Abstract
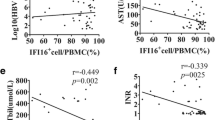
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a major public health problem, and HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (HBV-ACLF) has an extremely poor prognosis due to a lack of understanding of pathogenesis as well as a lack of effective treatments. Signals from the inhibitory receptor programmed death-1 (PD-1) have been demonstrated to be involved in regulating the pathogenesis of infectious diseases. However, the expression of PD-1 and its ligands in HBV-ACLF patients has yet to be evaluated. In this study, the expression of PD-1 and its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2, in liver biopsies from HBV-ACLF as well as chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. The results showed that all three molecules were observed in the HBV-ACLF samples and their levels were significantly higher than they were in CHB. Immunofluorescence double-staining showed that PD-1 was found on CD3+, CD8+ T cells, CD56+ NK cells, CD68+ macrophages, CK-18+ epithelial cells, and CD16+ monocytes. The PD-L1 expression was observed on all cell types detected and the PD-L2 was chiefly on CK-18+ epithelial cells and CD31+ endothelial cells. Interestingly, high levels of virus-induced procoagulant molecule fibrinogen-like protein 2 (FGL2) were observed in liver sections from HBV-ACLF, and PD-L1 and PD-L2 expression was also observed on FGL2+ cells in these patients. Our combined results suggest that the expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 may be biomarkers to identify and diagnose ACLF, and a clear understanding of their functional roles should further elucidate the pathogenesis of this disease.







Similar content being viewed by others
Reference List
Stravitz, R.T., and D.J. Kramer. 2009. Management of acute liver failure. Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology 6: 542–553.
Marsden, P.A., Q. Ning, L.S. Fung, X. Luo, Y. Chen, M. Mendicino, A. Ghanekar, J.A. Scott, T. Miller, C.W. Chan, M.W. Chan, W. He, R.M. Gorczynski, D.R. Grant, D.A. Clark, M.J. Phillips, and G.A. Levy. 2003. The Fgl2/fibroleukin prothrombinase contributes to immunologically mediated thrombosis in experimental and human viral hepatitis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 112: 58–66.
Liu, Q., Z. Liu, T. Wang, Q. Wang, X. Shi, and W. Dao. 2007. Characteristics of acute and sub-acute liver failure in China: nomination, classification and interval. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 22: 2101–2106.
Liu, M., C.W. Chan, I. McGilvray, Q. Ning, and G.A. Levy. 2001. Fulminant viral hepatitis: molecular and cellular basis, and clinical implications. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine 2001: 1–19.
Nishimura, H., M. Nose, H. Hiai, N. Minato, and T. Honjo. 1999. Development of lupus-like autoimmune diseases by disruption of the PD-1 gene encoding an ITIM motif-carrying immunoreceptor. Immunity 11: 141–151.
Dong, H., G. Zhu, K. Tamada, and L. Chen. 1999. B7-H1, a third member of the B7 family, co-stimulates T-cell proliferation and interleukin-10 secretion. Nature Medicine 5: 1365–1369.
Latchman, Y., C.R. Wood, T. Chernova, D. Chaudhary, M. Borde, I. Chernova, Y. Iwai, A.J. Long, J.A. Brown, R. Nunes, E.A. Greenfield, K. Bourque, V.A. Boussiotis, L.L. Carter, B.M. Carreno, N. Malenkovich, H. Nishimura, T. Okazaki, T. Honjo, A.H. Sharpe, and G.J. Freeman. 2001. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation. Nature Immunology 2: 261–268.
Nishimura, H., T. Okazaki, Y. Tanaka, K. Nakatani, M. Hara, A. Matsumori, S. Sasayama, A. Mizoguchi, H. Hiai, N. Minato, and T. Honjo. 2001. Autoimmune dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1 receptor-deficient mice. Science 291: 319–322.
Okazaki, T., Y. Tanaka, R. Nishio, T. Mitsuiye, A. Mizoguchi, J. Wang, M. Ishida, H. Hiai, A. Matsumori, N. Minato, and T. Honjo. 2003. Autoantibodies against cardiac troponin I are responsible for dilated cardiomyopathy in PD-1-deficient mice. Nature Medicine 9: 1477–1483.
Keir, M.E., M.J. Butte, G.J. Freeman, and A.H. Sharpe. 2008. PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity. Annual Review of Immunology 26: 677–704.
Iwai, Y., S. Terawaki, M. Ikegawa, T. Okazaki, and T. Honjo. 2003. PD-1 inhibits antiviral immunity at the effector phase in the liver. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 198: 39–50.
Jun, H., S.K. Seo, H.Y. Jeong, H.M. Seo, G. Zhu, L. Chen, and I.H. Choi. 2005. B7-H1 (CD274) inhibits the development of herpetic stromal keratitis (HSK). FEBS Letters 579: 6259–6264.
Barber, D.L., E.J. Wherry, D. Masopust, B. Zhu, J.P. Allison, A.H. Sharpe, G.J. Freeman, and R. Ahmed. 2006. Restoring function in exhausted CD8 T cells during chronic viral infection. Nature 439: 682–687.
Zhang, Z., J.Y. Zhang, E.J. Wherry, B. Jin, B. Xu, Z.S. Zou, S.Y. Zhang, B.S. Li, H.F. Wang, H. Wu, G.K. Lau, Y.X. Fu, and F.S. Wang. 2008. Dynamic programmed death 1 expression by virus-specific CD8 T cells correlates with the outcome of acute hepatitis B. Gastroenterology 134: 1938–1949.
