Abstract
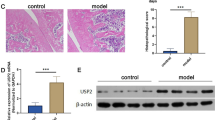
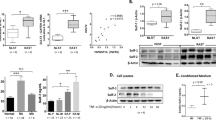
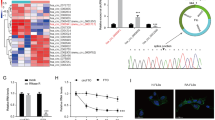
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease with high morbidity and mortality. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS) in the synovial tissues play critical roles in joint destruction. Recent studies implicate the sumoylation in the regulation of the inflammation and arthritis. Thus, we explored whether SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 is involved in the progression of RA using a mouse collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) model. The effects of UBC9 siRNA on cell invasion and migration in human RA-FLS were also assessed in vitro. Treatment with siRNA against UBC9 for 3 weeks reduced the arthritis score and joint destruction. The expression of SUMO-1 and UBC9 protein in CIA joints was inhibited by UBC9 knockdown. Serum levels of anti-collagen (CII) antibodies, vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGF-A), matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-3, and MMP-9 were also decreased in CIA mice. In vitro, UBC9 silencing inhibited the secretion of VEGF-A, MMP-3, and MMP-9 from TNF-α-stimulated human RA-FLS. TNF-α-induced RA-FLS proliferation and migration were significantly attenuated by UBC9 knockdown. These findings indicate that SUMO-conjugating enzyme UBC9 promotes proliferation and migration of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Inhibition of UBC9 activity may be a viable therapeutic target in amelioration of disease progression in RA by attenuating FLS proliferation, migration, and invasion.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choy, E.H., and G.S. Panayi. 2001. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. New England Journal of Medicine 344: 907–916.
Bottini, N., and G.S. Firestein. 2013. Duality of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in RA: passive responders and imprinted aggressors. Nature Reviews. Rheumatology 9: 24–33.
Ma, Y., and R.M. Pope. 2005. The role of macrophages in rheumatoid arthritis. Current Pharmaceutical Design 11: 569–580.
Firestein, G.S., F. Echeverri, M. Yeo, N.J. Zvaifler, and D.R. Green. 1997. Somatic mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene in rheumatoid arthritis synovium. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94: 10895–10900.
Muller-Ladner, U., T. Pap, R.E. Gay, M. Neidhart, and S. Gay. 2005. Mechanisms of disease: the molecular and cellular basis of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Nature Clinical Practice Rheumatology 1: 102–110.
Huber, L.C., O. Distler, I. Tarner, R.E. Gay, S. Gay, and T. Pap. 2006. Synovial fibroblasts: key players in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45: 669–675.
Muller-Ladner, U., J. Kriegsmann, B.N. Franklin, S. Matsumoto, T. Geiler, R.E. Gay, et al. 1996. Synovial fibroblasts of patients with rheumatoid arthritis attach to and invade normal human cartilage when engrafted into SCID mice. American Journal of Pathology 149: 1607–1615.
Tsai, C., L.A. Diaz Jr., N.G. Singer, L.L. Li, A.H. Kirsch, R. Mitra, et al. 1996. Responsiveness of human T lymphocytes to bacterial superantigens presented by cultured rheumatoid arthritis synoviocytes. Arthritis and Rheumatism 39: 125–136.
Tran, C.N., M.J. Davis, L.A. Tesmer, J.L. Endres, C.D. Motyl, C. Smuda, et al. 2007. Presentation of arthritogenic peptide to antigen-specific T cells by fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Arthritis and Rheumatism 56: 1497–1506.
Huber, L.C., J. Stanczyk, A. Jüngel, and S. Gay. 2007. Epigenetics in inflammatory rheumatic diseases. Arthritis and Rheumatism 56: 3523–3531.
Wilkinson, K.A., and J.M. Henley. 2010. Mechanisms, regulation and consequences of protein SUMOylation. Biochemistry Journal 428: 133–145.
Wang, Y., and M. Dasso. 2009. SUMOylation and deSUMOylation at a glance. Journal of Cell Science 122: 4249–4252.
Huber, L.C., J.H. Distler, F. Moritz, H. Hemmatazad, T. Hauser, B.A. Michel, et al. 2007. Trichostatin A prevents the accumulation of extracellular matrix in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced skin fibrosis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 56: 2755–2764.
Wooley, P.H., H.S. Luthra, J.M. Stuart, and C.S. David. 1981. Type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. I. Major histocompatibility complex (I region) linkage and antibody correlates. Journal of Experimental Medicine 154: 688–700.
