Abstract
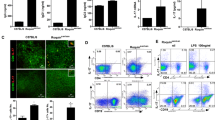
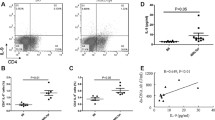
IL-33 is a new member of the IL-1 family that plays a role in inflammation. In this study, we evaluated the potential of IL-33 inhibition as a treatment for systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) using the lupus-prone model MRL/lpr mice and the underlying mechanisms of action. We treated mice with anti-mouse IL-33 antibody (anti-IL-33Ab) via intraperitoneal injection every other day from week 14 until week 20 for 6 weeks. A control group received the same amount of IgG control. Renal damage and mouse survival were compared. Cytokines, antibodies, immune complex, Tregs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and Th17 cells were also analyzed. Correlations between serum IL-33 and SLE disease activity index in human SLE were also investigated. MRL/lpr mice treated with anti-IL-33Ab showed reduced proteinuria and reduced serum anti-dsDNA levels. Nephritis, immune complex deposits, and the circulating antibodies and immune complex besides the mortality were significantly reduced by anti-IL-33Ab. Anti-IL-33Ab remarkably increased Tregs and MDSCs and reduced the Th17 cells and IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-17 levels in MRL/lpr mice. These results suggest that IL-33 inhibition may inhibit SLE via expansion of Tregs and MDSCs and inhibition of Th17 cells and proinflammatory responses, indicating that blockade of IL-33 has a protective effect on SLE.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurowska-Stolarska, M., A. Hueber, B. Stolarski, and I.B. McInnes. 2011. Interleukin-33: a novel mediator with a role in distinct disease pathologies. Journal of Internal Medicine 269: 29–35.
Lloyd, C.M. 2010. IL-33 family members and asthma–bridging innate and adaptive immune responses. Current Opinion in Immunology 22: 800–806.
Mirchandani, A.S., R.J. Salmond, and F.Y. Liew. 2012. Interleukin-33 and the function of innate lymphoid cells. Trends in Immunology 33: 389–396.
McLaren, J.E., D.R. Michael, R.C. Salter, T.G. Ashlin, C.J. Calder, A.M. Miller, et al. 2010. IL-33 reduces macrophage foam cell formation. The Journal of Immunology 185: 1222–1229.
Miller, A.M., D. Xu, D.L. Asquith, L. Denby, Y. Li, N. Sattar, et al. 2008. IL-33 reduces the development of atherosclerosis. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205: 339–346.
Moffatt, M.F., I.G. Gut, F. Demenais, D.P. Strachan, E. Bouzigon, S. Heath, et al. 2010. A large-scale, consortium-based genomewide association study of asthma. The New England Journal of Medicine 363: 1211–1221.
Xu, D., H.R. Jiang, P. Kewin, Y. Li, R. Mu, A.R. Fraser, et al. 2008. IL-33 exacerbates antigen-induced arthritis by activating mast cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 105: 10913–10918.
Talabot-Ayer, D., T. McKee, P. Gindre, S. Bas, D.L. Baeten, C. Gabay, et al. 2012. Distinct serum and synovial fluid interleukin (IL)-33 levels in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis. Joint, Bone, Spine 79: 32–37.
Humrich, J.Y., H. Morbach, R. Undeutsch, P. Enghard, S. Rosenberger, O. Weigert, et al. 2010. Homeostatic imbalance of regulatory and effector T cells due to IL-2 deprivation amplifies murine lupus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 204–209.
Trigunaite A, Khan A, Der E, Song A, Varikuti S, Jørgensen TN. Gr1(high) CD11b(+) cells suppress B cell differentiation and lupus-like disease in lupus-prone male mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2013. doi:10.1002/art.38048.
Gabrilovich, D.I., and S. Nagaraj. 2009. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nature Reviews Immunology 9: 162–174.
Peranzoni, E., S. Zilio, I. Marigo, L. Dolcetti, P. Zanovello, S. Mandruzzato, et al. 2010. Myeloid-derived suppressor cell heterogeneity and subset definition. Current Opinion in Immunology 22: 238–244.
Ioannou, M., T. Alissafi, I. Lazaridis, G. Deraos, J. Matsoukas, A. Gravanis, et al. 2012. Crucial role of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the regulation of central nervous system autoimmune disease. The Journal of Immunology 188: 1136–1146.
Fujii, W., E. Ashihara, H. Hirai, H. Nagahara, N. Kajitani, K. Fujioka, et al. 2013. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells play crucial roles in the regulation of mouse collagen-induced arthritis. The Journal of Immunology 191: 1073–1081.
Tsokos, G.C. 2011. Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England Journal of Medicine 365: 2110–2121.
Kim, Y.H., T.Y. Yang, C.S. Park, S.H. Ahn, B.K. Son, J.H. Kim, et al. 2012. Anti-IL-33 antibody has a therapeutic effect in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Allergy 67: 183–190.
