Abstract
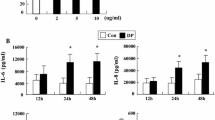
The PI3K pathway plays a major role in many vital cell processes. Our primary aim was to investigate signalling through PI3K for in vitro degranulation from allergen-primed eosinophils and neutrophils in allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma after seasonal and experimental allergen challenge. Nine patients with allergic rhinitis, eight with allergic asthma and four controls were studied during birch pollen season and after nasal and bronchial allergen challenge. Primed blood eosinophils and neutrophils were stimulated for in vitro degranulation with C3b-coated Sephadex particles, after prior incubation with Wortmannin, a PI3K inhibitor. The released amounts of eosinophil cationic protein (ECP), eosinophil peroxidase (EPO) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) were measured by radioimmunoassay. Wortmannin (10−6 to 10−9 M) inhibited ECP, EPO and MPO release in a dose-dependent manner in allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma in all three allergen challenge models. Inhibition of ECP release tended to be lower in the asthmatics in all allergen challenge models, statistically significant compared to the controls during season for 10−8 M Wortmannin (p = 0.01). A clear propensity towards less inhibition in the rhinitic patients was seen after nasal and bronchial challenge compared to seasonal exposure, significant for ECP (10−8 M Wortmannin; p = 0.034 and 0.002, respectively). Signalling through PI3K is clearly involved in ECP, EPO and MPO release in allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma irrespective of allergen challenge model. Allergic asthma demonstrated less inhibition of ECP release via PI3K during pollen season, indicating that other pathways play a greater role in eosinophil degranulation in allergic asthma than allergic rhinitis.



Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Venge, P. 2004. Review article: Monitoring allergic inflammation. Allergy 59: 26–32.
Hogan, S.P., H.F. Rosenberg, R. Moqbel, S. Phipps, P.S. Foster, P. Lacy, A.B. Kay, and M.E. Rothenberg. 2008. Eosinophils: Biological properties and role in health and disease. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 38: 709–750.
Fahly, J.V. 2009. Eosinophilic and neutrophilic inflammation in asthma. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society 6: 256–59.
Shaaban, R., M. Zureik, D. Soussan, C. Neukirch, J. Heinrich, J. Sunyer, M. Wjst, I. Cerveri, I. Pin, J. Bousquet, D. Jarvis, P.G. Burney, F. Neukirch, and B. Leynaert. 2008. Rhinitis and onset of asthma: A longitudinal population-based study. Lancet 372: 1049–57.
Nielsen, L.P., C.G. Peterson, and R. Dahl. 2009. Serum eosinophil granule proteins predict asthma risk in allergic rhinitis. Allergy 64: 733–7.
Kariyawasam, H.H., and D.S. Robinson. 2006. The eosinophil: The cell and its weapons, the cytokines, its locations. Seminars in Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 27: 117–27.
Melo, R.C., L.A. Spencer, A.M. Dvorak, and P.F. Wleer. 2008. Mechanisms of eosinophil secretion: Large vesicotubular carriers mediate transport and release of granule-derived cytokines and other proteins. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 83: 229–36.
Karawajczyk, M., L. Sevéus, R. Garcia, E. Björnsson, C.G.B. Peterson, G.M. Roomans, and P. Venge. 2000. Piecemeal degranulation of peripheral blood eosinophils: A study of allergic subjects during and out of the pollen season. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 34: 521–29.
Melo, R.C., and P.F. Weller. 2010. Piecemeal degranulation in human eosinophils: A distinct secretion mechanism underlying inflammatory responses. Histology and Histopathology 25: 1341–54.
Lampinen, M., M. Carlson, L.D. Håkansson, and P. Venge. 2004. Cytokine-regulated accumulation of eosinophils in inflammatory disease. Allergy 59(8): 793–805.
Carlson, M., L. Håkansson, C. Peterson, G. Stålenheim, and P. Venge. 1991. Secretion of granule proteins from eosinophils and neutrophils is increased in asthma. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 87: 27–33.
Blain, J.F., K. Maghni, S. Pelletier, and P. Sirois. 1999. Evidence for the activation of blood complement in Sephadex beads-induced lung inflammation in guinea pigs. Inflammation Research 48: 386–92.
Hawkins, P.T., K.E. Anderson, K. Davidson, and L.R. Stephens. 2006. Signalling through class I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochemical Society Transactions 34: 647–62.
