning, R.F. Diegelmann, and S. Spiegel. 2007. Regulation of fibroblast functions by lysophospholipid mediators: potential roles in wound healing. Wound Repair and Regeneration 15(5): 607–616.
Li, C., Y. Kong, H. Wang, S. Wang, H. Yu, X. Liu, et al. 2009. Homing of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells mediated by sphingosine 1-phosphate contributes to liver fibrosis. Journal of Hepatology 50(6): 1174–1183.
Yang, L., N. Chang, X. Liu, Z. Han, T. Zhu, C. Li, et al. 2012. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiate to hepatic myofibroblasts by transforming growth factor-β1 via sphingosine kinase/sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P)/S1P receptor axis. American Journal of Pathology 181(1): 85–97.
Man, K., K.T. Ng, T.K. Lee, C.M. Lo, C.K. Sun, X.L. Li, et al. 2005. FTY720 attenuates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury in normal and cirrhotic livers. American Journal of Transplantation 5(1): 40–49.
Zeng, X., T. Wang, C. Zhu, Y. Ye, B. Song, X. Lai, et al. 2012. FTY720 mediates activation suppression and G(0)/G (1) cell cycle arrest in a concanavalin A-induced mouse lymphocyte pan-activation model. Inflammation Research 61(6): 623–634.
Constandinou, C., N. Henderson, and J.P. Iredale. 2005. Modeling liver fibrosis in rodents. Methods in Molecular Medicine 117: 237–250.
Iredale, J.P. 2007. Models of liver fibrosis: exploring the dynamic nature of inflammation and repair in a solid organ. Journal of Clinical Investigation 117(3): 539–548.
Liu, K.X., Y. Kato, M. Yamazaki, O. Higuchi, T. Nakamura, and Y. Sugiyama. 1993. Decrease in the hepatic-clearance of hepatocyte growth-factor in carbon tetrachloride-intoxicated rats. Hepatology 17(4): 651–660.
Johnston, D.E., and C. Kroening. 1998. Mechanism of early carbon tetrachloride toxicity in cultured rat hepatocytes. Pharmacology and Toxicology 83(6): 231–239.
Luster, M.I., P.P. Simeonova, R.M. Gallucci, A. Bruccoleri, M.E. Blazka, and B. Yucesoy. 2001. Role of inflammation in chemical-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicology Letters 120(1–3): 317–321.
Luster, M.I., P.P. Simeonova, R.M. Gallucci, J.M. Matheson, and B. Yucesoy. 2000. Immunotoxicology: role of inflammation in chemical-induced hepatotoxicity. International Journal of Immunopharmacology 22(12): 1143–1147.
Yamakawa, Y., T. Doi, K. Kubota, H. Okayachi, N. Kudo, and Y. Kawashima. 2000. Modification of carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity by clofibric acid in rats. Journal of Health Science 46(2): 132–141.
Marques, T.G., E. Chaib, J.H. da Fonseca, A.C. Lourenco, F.D. Silva, M.A. Ribeiro Jr., et al. 2012. Review of experimental models for inducing hepatic cirrhosis by bile duct ligation and carbon tetrachloride injection. Acta Cirúrgica Brasileira 27(8): 589–594.
Raetsch, C., J.D. Jia, G. Boigk, M. Bauer, E.G. Hahn, E.O. Riecken, et al. 2002. Pentoxifylline downregulates profibrogenic cytokines and procollagen I expression in rat secondary biliary fibrosis. Gut 50(2): 241–247.
Peters, H., S. Martini, Y. Wang, F. Shimizu, H. Kawachi, S. Kramer, et al. 2004. Selective lymphocyte inhibition by FTY720 slows the progressive course of chronic anti-thy 1 glomerulosclerosis. Kidney International 66(4): 1434–1443.
Delbridge, M.S., B.M. Shrestha, A.T. Raftery, A.M. El Nahas, and J. Haylor. 2007. FTY720 reduces extracellular matrix expansion associated with ischemia-reperfusion induced injury. Transplantation Proceedings 39(10): 2992–2996.
Keller, C.D., P. Rivera Gil, M. Tolle, M. van der Giet, J. Chun, H.H. Radeke, et al. 2007. Immunomodulator FTY720 induces myofibroblast differentiation via the lysophospholipid receptor S1P3 and Smad3 signaling. American Journal of Pathology 170(1): 281–292.
Sobel, K., K. Menyhart, N. Killer, B. Renault, Y. Bauer, R. Studer, et al. 2013. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor agonists mediate pro-fibrotic responses in normal human lung fibroblasts via S1P2 and S1P3 receptors and Smad-independent signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry 288(21): 14839–14851.
Brunati, A.M., E. Tibaldi, A. Carraro, E. Gringeri, F. D'Amico, A. Toninello, et al. 2008. Cross-talk between PDGF and S1P signalling elucidates the inhibitory effect and potential antifibrotic action of the immunomodulator FTY720 in activated HSC-cultures. BBA Molecular Cell Research 1783(3): 347–359.
Yamanaka, M., D. Shegogue, H. Pei, S. Bu, A. Bielawska, J. Bielawski, et al. 2004. Sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) is induced by transforming growth factor-β and mediates TIMP-1 up-regulation. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279(52): 53994–54001.
Kono, Y., T. Nishiuma, Y. Nishimura, Y. Kotani, T. Okada, S. Nakamura, et al. 2007. Sphingosine kinase 1 regulates differentiation of human and mouse lung fibroblasts mediated by TGF-β1. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 37(4): 395–404.
