Abstract
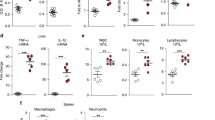
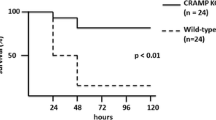
Murine hepatic Cyp4a mRNAs are markedly downregulated during inflammation. Here, we investigated the roles of Cyp4a10 and Cyp4a14 in the response to infection with C. rodentium. Absence of either Cyp4a gene attenuated or abrogated the changes in spleen weight, colon crypt length, hepatic cytokine, and acute phase protein mRNAs, and serum acute phase proteins and cytokines caused by infection. Cyp4a10 −/− mice on a low-salt diet had a similar hepatic acute phase response as those mice on a high-salt diet, suggesting that hypertension associated with this genotype is not the cause of their altered inflammatory response. In contrast, wild-type, Cyp4a10 −/−, and Cyp4a14 −/− mice showed similar responses to injected LPS. These results implicate Cyp4a10 and Cyp4a14 in the regulation of the host inflammatory response to enteropathogenic bacterial infection but not to acute aseptic inflammation. Understanding the mechanism of this role may lead to novel therapeutic approaches in some inflammatory diseases.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hardwick, J.P. 2008. Cytochrome P450 omega hydroxylase (CYP4) function in fatty acid metabolism and metabolic diseases. Biochemical Pharmacology 75: 2263–2275.
Johnson, E.F., C.N. Palmer, K.J. Griffin, and M.H. Hsu. 1996. Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in cytochrome P450 4A gene regulation. FASEB Journal 10: 1241–1248.
Sanders, R.J., R. Ofman, F. Valianpour, S. Kemp, and R.J. Wanders. 2005. Evidence for two enzymatic pathways for omega-oxidation of docosanoic acid in rat liver microsomes. Journal of Lipid Research 46: 1001–1008.
Gainer, J.V., A. Bellamine, E.P. Dawson, K.E. Womble, S.W. Grant, Y. Wang, L.A. Cupples, C.Y. Guo, S. Demissie, C.J. O’Donnell, N.J. Brown, M.R. Waterman, and J.H. Capdevila. 2005. Functional variant of CYP4A11 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid synthase is associated with essential hypertension. Circulation 111: 63–69.
Heng, Y.M., C.S. Kuo, P.S. Jones, R. Savory, R.M. Schulz, S.R. Tomlinson, T.J. Gray, and D.R. Bell. 1997. A novel murine P-450 gene, Cyp4a14, is part of a cluster of Cyp4a and Cyp4b, but not of CYP4F, genes in mouse and humans. Biochemical Journal 325(Pt 3): 741–749.
Powell, P.K., I. Wolf, R. Jin, and J.M. Lasker. 1998. Metabolism of arachidonic acid to 20-hydroxy-5,8,11,14-eicosatetraenoic acid by P450 enzymes in human liver: involvement of CYP4F2 and CYP4A11. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 285: 1327–1336.
Lasker, J.M., W.B. Chen, I. Wolf, B.P. Bloswick, P.D. Wilson, and P.K. Powell. 2000. Formation of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid, a vasoactive and natriuretic eicosanoid, in human kidney. Role of Cyp4F2 and Cyp4A11. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275: 4118–4126.
McGiff, J.C., and J. Quilley. 1999. 20-HETE and the kidney: resolution of old problems and new beginnings. American Journal of Physiology 277: R607–R623.
Miyata, N., and R.J. Roman. 2005. Role of 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (20-HETE) in vascular system. Journal of Smooth Muscle Research 41: 175–193.
Roman, R.J. 2002. P-450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in the control of cardiovascular function. Physiological Reviews 82: 131–185.
Sarkis, A., and R.J. Roman. 2004. Role of cytochrome P450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in hypertension. Current Drug Metabolism 5: 245–256.
King, L.M., J.V. Gainer, G.L. David, D. Dai, J.A. Goldstein, N.J. Brown, and D.C. Zeldin. 2005. Single nucleotide polymorphisms in the CYP2J2 and CYP2C8 genes and the risk of hypertension. Pharmacogenetics and Genomics 15: 7–13.