Medina-Tato, D.A., S.G. Ward, and M.L. Watson. 2007. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in lung disease: Leucocytes and beyond. Immunology 121: 448–61.
Pinho, V., D.G. Souza, M.M. Barsante, F.P. Hamer, M.S. De Freitas, A.G. Rossi, and M.M. Teixeira. 2005. Phosphoinositide-3 kinases critically regulate the recruitment and survival of eosinophils in vivo: Importance for the resolution of allergic inflammation. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 77: 800–10.
Pinho, V., R. de Castro Russo, F.A. Amaral, L.P. de Sousa, M.M. Barsante, D.G. de Souza, J.C. Alves-Filho, D.C. Cara, J.S. Hayflick, C. Rommel, T. Ruckle, A.G. Rossi, and M.M. Teixeira. 2007. Tissue- and stimulus-dependent role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms for neutrophil recruitment induced by chemoattractants in vivo. Journal of Immunology 179: 7891–98.
Powis, G., R. Bonjouklian, M.M. Berggren, A. Gallegos, R. Abraham, C. Ashendel, L. Zalkow, W.F. Matter, J. Dodge, G. Grindey, et al. 1994. Wortmannin, a potent and selective inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. Cancer Research 54: 2419–23.
Lindmo, K., and H. Stenmark. 2006. Regulation of membrane traffic by phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Journal of Cell Science 119: 605–14.
Ali, K., A. Bilancio, M. Thomas, W. Pearce, A.M. Gilfillan, C. Tkaczyk, N. Kuehn, A. Gray, J. Giddings, E. Peskett, R. Fox, I. Bruce, C. Walker, C. Sawyer, K. Okkenhaug, P. Finan, and B. Vanhaesebroeck. 2004. Essential role for the p110delta phosphoinositide 3-kinase in the allergic response. Nature 431: 1007–11.
Ito, N., T. Yokomizo, T. Sasaki, H. Kurosu, J. Penninger, Y. Kanaho, T. Katada, K. Hanaoka, and T. Shimizu. 2002. Requirement of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation and calcium influx for leukotriene B4-induced enzyme release. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277: 44898–904.
Kämpe, M., G. Stålenheim, C. Janson, I. Stolt, and M. Carlson. 2007. Systemic and local eosinophil inflammation during birch pollen season in allergic patients with predominant rhinitis or asthma. Clinical and Molecular Allergy 29: 1–8.
Kämpe, M., C. Janson, G. Stålenheim, I. Stolt, and M. Carlson. 2010. Experimental and seasonal exposure to birch pollen in allergic rhinitis and allergic asthma with regard to the inflammatory response. Clinical Respiratory Journal 4: 37–44.
Quanjer, P.H., G.J. Tammeling, J.E. Cotes, O.F. Pedersen, R. Peslin, and J.C. Yernault. 1993. Lung volumes and forced ventilatory flows. Report Working Party Standardization of Lung Function Tests, European Community for Steel and Coal. Official Statement of the European Respiratory Society. The European Respiratory Journal 16: 5–40.
Machado, L. 1985. Increased bronchial hypersensitivity after early and late bronchial reactions provoked by allergen inhalation. Allergy 40: 580–85.
Hansell, T.T., I.J. De Vries, T. Iff, S. Rihs, M. Wandzalik, S. Betz, K. Blaser, and C. Walker. 1991. An improved immunomagnetic procedure for the isolation of highly purified human blood eosinophils. Journal of Immunological Methods 145: 105–110.
Carlson, M., P. Venge, and M. Lampinen. 2011. C3b-induced eosinophil degranulation involves PI3-kinases and is inhibited by PKC activity. APMIS 119(2): 119–26. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0463.2010.02701.x. Epub 2010 Dec 1.
Winqvist, I., T. Olofsson, and I. Olsson. 1984. Mechanisms for eosinophil degranulation; release of the eosinophil cationic protein. Immunology 51: 1–8.
Kato, M., G.M. Kephart, N.J. Talley, J.M. Wagner, M.G. Sarr, M. Bonno, et al. 1998. Eosinophil infiltration and degranulation in normal human tissue. The Anatomical Record 252: 418–425.
Carlson, M., L. Håkansson, M. Kämpe, G. Stålenheim, C. Peterson, and P. Venge. 1992. Degranulation of eosinophils from pollen-atopic patients with asthma is increased during pollen season. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 89: 131–39.