Evans, A., A. Riva, H. Cooksley, S. Phillips, S. Puranik, A. Nathwani, S. Brett, S. Chokshi, and N.V. Naoumov. 2008. Programmed death 1 expression during antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B: Impact of hepatitis B e-antigen seroconversion. Hepatology 48: 759–769.
Xie, Z., Y. Chen, S. Zhao, Z. Yang, X. Yao, S. Guo, C. Yang, L. Fei, X. Zeng, B. Ni, and Y. Wu. 2009. Intrahepatic PD-1/PD-L1 up-regulation closely correlates with inflammation and virus replication in patients with chronic HBV infection. Immunological Investigations 38: 624–638.
Chen, Y., S. Wu, G. Guo, L. Fei, S. Guo, C. Yang, X. Fu, and Y. Wu. 2011. Programmed death (PD)-1-deficient mice are extremely sensitive to murine hepatitis virus strain-3 (MHV-3) infection. PLoS Pathogens 7: e1001347.
Li H, Wang C, Guo G, Gao C, Wu Y, Chen Y. 2012. The characteristic expression of B7-associated proteins in Langerhans cell sarcoma. Acta Histochemica 114:733–743.
Jin, H.T., R. Ahmed, and T. Okazaki. 2011. Role of PD-1 in regulating T-cell immunity. Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology 350: 17–37.
Francisco, L.M., P.T. Sage, and A.H. Sharpe. 2010. The PD-1 pathway in tolerance and autoimmunity. Immunology Reviews 236: 219–242.
Shin, T., G. Kennedy, K. Gorski, H. Tsuchiya, H. Koseki, M. Azuma, H. Yagita, L. Chen, J. Powell, D. Pardoll, and F. Housseau. 2003. Cooperative B7-1/2 (CD80/CD86) and B7-DC costimulation of CD4+ T cells independent of the PD-1 receptor. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 198: 31–38.
Tseng, S.Y., M. Otsuji, K. Gorski, X. Huang, J.E. Slansky, S.I. Pai, A. Shalabi, T. Shin, D.M. Pardoll, and H. Tsuchiya. 2001. B7-DC, a new dendritic cell molecule with potent costimulatory properties for T cells. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 193: 839–846.
Dong, H., S.E. Strome, D.R. Salomao, H. Tamura, F. Hirano, D.B. Flies, P.C. Roche, J. Lu, G. Zhu, K. Tamada, V.A. Lennon, E. Celis, and L. Chen. 2002. Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nature Medicine 8: 793–800.
Singh, A.K., P. Stock, and O. Akbari. 2011. Role of PD-L1 and PD-L2 in allergic diseases and asthma. Allergy 66: 155–162.
Watanabe, T., A. Bertoletti, and T.A. Tanoto. 2010. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway and T-cell exhaustion in chronic hepatitis virus infection. Journal of Viral Hepatitis 17: 453–458.
del Rio, M.L., L. Buhler, C. Gibbons, J. Tian, and J.I. Rodriguez-Barbosa. 2008. PD-1/PD-L1, PD-1/PD-L2, and other co-inhibitory signaling pathways in transplantation. Transplant International 21: 1015–1028.
Ma, S.W., X. Huang, Y.Y. Li, L.B. Tang, X.F. Sun, X.T. Jiang, Y.X. Zhang, J. Sun, Z.H. Liu, W.G. Abbott, Y.H. Dong, N.V. Naoumov, and J.L. Hou. 2012. High serum IL-21 levels after 12 weeks of antiviral therapy predict HBeAg seroconversion in chronic hepatitis B. Journal of Hepatology 56: 775–781.
Raziorrouh, B., W. Schraut, T. Gerlach, D. Nowack, N.H. Grüner, A. Ulsenheimer, R. Zachoval, M. Wächtler, M. Spannagl, J. Haas, H.M. Diepolder, and M.C. Jung. 2010. The immunoregulatory role of CD244 in chronic hepatitis B infection and its inhibitory potential on virus-specific CD8+ T-cell function. Hepatology 52: 1934–1947.
Loke, P., and J.P. Allison. 2003. PD-L1 and PD-L2 are differentially regulated by Th1 and Th2 cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 100(9): 5336–5341.
Ding, J.W., Q. Ning, M.F. Liu, A. Lai, J. Leibowitz, K.M. Peltekian, E.H. Cole, L.S. Fung, C. Holloway, P.A. Marsden, H. Yeger, M.J. Phillips, and G.A. Levy. 1997. Fulminant hepatic failure in murine hepatitis virus strain 3 infection: tissue-specific expression of a novel fgl2 prothrombinase. Journal of Virology 71: 9223–9230.
Li, C., L.S. Fung, S. Chung, A. Crow, N. Myers-Mason, M.J. Phillips, J.L. Leibowitz, E. Cole, C.A. Ottaway, and G. Levy. 1992. Monoclonal anti-prothrombinase (3D4.3) prevents mortality from murine hepatitis virus infection (MHV-3). The Journal of Experimental Medicine 176: 689–697.
Qin, X.H., V.W. Lee, Y.P. Wang, G.P. Zheng, Y. Wang, S.I. Alexander, and D.C. Harris. 2006. A protective role for programmed death 1 in progression of murine adriamycin nephropathy. Kidney International 70: 1244–1250.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC No. 81171585, 30872374 and 61141012).
Competing interests
None of the authors have any conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dayan Cao and Huan Xu are equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, D., Xu, H., Guo, G. et al. Intrahepatic Expression of Programmed Death-1 and its Ligands in Patients with HBV-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure. Inflammation 36, 110–120 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9525-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9525-7