Abstract
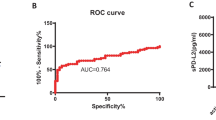
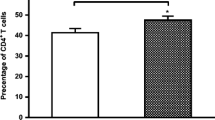
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is characterized by chronic inflammatory process that targets the synovial lining of diarthrodial joints. Programmed death 1 (PD-1) plays a key role in the negative regulation of the immune response. In the current study, we investigated the expression of PD-1 on peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in RA patients. Percentage of PD-1+ cells was measured by flow cytometry in 82 RA cases and 90 healthy controls. Results showed that PD-1 expression was significantly decreased in both peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in RA (p = 0.002 and p < 0.001, respectively). Similarly, serum levels of soluble PD-1 were also downregulated in RA cases. When comparing PD-1 level in RA patients with different clinical parameters, patients with positive C-reactive protein (CRP) revealed lower proportion of PD-1 on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells than those with negative CRP. Also, disease activity score of RA patients was inversely correlated with PD-1 expression on peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. These data suggested that PD-1 may act as a negative regulator in the pathogenesis and progression of RA.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Gravallese, E.M., Y. Harada, J.T. Wang, A.H. Gorn, T.S. Thornhill, and S.R. Goldring. 1998. Identification of cell types responsible for bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. American Journal of Pathology 152: 943–951.
Itonaga, I., Y. Fujikawa, A. Sabokbar, D.W. Murray, and N.A. Athanasou. 2000. Rheumatoid arthritis synovial macrophage-osteoclast differentiation is osteoprotegerin ligand-dependent. The Journal of Pathology 192: 97–104.
Gravallese, E.M., C. Manning, A. Tsay, A. Naito, C. Pan, E. Amento, et al. 2000. Synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis is a source of osteoclast differentiation factor. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 250–258.
Shigeyama, Y., T. Pap, P. Kunzler, B.R. Simmen, R.E. Gay, and S. Gay. 2000. Expression of osteoclast differentiation factor in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 43: 2523–2530.
Gracie, J.A., R.J. Forsey, W.L. Chan, A. Gilmour, B.P. Leung, M.R. Greer, et al. 1999. A proinflammatory role for IL-18 in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 104: 1393–1401.
Dong, H., G. Zhu, K. Tamada, and L. Chen. 1999. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nature Medicine 5: 1365–1369.
Latchman, Y., C.R. Wood, T. Chernova, D. Chaudhary, M. Borde, I. Chernova, et al. 2001. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nature Immunology 2: 261–268.
Nishimura, H., T. Okazaki, Y. Tanaka, K. Nakatani, M. Hara, A. Matsumori, et al. 2001. Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science 291: 319–322.
Okazaki, T., Y. Tanaka, R. Nishio, T. Mitsuiye, A. Mizoguchi, J. Wang, et al. 2003. Autoantibodies against cardiac troponin I are responsible for dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1-deficient mice. Nature Medicine 9: 1477–1483.
Keir, M.E., M.J. Butte, G.J. Freeman, and A.H. Sharpe. 2008. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annual Review of Immunology 26: 677–704.
Iwai, Y., S. Terawaki, M. Ikegawa, T. Okazaki, and T. Honjo. 2003. PD-1 inhibits antiviral immunity at the effector phase in the liver. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 198: 39–50.
Jun, H., S.K. Seo, H.Y. Jeong, H.M. Seo, G. Zhu, L. Chen, and I.H. Choi. 2005. B7-H1 (CD274) inhibits the development of herpetic stromal keratitis (HSK). FEBS Letters 579: 6259–6264.
Kong, E.K., L. Prokunina-Olsson, W.H. Wong, C.S. Lau, T.M. Chan, M. Alarcón-Riquelme, et al. 2005. A new haplotype of PDCD1 is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in Hong Kong Chinese. Arthritis and Rheumatism 52: 1058–1062.
