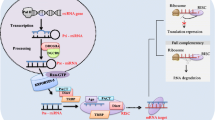
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a group of approximately 20–22-nucleotide-long non-coding RNAs that repress target gene expression through mRNA degradation and translation inhibition. MiRNA (miR)-146a, located in the second exon of the LOC285628 gene on human chromosome 5, is a negative regulator in immune and inflammatory responses. Studies have indicated that miR-146a is associated with the pathogenesis of several autoimmune diseases, such as systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and Sjögren’s syndrome. In this review, emphasis will be laid on the recent progress in the functional roles of miR-146a in these autoimmune diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Luo, X., L.M. Tsai, N. Shen, and D. Yu. 2010. Evidence for microRNA-mediated regulation in rheumatic diseases. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 69(Suppl I): i30–i36.
Taganov, K.D., M.P. Boldin, K.J. Chang, and D. Baltimore. 2006. NF-κB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103: 12481–12486.
Vyse, T.J., and B.L. Kotzin. 1996. Genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Current Opinion in Immunology 8: 843–851.
Tang, Y., X. Luo, H. Cui, X. Ni, M. Yuan, Y. Guo, X. Huang, H. Zhou, N. de Vries, P.P. Tak, S. Chen, and N. Shen. 2009. MicroRNA-146a contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis & Rheumatism 60: 1065–1075.
Vollmer, J., S. Tluk, C. Schmitz, S. Hamm, M. Jurk, A. Forsbach, S. Akira, K.M. Kelly, W.H. Reeves, S. Bauer, and A.M. Krieg. 2005. Immune stimulation mediated by autoantigen binding sites within small nuclear RNAs involves Toll-like receptors 7 and 8. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 202: 1575–1585.
Means, T.K., E. Latz, F. Hayashi, et al. 2005. Human lupus autoantibody-DNA complexes activate DCs through cooperation of CD32 and TLR9. Journal of Clinical Investigation 115: 407–417.
Barrat, F.J., T. Meeker, J. Gregorio, J.H. Chan, S. Uematsu, S. Akira, B. Chang, O. Duramad, and R.L. Coffman. 2005. Nucleic acids of mammalian origin can act as endogenous ligands for Toll-like receptors and may promote systemic lupus erythematosus. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 202: 1131–1139.
Uematsu, S., S. Sato, M. Yamamoto, T. Hirotani, H. Kato, F. Takeshita, M. Matsuda, C. Coban, K.J. Ishii, T. Kawai, O. Takeuchi, and S. Akira. 2005. Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase-1 plays an essential role for Toll-like receptor (TLR)7- and TLR9-mediated interferon-{alpha} induction. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 201: 915–923.
Kawai, T., S. Sato, K.J. Ishii, C. Coban, H. Hemmi, M. Yamamoto, K. Terai, M. Matsuda, J. Inoue, S. Uematsu, O. Takeuchi, and S. Akira. 2004. Interferon-α induction through Toll-like receptors involves a direct interaction of IRF7 with MyD88 and TRAF6. Nature Immunology 5: 1061–1068.
Schoenemeyer, A., B.J. Barnes, M.E. Mancl, E. Latz, N. Goutagny, P.M. Pitha, K.A. Fitzgerald, and D.T. Golenbock. 2005. The interferon regulatory factor, IRF5, is a central mediator of toll-like receptor 7 signaling. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280: 17005–17012.
Li, Q.J., J. Chau, P.J. Ebert, G. Sylvester, H. Min, G. Liu, R. Braich, M. Manoharan, J. Soutschek, P. Skare, L.O. Klein, M.M. Davis, and C.Z. Chen. 2007. miR-181a is an intrinsic modulator of t cell sensitivity and selection. Cell 129: 147–161.
Platanias, L.C. 2005. Mechanisms of type I and type II interferon mediated signalling. Nature Reviews Immunology 5: 375–386.
Dai, R., Y. Zhang, D. Khan, B. Heid, D. Caudell, O. Crasta, and S.A. Ahmed. 2010. Identification of a common lupus disease-associated microRNA expression pattern in three different murine models of lupus. PLoS One 5: e14302.
Pan, Q., X. Luo, and N. Chegini. 2010. microRNA 21: response to hormonal therapies and regulatory function in leiomyoma, transformed leiomyoma and leiomyosarcoma cells. Molecular Human Reproduction 16: 215–227.