Sekine, H., K.L. Graham, S. Zhao, M.K. Elliott, P. Ruiz, P.J. Utz, et al. 2006. Role of MHC-linked genes in autoantigen selection and renal disease in a murine model of systemic lupus erythematosus. The Journal of Immunology 177: 7423–7434.
Wellmann, U., M. Letz, A. Schneider, K. Amann, and T.H. Winkler. 2001. An Ig μ-heavy chain transgene inhibits systemic lupus erythematosus immunopathology in autoimmune (NZB × NZW)F1 mice. International Immunology 13: 1461–1469.
Lateef, A., and M. Petri. 2012. Unmet medical needs in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Research and Therapy 14(Suppl 4): S4.
Yang, Z., Y. Liang, W. Xi, C. Li, and R. Zhong. 2011. Association of increased serum IL-33 levels with clinical and laboratory characteristics of systemic lupus erythematosus in Chinese population. Clinical and Experimental Medicine 11: 75–80.
Mok, M.Y., F.P. Huang, W.K. Ip, Y. Lo, F.Y. Wong, E.Y. Chan, et al. 2010. Serum levels of IL-33 and soluble ST2 and their association with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49: 520–527.
Oboki, K., T. Ohno, N. Kajiwara, K. Arae, H. Morita, A. Ishii, et al. 2010. IL-33 is a crucial amplifier of innate rather than acquired immunity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 107: 18581–18586.
Hong, Y.S., S.J. Moon, Y.B. Joo, C.H. Jeon, M.L. Cho, J.H. Ju, et al. 2011. Measurement of interleukin-33 (IL-33) and IL-33 receptors (sST2 and ST2L) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Korean Medical Science 26: 1132–1139.
Kunisch, E., S. Chakilam, M. Gandesiri, and R.W. Kinne. 2012. IL-33 regulates TNF-α dependent effects in synovial fibroblasts. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 29: 530–540.
Yin, B., G. Ma, C.Y. Yen, Z. Zhou, G.X. Wang, C.M. Divino, et al. 2010. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells prevent type 1 diabetes in murine models. The Journal of Immunology 185: 5828–5834.
Wolf, D., K. Hochegger, A.M. Wolf, H.F. Rumpold, G. Gastl, H. Tilg, et al. 2005. CD4 + CD25+ regulatory T cells inhibit experimental anti-glomerular basement membrane glomerulonephritis in mice. Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 16: 1360–1370.
Weigert, O., C. von Spee, R. Undeutsch, L. Kloke, J.Y. Humrich, and G. Riemekasten. 2013. CD4 + Foxp3+ regulatory T cells prolong drug-induced disease remission in (NZBxNZW) F1 lupus mice. Arthritis Research and Therapy 15: R35.
Shin, M.S., N. Lee, and I. Kang. 2011. Effector T-cell subsets in systemic lupus erythematosus: update focusing on Th17 cells. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 23: 444–448.
Ambrosi, A., A. Espinosa, and M. Wahren-Herlenius. 2012. IL-17: a new actor in IFN-driven systemic autoimmune diseases. European Journal of Immunology 42: 2274–2284.
Ma, J., J. Yu, X. Tao, L. Cai, J. Wang, and S.G. Zheng. 2010. The imbalance between regulatory and IL-17-secreting CD4+ T cells in lupus patients. Clinical Rheumatology 29: 1251–1258.
Mengya, Z., M. Hanyou, L. Dong, L. Xiaohong, and Z. Lihua. 2013. Th17/Treg imbalance induced by increased incidence of atherosclerosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Clinical Rheumatology 32: 1045–1052.
Zhao, J., H. Wang, C. Dai, H. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Huang, et al. 2013. P2X7 blockade attenuates lupus nephritis by inhibiting NLRP3/ASC/caspase-1 activation. Arthritis and Rheumatism 65: 3176–3185.
Duan, L., J. Chen, H. Zhang, H. Yang, P. Zhu, A. Xiong, et al. 2012. Interleukin-33 ameliorates experimental colitis through promoting Th2/Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell responses in mice. Molecular Medicine 18: 753–761.
Jiang, H.R., M. Milovanović, D. Allan, W. Niedbala, A.G. Besnard, S.Y. Fukada, et al. 2012. IL-33 attenuates EAE by suppressing IL-17 and IFN-γ production and inducing alternatively activated macrophages. European Journal of Immunology 42: 1804–1814.
Mu, R., H.Q. Huang, Y.H. Li, C. Li, H. Ye, and Z.G. Li. 2010. Elevated serum interleukin 33 is associated with autoantibody production in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Rheumatology 37: 2006–2013.
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Lin, W. & Zheng, X. IL-33 Neutralization Suppresses Lupus Disease in Lupus-Prone Mice. Inflammation 37, 824–832 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9802-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9802-0