Abstract
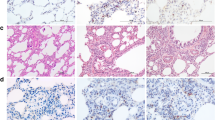
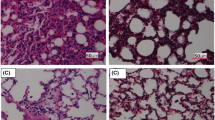
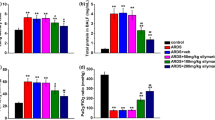
Oxidative stress and inflammation are involved in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury (ALI). Adrenomedullin (AM) is an endogenous peptide with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. This study investigated that whether AM treatment may ameliorate hyperoxia-induced ALI in rats via inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Rats were randomized to receive continuous intravenous infusion of AM or saline through a microosmotic pump, and then ALI was induced by exposing the animals in sealed cages >95% oxygen for 72 h. Exposure to hyperoxia caused lung injury as increased infiltration of inflammatory cells and disruption of lung architecture. AM administration markedly improved these changes. Additionally, AM administration significantly increased glutathione peroxidase and superoxide dismutase activities. Meanwhile, hyperoxia-induced increase of lipid hydroperoxide level was markedly reduced by AM treatment. Moreover, nuclear factor-kappa B-DNA-binding activity, and production of the inflammatory mediators interleukin-6, keratinocyte-derived chemokine, and matrix metalloproteinase 9, were significantly inhibited by AM treatment. AM ameliorates hyperoxia-induced ALI in rats by suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Papaiahgari, S., S.R. Kleeberger, H.Y. Cho, et al. 2004. NADPH oxidase and ERK signaling regulates hyperoxia-induced Nrf2-ARE transcriptional response in pulmonary epithelial cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 279: 42302–42312.
Itoh, T., H. Obata, S. Murakami, et al. 2007. Adrenomedullin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 293: L446–L452.
Müller, H.C., M. Witzenrath, T. Tschernig, et al. 2010. Adrenomedullin attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in mice. Thorax 65: 1077–1084.
Bloomfield, G.L., S. Holloway, P.C. Ridings, et al. 1997. Pretreatment with inhaled nitric oxide inhibits neutrophil migration and oxidative activity resulting in attenuated sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 25: 584–593.
Hess, M.L., E. Okabe, and H.A. Kontos. 1981. Proton and free oxygen radical interaction with the calcium transport system of cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology 13: 767–772.
Rosen, H., and S.J. Klebanoff. 1979. Hydroxyl radical generation by polymorphonuclear leukocytes measured by electron spin resonance spectroscopy. Journal of Clinical Investigation 64: 1725–1729.
Rahman, I., and W. MacNee. 2000. Oxidative stress and regulation of glutathione in lung inflammation. The European Respiratory Journal 16: 534–554.
Comhair, S.A., and S.C. Erzurum. 2002. Antioxidant responses to oxidant-mediated lung diseases. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 283: L246–L255.
Reddy, N.M., S.R. Kleeberger, T.W. Kensler, et al. 2009. Disruption of Nrf2 impairs the resolution of hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice. Journal of Immunology 182: 7264–7271.
Weiss, S.J. 1989. Tissue destruction by neutrophils. The New England Journal of Medicine 320: 365–376.
Fan, J., R.D. Ye, and A.B. Malik. 2001. Transcriptional mechanisms of acute lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 281: L1037–L1050.
Hagiwara, S., H. Iwasaka, K. Togo, et al. 2008. A neutrophil elastase inhibitor, sivelestat, reduces lung injury following endotoxin-induced shock in rats by inhibiting HMGB1. Inflammation 31: 227–234.
Kitamura, K., K. Kangawa, M. Kawamoto, et al. 1993. Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human pheochromocytoma. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 192: 553–560.
Elsasser, T.H., and S. Kahl. 2002. Adrenomedullin has multiple roles in disease stress: development and remission of the inflammatory response. Microscopy Research and Technique 57: 120–129.
Shimosawa, T., Y. Shibagaki, K. Ishibashi, et al. 2002. Adrenomedullin, an endogenous peptide, counteracts cardiovascular damage. Circulation 105: 106–111.
Kim, J.Y., J.H. Yim, J.H. Cho, et al. 2006. Adrenomedullin regulates cellular glutathione content via modulation of gamma-glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit expression. Endocrinology 147: 1357–1364.
Rahman, M., A. Nishiyama, P. Guo, et al. 2006. Effects of adrenomedullin on cardiac oxidative stress and collagen accumulation in aldosterone-dependent malignant hypertensive rats. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 318: 1323–1329.
Murakami, K., R. McGuire, R.A. Cox, et al. 2002. Heparin nebulization attenuates acute lung injury in sepsis following smoke inhalation in sheep. Shock 18: 236–241.
Kozar, R.A., C.J. Weibel, J. Cipolla, et al. 2000. Antioxidant enzymes are induced during recovery from acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 28: 2486–2491.
Sciuto, A.M., M.B. Cascio, T.S. Moran, et al. 2003. The fate of antioxidant enzymes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid over 7 days in mice with acute lung injury. Inhalation Toxicology 15: 675–685.
Hassoun, E.A., and J. Cearfoss. 2011. Dichloroacetate- and trichloroacetate-induced modulation of superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase activities and glutathione level in the livers of mice after subacute and subchronic exposure. Toxicological and Environmental Chemistry 93: 332–344.
Kim, S.M., J.Y. Kim, S. Lee, et al. 2010. Adrenomedullin protects against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell death by suppression of reactive oxygen species via thiol redox systems. FEBS Letters 584: 213–218.