Lu, J., B.C. Kwan, F.M. Lai, L.S. Tam, E.K. Li, K.M. Chow, G. Wang, P.K. Li, and C.C. Szeto. 2012. Glomerular and tubulointerstitial miR-638, miR-198 and miR-146a expression in lupus nephritis. Nephrology (Carlton, Vic.). doi:10.1111/j.1440-1797.2012.01573.x.
Pauley, K.M., S. Cha, and E.K. Chan. 2009. MicroRNA in autoimmunity and autoimmune diseases. Journal of Autoimmunity 32: 189–194.
Lu, L.F., M.P. Boldin, A. Chaudhry, L.L. Lin, K.D. Taganov, T. Hanada, A. Yoshimura, D. Baltimore, and A.Y. Rudensky. 2010. Function of miR-146a in controlling Treg cell-mediated regulation of Th1 responses. Cell 142: 914–929.
Luo, X., W. Yang, D.Q. Ye, H. Cui, Y. Zhang, N. Hirankarn, X. Qian, Y. Tang, Y.L. Lau, N. de Vries, P.P. Tak, B.P. Tsao, and N. Shen. 2011. A functional variant in microRNA-146a promoter modulates its expression and confers disease risk for systemic lupus erythematosus. PLoS Genet 7: e1002128.
Zhang, J., B. Yang, B. Ying, D. Li, Y. Shi, X. Song, B. Cai, Z. Huang, Y. Wu, and L. Wang. 2011. Association of pre-microRNAs genetic variants with susceptibility in systemic lupus erythematosus. Molecular Biology Reports 38: 1463–1468.
Löfgren, S.E., Frostegård, J., Truedsson, L., Pons-Estel, B.A., D'Alfonso, S., Witte, T., Lauwerys, B.R., Endreffy, E., Kovács, L., Vasconcelos, C., Martins, da. Silva. B., Kozyrev, S.V., Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. 2012. Genetic association of miRNA-146a with systemic lupus erythematosus in Europeans through decreased expression of the gene. Genes and Immunity doi:10.1038/gene.2011.84.
Morgan, A.W., J.I. Robinson, P.G. Conaghan, S.G. Martin, E.M. Hensor, M.D. Morgan, L. Steiner, H.A. Erlich, H.C. Gooi, A. Barton, J. Worthington, and P. Emery. 2010. Evaluation of the rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility loci HLA-DRB1, PTPN22, OLIG3/TNFAIP3, STAT4 and TRAF1/C5 in an inception Cohort. Arthritis Research & Therapy 12: R57.
Nakasa, T., H. Shibuya, Y. Nagata, T. Niimoto, and M. Ochi. 2011. The inhibitory effect of microRNA-146a expression on bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 63: 1582–1590.
Murata, K., H. Yoshitomi, S. Tanida, M. Ishikawa, K. Nishitani, H. Ito, and T. Nakamura. 2010. Plasma and synovial fluid microRNAs as potential biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 12: R86.
Nakasa, T., S. Miyaki, A. Okubo, M. Hashimoto, K. Nishida, M. Ochi, and H. Asahara. 2008. Expression of MicroRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58: 1284–1292.
Franzoso, G., L. Carlson, L. Xing, L. Poljak, E.W. Shores, K.D. Brown, A. Leonardi, T. Tran, B.F. Boyce, and U. Siebenlist. 1997. Requirement for NF-kB in osteoclast and B-cell development. Genes & Development 11: 3482–3496.
Clohisy, J.C., B.C. Roy, C. Biondo, E. Frazier, D. Willis, S.L. Teitelbaum, and Y. Abu-Amer. 2003. Direct inhibition of NF-κB blocks bone erosion associated with inflammatory arthritis. Journal of Immunology 171: 5547–5553.
Pauley, K.M., M. Satoh, A.L. Chan, M.R. Bubb, W.H. Reeves, and E.K. Chan. 2008. Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Research & Therapy 10: R101.
Li, J., Y. Wan, Q. Guo, L. Zou, J. Zhang, Y. Fang, J. Zhang, J. Zhang, X. Fu, H. Liu, L. Lu, and Y. Wu. 2010. Research article altered microRNA expression profile with miR-146a upregulation in CD4+ T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 12: R81.
Ryu, S.W., S.K. Chae, K.J. Lee, and E. Kim. 1999. Identification and characterization of human Fas associated aactor 1, hFAF1. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 262: 388–394.
