Abstract
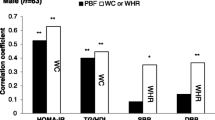
This study assessed the potential association of some proinflammatory markers with adiposity (total vs. central) and metabolic features in young adults. Measurements included body composition, lifestyle features, blood biochemical, and selected inflammatory indicators on 154 healthy subjects (53 M/101 F; 21.5 ± 3 years; 22.1 ± 2.6 kg/m2). Those subjects with higher waist circumference (WC) and waist–hip ratio (WHR) showed higher (P < 0.05) C-reactive protein (CRP), complement C3, interleukin-6 (IL6), and retinol binding protein-4 (RBP4) concentrations, while only IL6 was positively associated with total body fat (%). Furthermore, CRP and RBP4 were higher in former/current smokers, as compared to never smokers (P < 0.05). Some indicators of glucose (homeostasis model assessment—insulin resistance) and lipid metabolism (total cholesterol/high density lipoprotein—cholesterol and triglycerides) were positively associated with the assayed inflammatory markers (P < 0.05). The findings of this cross-sectional study indicate that central adiposity-related indicators (WC/WHR) correlated better than those assessing total adiposity with plasma proinflammatory markers, which additionally were associated with lifestyle and metabolic features in healthy young adults.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bastard, J.P., M. Maachi, C. Lagathu, M.J. Kim, M. Caron, H. Vidal, J. Capeau, and B. Feve. 2006. Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance. European Cytokine Network 17: 4–12.
Van Gaal, L.F., I.L. Mertens, and C.E. De Block. 2006. Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature 444: 875–880.
Zulet, M.A., B. Puchau, C. Navarro, A. Marti, and J.A. Martínez. 2007. Inflammatory biomarkers: The link between obesity and associated pathologies. Nutrición Hospitalaria 22: 511–527.
Bastard, J.P., C. Jardel, E. Bruckert, P. Blondy, J. Capeau, M. Laville, H. Vidal, and B. Hainque. 2000. Elevated levels of interleukin 6 are reduced in serum and subcutaneous adipose tissue of obese women after weight loss. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 85: 3338–3342.
Hermsdorff, H.H.M., M.A. Zulet, I. Abete, and J.A. Martínez. 2009. Discriminated benefits of a Mediterranean dietary pattern within a hypocaloric diet program on plasma RBP4 concentrations and other inflammatory markers in obese subjects. Endocrine 36: 445–451. doi:410.1007/s12020-12009-19248-12021.
Vitkova, M., E. Klimcakova, M. Kovacikova, C. Valle, C. Moro, J. Polak, J. Hanacek, F. Capel, N. Viguerie, B. Richterova, M. Bajzova, J. Hejnova, V. Stich, and D. Langin. 2007. Plasma levels and adipose tissue messenger ribonucleic acid expression of retinol-binding protein 4 are reduced during calorie restriction in obese subjects but are not related to diet-induced changes in insulin sensitivity. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 92: 2330–2335.
Choi, E.Y., E.H. Park, Y.S. Cheong, I. Rheem, S.G. Park, and S. Yoo. 2006. Association of C-reactive protein with the metabolic risk factors among young and middle-aged Koreans. Metabolism 55: 415–421.
Graham, T.E., Q. Yang, M. Bluher, A. Hammarstedt, T.P. Ciaraldi, R.R. Henry, C.J. Wason, A. Oberbach, P.A. Jansson, U. Smith, and B.B. Kahn. 2006. Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance in lean, obese, and diabetic subjects. The New England Journal of Medicine 354: 2552–2563.
Puchau, B., M.A. Zulet, A. González de Echavarri, I. Navarro-Blasco, and J.A. Martínez. 2009. Selenium intake reduces serum C3, an early marker of metabolic syndrome manifestations, in healthy young adults. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 63: 858–864.
Yang, Q., T.E. Graham, N. Mody, F. Preitner, O.D. Peroni, J.M. Zabolotny, K. Kotani, L. Quadro, and B.B. Kahn. 2005. Serum retinol binding protein 4 contributes to insulin resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nature 436: 356–362.
Yudkin, J.S., M. Kumari, S.E. Humphries, and V. Mohamed-Ali. 2000. Inflammation, obesity, stress and coronary heart disease: Is interleukin-6 the link? Atherosclerosis 148: 209–214.
Engstrom, G., B. Hedblad, K.F. Eriksson, L. Janzon, and F. Lindgarde. 2005. Complement C3 is a risk factor for the development of diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Diabetes 54: 570–575.
Chan, J.C., J.C. Cheung, C.D. Stehouwer, J.J. Emeis, P.C. Tong, G.T. Ko, and J.S. Yudkin. 2002. The central roles of obesity-associated dyslipidaemia, endothelial activation and cytokines in the metabolic syndrome—an analysis by structural equation modelling. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 26: 994–1008.