Miller, A.V., S.E. Alvarez, S. Spiegel, and D.A. Lebman. 2008. Sphingosine kinases and sphingosine-1-phosphate are critical for transforming growth factor β-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1 and 2 activation and promotion of migration and invasion of esophageal cancer cells. Molecular and Cellular Biology 28(12): 4142–4151.
Donati, C., F. Cencetti, C. De Palma, E. Rapizzi, S. Brunelli, G. Cossu, et al. 2009. TGFβ protects mesoangioblasts from apoptosis via sphingosine kinase-1 regulation. Cellular Signalling 21(2): 228–236.
Gellings Lowe, N., J.S. Swaney, K.M. Moreno, and R.A. Sabbadini. 2009. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and sphingosine kinase are critical for transforming growth factor-β-stimulated collagen production by cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovascular Research 82(2): 303–312.
Cencetti, F., C. Bernacchioni, P. Nincheri, C. Donati, and P. Bruni. 2010. Transforming growth factor-β1 induces transdifferentiation of myoblasts into myofibroblasts via up-regulation of sphingosine kinase-1/S1P3 axis. Molecular Biology of the Cell 21(6): 1111–1124.
Lebman, D.A., and S. Spiegel. 2008. Thematic review series: Sphingolipids. Cross-talk at the crossroads of sphingosine-1-phosphate, growth factors, and cytokine signaling. Journal of Lipid Research 49(7): 1388–1394.
Higashiyama, R., T. Moro, S. Nakao, K. Mikami, H. Fukumitsu, Y. Ueda, et al. 2009. Negligible contribution of bone marrow-derived cells to collagen production during hepatic fibrogenesis in mice. Gastroenterology 137(4): 1459–1466. e1.
Terai, S., T. Ishikawa, K. Omori, K. Aoyama, Y. Marumoto, Y. Urata, et al. 2006. Improved liver function in patients with liver cirrhosis after autologous bone marrow cell infusion therapy. Stem Cells 24(10): 2292–2298.
Spiegel, S., D. English, and S. Milstien. 2002. Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling: providing cells with a sense of direction. Trends in Cell Biology 12(5): 236–242.
Meriane, M., S. Duhamel, L. Lejeune, J. Galipeau, and B. Annabi. 2006. Cooperation of matrix metalloproteinases with the RhoA/Rho kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase-1/extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways is required for the sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced mobilization of marrow-derived stromal cells. Stem Cells 24(11): 2557–2565.
Jaganathan, B.G., B. Ruester, L. Dressel, S. Stein, M. Grez, E. Seifried, et al. 2007. Rho inhibition induces migration of mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells 25(8): 1966–1974.
Paik, J.H., S. Chae, M.J. Lee, S. Thangada, and T. Hla. 2001. Sphingosine 1-phosphate-induced endothelial cell migration requires the expression of EDG-1 and EDG-3 receptors and Rho-dependent activation of αvβ3- and β1-containing integrins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276(15): 11830–11837.
Okamoto, H., N. Takuwa, T. Yokomizo, N. Sugimoto, S. Sakurada, H. Shigematsu, et al. 2000. Inhibitory regulation of Rac activation, membrane ruffling, and cell migration by the G protein-coupled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor EDG5 but not EDG1 or EDG3. Molecular and Cellular Biology 20(24): 9247–9261.
Sugimoto, N., N. Takuwa, H. Okamoto, S. Sakurada, and Y. Takuwa. 2003. Inhibitory and stimulatory regulation of Rac and cell motility by the G12/13-Rho and Gi pathways integrated downstream of a single G protein-coupled sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor isoform. Molecular and Cellular Biology 23(5): 1534–1545.
Sanna, M.G., J. Liao, E. Jo, C. Alfonso, M.Y. Ahn, M.S. Peterson, et al. 2004. Sphingosine 1-phosphate (S1P) receptor subtypes S1P1 and S1P3, respectively, regulate lymphocyte recirculation and heart rate. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279(14): 13839–13848.
Goparaju, S.K., P.S. Jolly, K.R. Watterson, M. Bektas, S. Alvarez, S. Sarkar, et al. 2005. The S1P2 receptor negatively regulates platelet-derived growth factor-induced motility and proliferation. Molecular and Cellular Biology 25(10): 4237–4249.
Li, C., X. Jiang, L. Yang, X. Liu, S. Yue, and L. Li. 2009. Involvement of sphingosine 1-phosphate (SIP)/S1P3 signaling in cholestasis-induced liver fibrosis. American Journal of Pathology 175(4): 1464–1472.
Acknowledgments
We thank Professor Lingsong Li for his scientific advice. This work was supported through the Grants 863 Program (2009DFB30300) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
Absolute number of circulating BMSCs during liver fibrogenesis. Mice were induced by CCl4 administration for 4 weeks, with or without FTY720 treatment. The number of circulating BMSCs at different time points after OO or CCl4 injection, with or without FTY720 treatment. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 vs. CCl4-treated alone (n = 16 per group). (JPEG 643 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Y., Wang, H., Wang, S. et al. FTY720, a Sphingosine-1 Phosphate Receptor Modulator, Improves Liver Fibrosis in a Mouse Model by Impairing the Motility of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Inflammation 37, 1326–1336 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9877-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9877-2