Erjefält, J.S., L. Greiff, M. Andersson, E. Ädelroth, P.K. Jeffery, and C.G. Persson. 2001. Degranulation patterns of eosinophil granulocytes as determinants of eosinophil driven disease. Thorax 56: 341–44.
Tomassini, M., A. Tsicopoulos, P.C. Tai, V. Gruart, A.B. Tonnel, L. Prin, A. Capron, and M. Capron. 1991. Release of granule proteins by eosinophils from allergic and nonallergic patients with eosinophilia on immunoglobulin-dependent activation. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 88: 365–75.
Bracke, M., P.J. Coffer, J.W. Lammers, and L. Koenderman. 1998. Analysis of signal transduction pathways regulating cytokine-mediated Fc receptor activation on human eosinophils. Journal of Immunology 161: 6768–74.
Kato M, Kita H, Tokuyama K, Morikawa A. 1998. Cross-linking of the beta2 integrin, CD11b⁄ CD18, on human eosinophils induces protein tyrosine phosphorylation and cellular degranulation. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 117 (Suppl 1):68–71.
Egesten, A., and J. Malm. 1998. eosinophil leukocyte degranualtion in response to serum-opsonized beads: C5a and platelet-activating factor enhance ECP release, with roles for protein kinases A and C. Allergy 53: 1066–73.
Horie, S., and H. Kita. 1994. CD11b/CD18 (Mac-1) is required for degranulation of human eosinophils induced by human recombinant granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor and platelet-activating factor. Journal of Immunology 152: 5457–67.
Kaneko, M., S. Horie, M. Kato, G.J. Gleich, and H. Kita. 1995. A crucial role for beta 2 integrin in the activation of eosinophils stimulated by IgG. Journal of Immunology 155: 2631–41.
Andrews S, Stephens LR, Hawkins PT. 2007. PI3K class IB pathway in neutrophils. Sci STKE (407):cm3.
Adamko, D.J., Y. Wu, G.J. Gleich, P. Lacy, and R. Moqbel. 2004. The induction of eosinophil peroxidase release: Improved methods of measurement and stimulation. Journal of Immunological Methods 291: 101–08.
Adamko, D.J., Y. Wu, F. Ajamian, R. Ilarraza, R. Moqbel, and G.J. Gleich. 2008. The effect of cationic charge on release of eosinophil mediators. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 122: 383–90.
Fahly, J.V., K.W. Kim, J. Liu, and H.A. Boushey. 1995. Prominent neutrophilic inflammation in sputum from subjects with asthma exacerbation. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 95: 843–52.
Drews, A.C., M.M.M. Pizzichini, E. Pizzichini, M.U. Peireira, P.M. Pitrez, M.H. Jones, P.D. Sly, and R.T. Stein. 2009. Neutrophilic inflammation is a main feature of induced sputum in nonatopic asthmatic children. Allergy 64: 1597–601.
Monteseirín, J. 2009. Neutrophils and asthma. Journal of Investigational Allergology & Clinical Immunology 19: 340–354.
Wymann, M.P., K. Björklöf, R. Calvez, P. Finan, M. Thomast, A. Trifilieff, M. Barbier, F. Altruda, E. Hirsch, and M. Laffargue. 2003. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase gamma: A key modulator in inflammation and allergy. Biochemical Society Transactions 31: 275–80.
Wymann, M.P., M. Zvelebil, and M. Laffargue. 2003. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling–Which way to target? Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 24: 366–76.
Acknowledgement
The study was supported financially by the Swedish Association against Asthma and Allergy, the Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation and Bror Hjerpstedt’s Foundation. The nurses Signe Svedberg Brandt and Katarina Göthberg are acknowledged for the skilful technical assistance. We also acknowledge Dominic-Luc Webb, Hepatology and Gastroenterology Group, Dept of Medical Sciences, Uppsala University, for skilful linguistic review.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
Mary Kämpe, Marie Carlson and Gunnemar Stålenheim designed the study and were responsible, together with Christer Janson, for analysing and interpreting the results as well as critically revising the manuscript. Maria Lampinen was involved in drafting the manuscript and the figures. Ingrid Stolt carried out the assays and assisted in the statistical analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kämpe, M., Lampinen, M., Stolt, I. et al. PI3-Kinase Regulates Eosinophil and Neutrophil Degranulation in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis and Allergic Asthma Irrespective of Allergen Challenge Model. Inflammation 35, 230–239 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9309-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9309-5