Liu, X., J. Wu, H. Liu, G. Lai, and Y. Zhao. 2012. Disturbed ratio of renal 20-HETE/EETs is involved in androgen-induced hypertension in cytochrome P450 4F2 transgenic mice. Gene 505: 352–359.
Athirakul, K., J.A. Bradbury, J.P. Graves, L.M. DeGraff, J. Ma, Y. Zhao, J.F. Couse, R. Quigley, D.R. Harder, X. Zhao, J.D. Imig, T.L. Pedersen, J.W. Newman, B.D. Hammock, A.J. Conley, K.S. Korach, T.M. Coffman, and D.C. Zeldin. 2008. Increased blood pressure in mice lacking cytochrome P450 2J5. FASEB Journal 22: 4096–4108.
Holla, V.R., F. Adas, J.D. Imig, X. Zhao, E. Price Jr., N. Olsen, W.J. Kovacs, M.A. Magnuson, D.S. Keeney, M.D. Breyer, J.R. Falck, M.R. Waterman, and J.H. Capdevila. 2001. Alterations in the regulation of androgen-sensitive Cyp 4a monooxygenases cause hypertension. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 98: 5211–5216.
Nakagawa, K., V.R. Holla, Y. Wei, W.H. Wang, A. Gatica, S. Wei, S. Mei, C.M. Miller, D.R. Cha, E. Price Jr., R. Zent, A. Pozzi, M.D. Breyer, Y. Guan, J.R. Falck, M.R. Waterman, and J.H. Capdevila. 2006. Salt-sensitive hypertension is associated with dysfunctional Cyp4a10 gene and kidney epithelial sodium channel. Journal of Clinical Investigation 116: 1696–1702.
Chaluvadi, M.R., R.D. Kinloch, B.A. Nyagode, T.A. Richardson, M.J. Raynor, M. Sherman, L. Antonovic, H.W. Strobel, D.L. Dillehay, and E.T. Morgan. 2009. Regulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 expression in mice with intestinal or systemic infections of Citrobacter rodentium. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 37: 366–374.
Nyagode, B.A., C.M. Lee, and E.T. Morgan. 2010. Modulation of hepatic cytochrome P450s by Citrobacter rodentium infection in interleukin-6- and interferon-{gamma}-null mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 335: 480–488.
Richardson, T.A., M. Sherman, L. Antonovic, S.S. Kardar, H.W. Strobel, D. Kalman, and E.T. Morgan. 2006. Hepatic and renal cytochrome p450 gene regulation during Citrobacter rodentium infection in wild-type and toll-like receptor 4 mutant mice. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 34: 354–360.
Richardson, T.A., and E.T. Morgan. 2005. Hepatic cytochrome P450 gene regulation during endotoxin-induced inflammation in nuclear receptor knockout mice. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 314: 703–709.
Livak, K.J., and T.D. Schmittgen. 2001. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25: 402–408.
Quigley, R., S. Chakravarty, X. Zhao, J.D. Imig, and J.H. Capdevila. 2009. Increased renal proximal convoluted tubule transport contributes to hypertension in Cyp4a14 knockout mice. Nephron. Physiology 113: 23–28.
Cray, C., J. Zaias, and N.H. Altman. 2009. Acute phase response in animals: a review. Comparative Medicine 59: 517–526.
Murata, H., N. Shimada, and M. Yoshioka. 2004. Current research on acute phase proteins in veterinary diagnosis: an overview. Veterinary Journal 168: 28–40.
Kinloch, R.D., C.M. Lee, N. van Rooijen, and E.T. Morgan. 2011. Selective role for tumor necrosis factor-alpha, but not interleukin-1 or Kupffer cells, in down-regulation of CYP3A11 and CYP3A25 in livers of mice infected with a noninvasive intestinal pathogen. Biochemical Pharmacology 82: 312–321.