Kraja, A.T., M.A. Province, D. Arnett, L. Wagenknecht, W. Tang, P.N. Hopkins, L. Djousse, and I.B. Borecki. 2007. Do inflammation and procoagulation biomarkers contribute to the metabolic syndrome cluster? Nutrition and Metabolism (Lond) 4: 28.
Festa, A., R. D'Agostino Jr., K. Williams, A.J. Karter, E.J. Mayer-Davis, R.P. Tracy, and S.M. Haffner. 2001. The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders 25: 1407–1415.
Hermsdorff, H.H.M., B. Puchau, M.A. Zulet, and J.A. Martínez. 2010. Association of body fat distribution with proinflammatory gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from young adult subjects. OMICS 14: 1–11. doi:10.1089/omi.2009.0125.
Lapice, E., S. Maione, L. Patti, P. Cipriano, A.A. Rivellese, G. Riccardi, and O. Vaccaro. 2009. Abdominal adiposity is associated with elevated C-reactive protein independent of BMI in healthy nonobese people. Diabetes Care 32: 1734–1736.
Qi, Q., Z. Yu, X. Ye, F. Zhao, P. Huang, F.B. Hu, O.H. Franco, J. Wang, H. Li, Y. Liu, and X. Lin. 2007. Elevated retinol-binding protein 4 levels are associated with metabolic syndrome in Chinese people. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 92: 4827–4834.
Hermsdorff, H.H.M., M.A. Zulet, B. Puchau, J. Bressan, and J.A. Martínez. 2009. Association of retinol-binding protein-4 with dietary selenium intake and other lifestyle features in young healthy women. Nutrition 25: 392–399.
Salas-Salvadó, J., M.A. Rubio, M. Barbany, B. Moreno, and G.C.d l SEEDO. 2007. Consenso SEEDO 2007 para la evaluación del sobrepeso y la obesidad y el establecimiento de criterios de intervención terapéutica. Medicina Clínica (Barcelona) 128: 184–196.
Pérez, S., M.D. Parra, B. Martínez de Morentin, M.C. Rodríguez, and J.A. Martínez. 2005. Evaluación de la variabilidad intraindividual de la medida de composición corporal mediante bioimpedancia en voluntarias sanas y su relación con el índice de masa corporal y el pliegue tricipital. Enfermería Clínica 15: 307–314.
Durnin, J.V., and J. Womersley. 1974. Body fat assessed from total body density and its estimation from skinfold thickness: measurements on 481 men and women aged from 16 to 72 years. The British Journal of Nutrition 32: 77–97.
Siri, W.E. 1956. The gross composition of the body. Advances in Biological and Medical Physics 4: 239–280.
Whitworth, J.A., and J. Chalmers. 2004. World Health Organisation-International Society of Hypertension (WHO/ISH) hypertension guidelines. Clinical and Experimental Hypertension 26: 747–752.
Friedewald, W.T., R.I. Levy, and D.S. Fredrickson. 1972. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clinical Chemistry 18: 499–502.
Matthews, D.R., J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, B.A. Naylor, D.F. Treacher, and R.C. Turner. 1985. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28: 412–419.
Sánchez-Villegas, A., M. Delgado-Rodriguez, M.A. Martínez-González, and J. De Irala-Estevez. 2003. Gender, age, socio-demographic and lifestyle factors associated with major dietary patterns in the Spanish Project SUN (Seguimiento Universidad de Navarra). European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 57: 285–292.
Ching, P.L., W.C. Willett, E.B. Rimm, G.A. Colditz, S.L. Gortmaker, and M.J. Stampfer. 1996. Activity level and risk of overweight in male health professionals. American Journal of Public Health 86: 25–30.
Martínez-González, M.A., C. López-Fontana, J.J. Varo, A. Sánchez-Villegas, and J.A. Martínez. 2005. Validation of the Spanish version of the physical activity questionnaire used in the Nurses' Health Study and the Health Professionals' Follow-up Study. Public Health Nutrition 8: 920–927.
Chouraki, V., A. Wagner, J. Ferrieres, F. Kee, A. Bingham, B. Haas, J.B. Ruidavets, A. Evans, P. Ducimetiere, P. Amouyel, and J. Dallongeville. 2008. Smoking habits, waist circumference and coronary artery disease risk relationship: The PRIME study. European Journal of Cardiovascular Prevention and Rehabilitation 15: 625–630.
Romero-Corral, A., V.K. Somers, J. Sierra-Johnson, Y. Korenfeld, S. Boarin, J. Korinek, M.D. Jensen, G. Parati, and F. Lopez-Jimenez. 2010. Normal weight obesity: A risk factor for cardiometabolic dysregulation and cardiovascular mortality. European Heart Journal 31: 737–746.
Martínez-González, M.A., J. de Irala, and F.J. Faulin-Fajardo. 2001. Bioestadística Amigable. Madrid: Díaz de Santos.
Santos, A.C., C. Lopes, J.T. Guimaraes, and H. Barros. 2005. Central obesity as a major determinant of increased high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in metabolic syndrome. International Journal of Obesity (Lond) 29: 1452–1456.