Rabbani, Z.N., M.S. Anscher, R.J. Folz, et al. 2005. Overexpression of extracellular superoxide dismutase reduces acute radiation induced lung toxicity. BMC Cancer 5: 59.
Oury, T.D., L.M. Schaefer, C.L. Fattman, et al. 2002. Depletion of pulmonary EC-SOD after exposure to hyperoxia. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 283: L777–L784.
Liu, J., T. Shimosawa, H. Matsui, et al. 2007. Adrenomedullin inhibits angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress via Csk-mediated inhibition of Src activity. American Journal of Physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology 292: H1714–H1721.
Fink, M.P. 2002. Role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Current Opinion in Critical Care 8: 6–11.
Dreger, H., K. Westphal, A. Weller, et al. 2009. Nrf2-dependent upregulation of antioxidative enzymes: a novel pathway for proteasome inhibitor-mediated cardioprotection. Cardiovascular Research 83: 354–361.
Pugazhenthi, S., L. Akhov, G. Selvaraj, et al. 2007. Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression by demethoxy curcuminoids through Nrf2 by a PI3-kinase/Akt-mediated pathway in mouse β cells. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism 293: E645–E655.
Okumura, H., N. Nagaya, T. Itoh, et al. 2004. Adrenomedullin infusion attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. Circulation 109: 242–248.
Shapiro, H., I. Kagan, M. Shalita-Chesner, et al. 2010. Inhaled aerosolized insulin: a “topical” anti-inflammatory treatment for acute lung injury and respiratory distress syndrome? Inflammation 33: 315–319.
Schmeck, B., P.D. N’Guessan, M. Ollomang, et al. 2007. Legionella pneumophila-induced NF-kappaB-and MAPK-dependent cytokine release by lung epithelial cells. The European Respiratory Journal 29: 25–33.
Lee, E.G., S.I. Lee, H.J. Chae, et al. 2011. Adrenomedullin Inhibits IL-1beta-Induced Rheumatoid Synovial Fibroblast Proliferation and MMPs, COX-2 and PGE2 Production. Inflammation. doi:10.1007/s10753-010-9239-7
Jin, D., K. Otani, K. Yamahara, et al. 2011. Adrenomedullin reduces expression of adhesion molecules on lymphatic endothelial cells. Regulatory Peptides 166: 21–27.
Boland, C., V. Collet, E. Laterre, et al. 2011. Electrical vagus nerve stimulation and nicotine effects in peritonitis-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inflammation 34(1): 29–35.
Yang, S., M. Zhou, D.E. Fowler, et al. 2002. Mechanisms of the beneficial effect of adrenomedullin and adrenomedullin-binding protein-1 in sepsis: down-regulation of proinflammatory cytokines. Critical Care Medicine 30: 2729–2735.
Lee, B.H., T.J. Lee, J.W. Jung, et al. 2009. The role of keratinocyte-derived chemokine in hemorrhage-induced acute lung injury in mice. Journal of Korean Medical Science 24: 775–781.
Saito, Y., C. Nakagawa, H. Uchida, et al. 2001. Adrenomedullin suppresses fMLP-induced upregulation of CD11b of human neutrophils. Inflammation 25: 197–201.
Yousufzai, S.Y., N. Ali, and A.A. Abdel-Latif. 1999. Effects of adrenomedullin on cyclic AMP formation and on relaxation in iris sphincter smooth muscle. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science 40: 3245–3253.
Hippenstiel, S., M. Witzenrath, B. Schmeck, et al. 2002. Adrenomedullin reduces endothelial hyperpermeability. Circulation Research 91: 618–625.
Hocke, A.C., B. Temmesfeld-Wollbrueck, B. Schmeck, et al. 2006. Perturbation of endothelial junction proteins by Staphylococcus aureus alpha-toxin: inhibition of endothelial gap formation by adrenomedullin. Histochemistry and Cell Biology 126: 305–316.
Temmesfeld-Wollbrück, B., B. Brell, C. zu Dohna, et al. 2009. Adrenomedullin reduces intestinal epithelial permeability in vivo and in vitro. American Journal of Physiology. Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 297: G43–G51.
Nagase, H., and J.F. Woessner Jr. 1999. Matrix metalloproteinases. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 274: 21491–21494.
Gushima, Y., K. Ichikado, M. Suga, et al. 2001. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases in pigs with hyperoxia-induced acute lung injury. The European Respiratory Journal 18: 827–837.
Kim, J.H., M.H. Suk, D.W. Yoon, et al. 2006. Inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-9 prevents neutrophilic in flammation in ventilator-induced lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 291: L580–L587.
Kong, M.Y., A. Gaggar, Y. Li, et al. 2009. Matrix metalloproteinase activity in pediatric acute lung injury. International Journal of Medical Sciences 6: 9–17.
Tacon, C.E., S. Wiehler, N.S. Holden, et al. 2010. Human rhinovirus infection up-regulates MMP-9 production in airway epithelial cells via NF-{kappa}B. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 43: 201–209.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Chao Zhu, Jin-Cai Chen, Juan Yao, and Li-Ping Chen for excellent assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tao, W., Shu, YS., Miao, QB. et al. Attenuation of Hyperoxia-induced Lung Injury in Rats by Adrenomedullin. Inflammation 35, 150–157 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9300-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-011-9300-1