Abstract
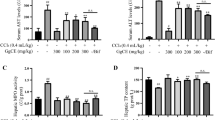
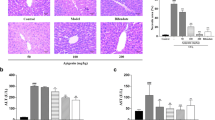
Recently, an increasing number of studies suggest that oxidative stress and inflammation are associated with hepatocellular injuries. Thus, we aimed to evaluate the potential hepatoprotective role of tadehaginoside (TA) on liver lesions induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). The results in vitro suggested that TA dose-dependently suppressed the cell proliferation of HepG2 cells, whereas the phosphorylated level of IκBα in cells was effectively inactivated. The study in vivo showed that TA significantly lowered the serum concentrations of alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), immunoglobulin E (IgE), and leukotriene (LT) in CCl4-lesioned rats. Pathological examination indicated that CCl4-induced hepatocellular damage was effectively mitigated by TA treatment. Meanwhile, the contents of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-GCS), glutathione (GSH), and catalase (CAT) in liver tissue were gradually elevated. In addition, cytochrome c oxidase (COX) mRNA expression in hepatocytes was markedly upregulated, and nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (Keapl) levels were progressively increased. Furthermore, the tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) and nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB)-expressed protein were downregulated. These findings demonstrate that tadehaginoside effectively protects against CCl4-induced oxidative injury and inflammatory reaction in hepatocytes, in which the underlying mechanisms are involved in activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway and inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, thereby attenuating oxidative stress and reducing the inflammation in liver cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, H., C.S. Li, and W. Wang. 2005. Sickle cell hepatopathy: clinical presentation, treatment, and outcome in pediatric and adult patients. Pediatric Blood & Cancer 45(2): 184–190.
Tang, Y., Z. Bian, L. Zhao, Y. Liu, S. Liang, Q. Wang, X. Han, Y. Peng, X. Chen, L. Shen, D. Qiu, Z. Li, and X. Ma. 2011. Interleukin-17 exacerbates hepatic steatosis and inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 166(2): 281–290.
Jones DP (2006) Redefining oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 81865–79.
Park, J.S., J.H. Chyun, Y.K. Kim, L.L. Line, and B.P. Chew. 2010. Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans. Nutrition & Metabolism (London) 7: 18–24.
Czaja, M.J. 2007. Cell signaling in oxidative stress-induced liver injury. Seminars in Liver Disease 27(4): 378–389.
Maritim, A.C., R.A. Sanders, and J.B. Watkins 3rd. 2003. Diabetes, oxidative stress, and antioxidants: a review. Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology 17: 24–38.
Zhang, Y., L. Wu, Y. Wang, M. Zhang, L. Li, D. Zhu, X. Li, H. Gu, C.Y. Zhang, and K. Zen. 2012. Protective role of estrogen-induced miRNA-29 expression in carbon tetrachloride-induced mouse liver injury. Journal of Biological Chemistry 287: 14851–14862.
Saller, R., R. Meier, and R. Brignoli. 2001. The use of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs 61: 2035–2063.
Ahmad, I., S. Shukla, A. Kumar, B.K. Singh, V. Kumar, A.K. Chauhan, D. Singh, H.P. Pandey, and C. Singh. 2013. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of N-acetyl cysteine and silymarin-mediated protection against maneb- and paraquat-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Chemico-Biological Interactions 201: 9–18.
Xiang, W., R.T. Li, Y.L. Mao, H.J. Zhang, S.H. Li, Q.S. Song, and H.D. Sun. 2005. Four new prenylated isoflavonoids in Tadehagi triquetrum. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 53: 267–271.
Zhou, X.D., L.Y. Shi, D.Y. Yu, H.B. Shi, Y.B. Miao, L. Tang, B.M. Feng, and Y.Q. Wang. 2011. Effect of active part extracted from Tadehagi triquetrum (Linn.) Ohashi on type I allergy induced by immunoglobulin E. Central South Pharmacy 9: 35–38.
Chávez, E., L. Castro-Sánchez, M. Shibayama, V. Tsutsumi, E. Pérez Salazar, M.G. Moreno, and P. Muriel. 2012. Effects of acetyl salicylic acid and ibuprofen in chronic liver damage induced by CCl4. Journal of Applied Toxicology 32: 51–59.
Podymova, S.D. 2012. Parenteral acute viral hepatitis: current diagnosis, prevention and treatment. Eksp Klin Gastroenterol 6: 76–85.
Søgaard, K.K., E. Horváth-Puhó, H. Grønbaek, P. Jepsen, H. Vilstrup, and H.T. Sørensen. 2009. Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with liver disease: a nationwide population-based case-control study. American Journal of Gastroenterology 104: 96–101.
Jamjute, P., A. Ahmad, T. Ghosh, and P. Banfield. 2009. Liver function test and pregnancy. Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine 22: 274–283.