Nishida, M., T. Moriyama, Y. Sugita, and K. Yamauchi-Takihara. 2007. Abdominal obesity exhibits distinct effect on inflammatory and anti-inflammatory proteins in apparently healthy Japanese men. Cardiovascular Diabetology 6: 27.
Hermsdorff, H.H.M., and J.B. Monteiro. 2004. Visceral, subcutaneous or intramuscular fat: Where is the problem? Arquivos Brasileiros de Endocrinologia e Metabologia 48: 803–811.
WHO. 2000. World Health Organization. Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation. World Health Organ Tech Rep 894: 1–253.
SEEDO. 2000. Sociedad Espanola para el Estudio de la Obesidad. Consenso SEEDO´2000 para la evaluación del sobrepeso y la obesidad y el establecimiento de criterios de intervención terapéutica. Med Clin (Barc) 115: 587–597.
Aeberli, I., R. Biebinger, R. Lehmann, D. L'Allemand, G.A. Spinas, and M.B. Zimmermann. 2007. Serum retinol-binding protein 4 concentration and its ratio to serum retinol are associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome components in children. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 92: 4359–4365.
Reinehr, T., B. Stoffel-Wagner, and C.L. Roth. 2008. Retinol-binding protein 4 and its relation to insulin resistance in obese children before and after weight loss. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism 93: 2287–2293.
Vikram, N.K., A. Misra, M. Dwivedi, R. Sharma, R.M. Pandey, K. Luthra, A. Chatterjee, V. Dhingra, B.L. Jailkhani, K.K. Talwar, and R. Guleria. 2003. Correlations of C-reactive protein levels with anthropometric profile, percentage of body fat and lipids in healthy adolescents and young adults in urban North India. Atherosclerosis 168: 305–313.
Warnberg, J., E. Nova, L.A. Moreno, J. Romeo, M.I. Mesana, J.R. Ruiz, F.B. Ortega, M. Sjostrom, M. Bueno, and A. Marcos. 2006. Inflammatory proteins are related to total and abdominal adiposity in a healthy adolescent population: the AVENA Study. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 84: 505–512.
Wannamethee, S.G., G.D. Lowe, A.G. Shaper, A. Rumley, L. Lennon, and P.H. Whincup. 2005. Associations between cigarette smoking, pipe/cigar smoking, and smoking cessation, and haemostatic and inflammatory markers for cardiovascular disease. European Heart Journal 26: 1765–1773.
Levitzky, Y.S., C.Y. Guo, J. Rong, M.G. Larson, R.E. Walter, J.F. Keaney Jr., P.A. Sutherland, A. Vasan, I. Lipinska, J.C. Evans, and E.J. Benjamin. 2008. Relation of smoking status to a panel of inflammatory markers: The Framingham offspring. Atherosclerosis 201: 217–224.
Lee, J.W., J.A. Im, H.R. Lee, J.Y. Shim, B.S. Youn, and D.C. Lee. 2007. Visceral adiposity is associated with serum retinol binding protein-4 levels in healthy women. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15: 2225–2232.
Park, H.S., J.Y. Park, and R. Yu. 2005. Relationship of obesity and visceral adiposity with serum concentrations of CRP, TNF-alpha and IL-6. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice 69: 29–35.
Pou, K.M., J.M. Massaro, U. Hoffmann, R.S. Vasan, P. Maurovich-Horvat, M.G. Larson, J.F. Keaney Jr., J.B. Meigs, I. Lipinska, S. Kathiresan, J.M. Murabito, C.J. O'Donnell, E.J. Benjamin, and C.S. Fox. 2007. Visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue volumes are cross-sectionally related to markers of inflammation and oxidative stress: The Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 116: 1234–1241.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank our physician Blanca E. Martínez de Morentin, our nurse Salomé Pérez, and our technician Verónica Ciaurriz for excellent technical assistance. This work was supported by Health Department of the Government of Navarra (22/2007) and by Línea Especial about Nutrition, Obesity and Health (University of Navarra LE/97). The Capes Foundation, Ministry of Education of Brazil as well as IBERCAJA and ADA fellowships scheme of the University of Navarra also provided research grants to HHM Hermsdorff (no. 3756/05-0) and B Puchau, respectively.
Contributors
HHMH: Design, field work, data collection, analysis, and writing of the manuscript. BP: Design, field work, and data collection. MZ: project coleader, design, financial management, and editing the manuscript. JAM: project leader, general coordination, design, financial management, and editing of the manuscript. None of the contributing authors had any financial or personal interests in any of the bodies sponsoring this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermsdorff, H.H.M., Zulet, M.Á., Puchau, B. et al. Central Adiposity Rather Than Total Adiposity Measurements Are Specifically Involved in the Inflammatory Status from Healthy Young Adults. Inflammation 34, 161–170 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9219-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9219-y