Minakuchi, Y., F. Takeshita, N. Kosaka, H. Sasaki, Y. Yamamoto, M. Kouno, et al. 2004. Atelocollagen-mediated synthetic small interfering RNA delivery for effective gene silencing in vitro and in vivo. Nucleic Acids Research 32: e109.
Tarrant, T.K., P. Liu, R.R. Rampersad, D. Esserman, L.R. Rothlein, R.G. Timoshchenko, et al. 2012. Decreased Th17 and antigen-specific humoral responses in CX3 CR1-deficient mice in the collagen- induced arthritis model. Arthritis and Rheumatism 64: 1379–1387.
Nishikawa, M., A. Myoui, T. Tomita, K. Takahi, A. Nampei, and H. Yoshikawa. 2003. Prevention of the onset and progression of collagen-induced arthritis in rats by the potent p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor FR167653. Arthritis and Rheumatism 48: 2670–2681.
Aletaha, D., T. Neogi, A.J. Silman, J. Funovits, D.T. Felson, C.O. Bingham 3rd, et al. 2010. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis and Rheumatism 62: 2569–2581.
Yoshioka, Y., E. Kozawa, H. Urakawa, E. Arai, N. Futamura, L. Zhuo, et al. 2013. Suppression of hyaluronan synthesis alleviates inflammatory responses in murine arthritis and in human rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis and Rheumatism 65: 1160–1170.
Cha, H.S., S. Rosengren, D.L. Boyle, and G.S. Firestein. 2010. PUMA regulation and proapoptotic effects in fibroblast-like synoviocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:587–92.
Dinatale BC, Perdew GH. Protein function analysis: rapid, cell-based siRNA-mediated ablation of endogenous expression with simultaneous ectopic replacement. Cytotechnology 62: 95–100.
Lee, M.S., S.A. Yoo, C.S. Cho, P.G. Suh, W.U. Kim, and S.H. Ryu. 2006. Serum amyloid A binding to formyl peptide receptor-like 1 induces synovial hyperplasia and angiogenesis. Journal of Immunology 177: 5585–5594.
Chang, S.K., Z. Gu, and M.B. Brenner. 2010. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes in inflammatory arthritis pathology: the emerging role of cadherin-11. Immunology Reviews 233: 256–266.
Afuwape, A.O., S. Kiriakidis, and E.M. Paleolog. 2002. The role of the angiogenic molecule VEGF in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Histology and Histopathology 17: 961–972.
Franz, J.K., T. Pap, K.M. Hummel, M. Nawrath, W.K. Aicher, Y. Shigeyama, et al. 2000. Expression of sentrin, a novel antiapoptotic molecule, at sites of synovial invasion in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 599–607.
Liacini, A., J. Sylvester, W.Q. Li, and M. Zafarullah. 2002. Inhibition of interleukin-1-stimulated MAP kinases, activating protein-1 (AP-1) and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) transcription factors down-regulates matrix metalloproteinase gene expression in articular chondrocytes. Matrix Biology 21: 251–262.
Liacini, A., J. Sylvester, W.Q. Li, W. Huang, F. Dehnade, M. Ahmad, et al. 2003. Induction of matrix metalloproteinase-13 gene expression by TNF-alpha is mediated by MAP kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB transcription factors in articular chondrocytes. Experimental Cell Research 288: 208–217.
Desterro, J.M., M.S. Rodriguez, and R.T. Hay. 1998. SUMO-1 modification of IkappaBalpha inhibits NF-kappaB activation. Molecular Cell 2: 233–239.
Huang, T.T., S.M. Wuerzberger-Davis, Z.H. Wu, and S. Miyamoto. 2003. Sequential modification of NEMO/IKKgamma by SUMO-1 and ubiquitin mediates NF-kappaB activation by genotoxic stress. Cell 115: 565–576.
Saltzman, A., G. Searfoss, C. Marcireau, M. Stone, R. Ressner, R. Munro, et al. 1998. hUBC9 associates with MEKK1 and type I TNF-alpha receptor and stimulates NFkappaB activity. FEBS Letters 425: 431–435.
Navarro-Millán, I., and J.R. Curtis. 2013. Newest clinical trial results with antitumor necrosis factor and nonantitumor necrosis factor biologics for rheumatoid arthritis. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 25: 384–390.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Faxin Li and Xueyan Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, F., Li, X., Kou, L. et al. SUMO-Conjugating Enzyme UBC9 Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 37, 1134–1141 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9837-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9837-x