Prokunina, L., L. Padyukov, A. Bennet, U. de Faire, B. Wiman, J. Prince, et al. 2004. Association of the PD-1.3A allele of the PDCD1 gene in patients with rheumatoid arthritis negative for rheumatoid factor and the shared epitope. Arthritis and Rheumatism 50: 1770–1773.
Wan, B., H. Nie, A. Liu, G. Feng, D. He, R. Xu, et al. 2006. Aberrant regulation of synovial T cell activation by soluble costimulatory molecules in rheumatoid arthritis. The Journal of Immunology 177: 8844–8850.
Kobayashi, M., S. Kawano, S. Hatachi, C. Kurimoto, T. Okazaki, Y. Iwai, et al. 2005. Enhanced expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1)/PD-L1 in salivary glands of patients with Sjogren's syndrome. The Journal of Rheumatology 32: 2156–2163.
Barber, D.L., E.J. Wherry, D. Masopust, B. Zhu, J.P. Allison, A.H. Sharpe, et al. 2006. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439: 682–687.
Zhang, Z., J.Y. Zhang, E.J. Wherry, B. Jin, B. Xu, Z.S. Zou, et al. 2008. Dynamic programmed death 1 expression by virus specific CD8 T cells correlates with the outcome of acute hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 134: 1938–1949.
Evans, A., A. Riva, H. Cooksley, S. Phillips, S. Puranik, A. Nathwani, et al. 2008. Programmed death 1 expression during antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Impact of hepatitis B e-antigen seroconversion. Hepatology 48: 759–769.
Xie, Z., Y. Chen, S. Zhao, Z. Yang, X. Yao, S. Guo, et al. 2009. Intrahepatic PD-1/PD-L1 up-regulation closely correlates with inflammation and virus replication in patients with chronic HBV infection. Immunological Investigations 38: 624–638.
Chen, Y., S. Wu, G. Guo, L. Fei, S. Guo, C. Yang, et al. 2011. Programmed death (PD)-1-deficient mice are extremely sensitive to murine hepatitis virus strain-3 (MHV-3) infection. PLoS Pathogens 7: e1001347.
Li, H., C. Wang, G. Guo, C. Gao, Y. Wu, and Y. Chen. 2012. The characteristic expression of B7-associated proteins in Langerhans cell sarcoma. Acta Histochemica 114: 733–743.
Jin, H.T., R. Ahmed, and T. Okazaki. 2011. Role of PD-1 in regulating T-cell immunity. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology 350: 17–37.
Francisco, L.M., P.T. Sage, and A.H. Sharpe. 2010. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunology Reviews 236: 219–242.
Shin, T., G. Kennedy, K. Gorski, H. Tsuchiya, H. Koseki, M. Azuma, et al. 2003. Cooperative B7-1/2 (CD80/CD86) and B7-DC costimulation of CD4+ T cells independent of the PD-1 receptor. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 198: 31–38.
Tseng, S.Y., M. Otsuji, K. Gorski, X. Huang, J.E. Slansky, S.I. Pai, et al. 2001. B7-DC, a new dendritic cell molecule with potent costimulatory properties for T cells. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 193: 839–846.
Dong, H., S.E. Strome, D.R. Salomao, H. Tamura, F. Hirano, D.B. Flies, et al. 2002. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nature Medicine 8: 793–800.
Singh, A.K., P. Stock, and O. Akbari. 2011. Role of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in allergic diseases and asthma. Allergy 66: 155–162.
Watanabe, T., A. Bertoletti, and T.A. Tanoto. 2010. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis virus infection. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 17: 453–458.
del Rio, M.L., L. Buhler, C. Gibbons, J. Tian, and J.I. Rodriguez-Barbosa. 2008. PD-1/PD-L1, PD-1/PD-L2, and other co-inhibitory signaling pathways in transplantation. Transplant International 21: 1015–1028.
Conflict of Interest
No competing financial interests exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shufeng Li and Wensheng Liao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Liao, W., Chen, M. et al. Expression of Programmed Death-1 (PD-1) on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Inflammation 37, 116–121 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9718-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-013-9718-8