Chen, Z.Y. 2007. Progress of studies on the Desmodium triquatrub (L.) DC. Strait Pharmaceutical Journal 19: 72–75.
Djukanović, R., S.J. Wilson, M. Kraft, N.N. Jarjour, M. Steel, K.F. Chung, W. Bao, A. Fowler-Taylor, J. Matthews, W.W. Busse, S.T. Holgate, and J.V. Fahy. 2004. Effects of treatment with anti-immunoglobulin E antibody omalizumab on airway inflammation in allergic asthma. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 170: 583–593.
Devi, N.S., and M. Doble. 2012. Leukotriene c4 synthase: upcoming drug target for inflammation. Current Drug Targets 13: 1107–1118.
Valko, M., M. Izakovic, M. Mazur, C.J. Rhodes, and J. Telser. 2004. Role of oxygen radicals in DNA damage and cancer incidence. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry 266: 37–56.
Jomova, K., and M. Valko. 2011. Advances in metal-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Toxicology 283: 65–87.
Kondo, T., Y. Higashiyama, S. Goto, T. Iida, S. Cho, M. Iwanaga, K. Mori, M. Tani, and Y. Urata. 1999. Regulation of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase expression in response to oxidative stress. Free Radical Research 31: 325–334.
Slaughter, M.R., H. Thakkar, and P.J. O’Brien. 2003. Differential expression of the lenticular antioxidant system in laboratory animals: a determinant of species predilection to oxidative stress-induced ocular toxicity? Current Eye Research 26: 15–23.
Pecina, P., H. Houstková, H. Hansíková, J. Zeman, and J. Houstek. 2004. Genetic defects of cytochrome c oxidase assembly. Physiological Research 1: 213–223.
Fontanesi, F., I.C. Soto, D. Horn, and A. Barrientos. 2006. Assembly of mitochondrial cytochrome c-oxidase, a complicated and highly regulated cellular process. American Journal of Physiology Cellular Physiology 291: 1129–1147.
Boer, L.A., J.P. Panatto, D.A. Fagundes, C. Bassani, I.C. Jeremias, J.F. Daufenbach, G.T. Rezin, L. Constantino, F. Dal-Pizzol, and E.L. Streck. 2009. Inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory chain in the brain of rats after hepatic failure induced by carbon tetrachloride is reversed by antioxidants. Brain Research Bulletin 80: 75–78.
Kang, K.W., S.J. Lee, and S.G. Kim. 2005. Molecular mechanism of nrf2 activation by oxidative stress. Antioxidants and Redox Signaling 7: 1664–1673.
Nguyen, T., C.S. Yang, and C.B. Pickett. 2004. The pathways and molecular mechanisms regulating Nrf2 activation in response to chemical stress. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 37: 433–441.
Zhang, D.D. 2006. Mechanistic studies of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway. Drug Metabolism Reviews 38: 769–789.
Kaspar, J.W., S.K. Niture, and A.K. Jaiswal. 2009. Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 47: 1304–1309.
van Muiswinkel, F.L., and H.B. Kuiperij. 2005. The Nrf2-ARE signalling pathway: promising drug target to combat oxidative stress in neurodegenerative disorders. Current Drug Targets CNS and Neurological Disorders 4: 267–281.
Johnson, J.A., D.A. Johnson, A.D. Kraft, M.J. Calkins, R.J. Jakel, M.R. Vargas, and P.C. Chen. 2008. The Nrf2-ARE pathway: an indicator and modulator of oxidative stress in neurodegeneration. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1147: 61–69.
Li, R., L. Xu, T. Liang, Y. Li, S. Zhang, and X. Duan. 2013. Puerarin mediates hepatoprotection against CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis rats through attenuation of inflammation response and amelioration of metabolic function. Food and Chemical Toxicology 52: 69–75.
DiDonato, J.A., F. Mercurio, and M. Karin. 2012. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunological Reviews 246: 379–400.
Guo, C., L. Xu, Q. He, T. Liang, X. Duan, and R. Li. 2013. Anti-fibrotic effects of puerarin on CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats possibly through the regulation of PPAR-γ expression and inhibition of PI3K/Akt pathway. Food and Chemical Toxicology 56: 436–442.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mr. Jiaquan Li for his excellent technical support.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest and are responsible for the contents of this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Aicun Tang and Xiaoyu Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, A., Chen, X., Lu, Q. et al. Antihepatotoxic Effect of Tadehaginoside, Extracted from Tadehagi triquetrum (L.), Against CCl4-Lesioned Rats Through Activating the Nrf2 Signaling Pathway and Attenuating the Inflammatory Response. Inflammation 37, 1006–1014 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9821-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-9821-5