Tunctan, B., B. Korkmaz, A.N. Sari, M. Kacan, D. Unsal, M.S. Serin, C.K. Buharalioglu, S. Sahan-Firat, T. Cuez, W.H. Schunck, J.R. Falck, and K.U. Malik. 2013. 5,14-HEDGE, a 20-HETE mimetic, reverses hypotension and improves survival in a rodent model of septic shock: contribution of soluble epoxide hydrolase, CYP2C23, MEK1/ERK1/2/IKKbeta/IkappaB-alpha/NF-kappaB pathway, and proinflammatory cytokine formation. Prostaglandins and Other Lipid Mediators 102–103: 31–41.
Ng, V.Y., Y. Huang, L.M. Reddy, J.R. Falck, E.T. Lin, and D.L. Kroetz. 2007. Cytochrome P450 eicosanoids are activators of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 35: 1126–1134.
Delerive, P., K. De Bosscher, S. Besnard, W. Vanden Berghe, J.M. Peters, F.J. Gonzalez, J.C. Fruchart, A. Tedgui, G. Haegeman, and B. Staels. 1999. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha negatively regulates the vascular inflammatory gene response by negative cross-talk with transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. Journal of Biological Chemistry 274: 32048–32054.
Muller, D.N., C. Schmidt, E. Barbosa-Sicard, M. Wellner, V. Gross, H. Hercule, M. Markovic, H. Honeck, F.C. Luft, and W.H. Schunck. 2007. Mouse Cyp4a isoforms: enzymatic properties, gender- and strain-specific expression, and role in renal 20-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid formation. Biochemical Journal 403: 109–118.
Dierks, E.A., S.C. Davis, and P.R. Ortiz de Montellano. 1998. Glu-320 and Asp-323 are determinants of the CYP4A1 hydroxylation regiospecificity and resistance to inactivation by 1-aminobenzotriazole. Biochemistry 37: 1839–1847.
Xu, Z., L. Chen, L. Leung, T.S. Yen, C. Lee, and J.Y. Chan. 2005. Liver-specific inactivation of the Nrf1 gene in adult mouse leads to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatic neoplasia. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102: 4120–4125.
Christmas, P., K. Tolentino, V. Primo, K.Z. Berry, R.C. Murphy, M. Chen, D.M. Lee, and R.J. Soberman. 2006. Cytochrome P-450 4F18 is the leukotriene B4 omega-1/omega-2 hydroxylase in mouse polymorphonuclear leukocytes: identification as the functional orthologue of human polymorphonuclear leukocyte CYP4F3A in the down-regulation of responses to LTB4. Journal of Biological Chemistry 281: 7189–7196.
Lee, S.S., T. Pineau, J. Drago, E.J. Lee, J.W. Owens, D.L. Kroetz, P.M. Fernandez-Salguero, H. Westphal, and F.J. Gonzalez. 1995. Targeted disruption of the alpha isoform of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gene in mice results in abolishment of the pleiotropic effects of peroxisome proliferators. Molecular and Cellular Biology 15: 3012–3022.
Barclay, T.B., J.M. Peters, M.B. Sewer, L. Ferrari, F.J. Gonzalez, and E.T. Morgan. 1999. Modulation of cytochrome P-450 gene expression in endotoxemic mice is tissue specific and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha dependent. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 290: 1250–1257.
Pan, J., Q. Xiang, S. Ball, J. Scatina, J. Kao, and J.Y. Hong. 2003. Lipopolysaccharide-mediated modulation of cytochromes P450 in Stat1 null mice. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 31: 392–397.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases [Grant R01 DK072372]. We are grateful to Dr. Jorge Capdevila, Vanderbilt University for providing the Cyp4a-deficient mice that were used to establish our breeding colonies. The technical assistance of Mr. William Watkins, Dr. Matthew Merrell and Dr. Choon-Myung Lee is gratefully acknowledged. We wish to thank Dr. Dean P. Jones and Mr. Yongliang Liang (Clinical Biomarkers Laboratory, Department of Medicine, Emory University) for access to equipment used to quantify serum cytokines.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 2800 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nyagode, B.A., Williams, I.R. & Morgan, E.T. Altered Inflammatory Responses to Citrobacter rodentium Infection, but not Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide, in Mice Lacking the Cyp4a10 or Cyp4a14 Genes. Inflammation 37, 893–907 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9809-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9809-6