Ryu, S.W., and E. Kim. 2001. Apoptosis Induced by human Fas-associated aactor 1, hFAF1, requires its ubiquitin homologous domain, but not the Fas-binding domain. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 286: 1027–1032.
Park, M.Y., H.D. Jang, S.Y. Lee, K.J. Lee, and E. Kim. 2004. Fas-associated factor-1 Inhibits nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activity by interfering with nuclear translocation of the RelA (p65) subunit of NF-κB. Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 1544–1549.
Curtale, G., F. Citarella, C. Carissimi, M. Goldoni, N. Carucci, V. Fulci, D. Franceschini, F. Meloni, V. Barnaba, and G. Macino. 2010. An emerging player in the adaptive immune response: microRNA-146a is a modulator of IL-2 expression and activation-induced cell death in T lymphocytes. Blood 115: 265–273.
Ryu, S.W., S.J. Lee, M.Y. Park, J.I. Jun, Y.K. Jung, and E. Kim. 2003. Fas-associated factor 1, FAF1, is a member of fas death-inducing signaling complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry 178: 24003–24010.
Niimoto, T., T. Nakasa, M. Ishikawa, A. Okuhara, B. Izumi, M. Deie, O. Suzuki, N. Adachi, and M. Ochi. 2010. MicroRNA-146a expresses in interleukin-17 producing T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 11: 209.
Yoshimura, A., T. Naka, and M. Kubo. 2007. SOCS proteins, cytokine signalling and immune regulation. Nature Reviews Immunology 7: 454–465.
Lu, L.F., T.H. Thai, D.P. Calado, A. Chaudhry, M. Kubo, K. Tanaka, G.B. Loeb, H. Lee, A. Yoshimura, K. Rajewsky, and A.Y. Rudensky. 2009. Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells through targeting SOCS1. Immunity 30: 80–91.
Chatzikyriakidou, A., P.V. Voulgari, I. Georgiou, and A.A. Drosos. 2010. A polymorphism in the 3′-UTR of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK1), a target gene of miR-146a, is associated with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility. Joint, Bone, Spine 77: 411–413.
Yang, B., J.L. Zhang, Y.Y. Shi, D.D. Li, J. Chen, Z.C. Huang, B. Cai, X.B. Song, L.X. Li, B.W. Ying, and L.L. Wang. 2011. Association study of single nucleotide polymorphisms in pre-miRNA and rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population. Molecular Biology Reports 38: 4913–4919.
Pauley, K.M., C.M. Stewart, A.E. Gauna, L.C. Dupre, R. Kuklani, A.L. Chan, B.A. Pauley, W.H. Reeves, E.K. Chan, and S. Cha. 2011. Altered miR-146a expression in Sjögren’s syndrome and its functional role in innate immunity. European Journal of Immunology 41: 2029–2039.
Bombardieri, M., F. Barone, V. Pittoni, C. Alessandri, P. Conigliaro, M.C. Blades, R. Priori, I.B. McInnes, G. Valesini, and C. Pitzalis. 2004. Increased circulating levels and salivary gland expression of interleukin-18 in patients with Sjögren's syndrome: relationship with autoantibody production and lymphoid organization of the periductal inflammatory infiltrate. Arthritis Research & Therapy 6: R447–R456.
Eriksson, P., C. Andersson, C. Ekerfelt, J. Ernerudh, and T. Skogh. 2004. Relationship between serum levels of IL-18 and IgG1 in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis and healthy controls. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 137: 617–620.
Szodoray, P., P. Alex, J.G. Brun, M. Centola, and R. Jonsson. 2004. Circulating cytokines in primary Sjögren’s syndrome determined by a multiplex cytokine array system. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 59: 592–599.
Yamano, S., J.C. Atkinson, B.J. Baum, and P.C. Fox. 1999. Salivary gland cytokine expression in NOD and normal BALB/c Mice. Clinical Immunology 92: 265–275.
Zilahi, E., T. Tarr, G. Papp, Z. Griger, S. Sipka, and M. Zeher. 2011. Increased microRNA-146a/b, TRAF6 gene and decreased IRAK1 gene expressions in the peripheral mononuclear cells of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Immunology Letters. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2011.09.006.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was partly supported by grants from the key program of National Natural Science Foundation of China 30830089 and 81172764.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Wang-Dong Xu and Man-Man Lu contributed equally to this work and should be considered co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, WD., Lu, MM., Pan, HF. et al. Association of MicroRNA-146a with Autoimmune Diseases. Inflammation 35, 1525–1529 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9467-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-012-9467-0