Abstract
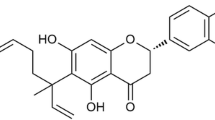
Cryptotanshinone (CTS), a major constituent extracted from the medicinal herb Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge, has well-documented antioxidative and anti-inflammatory effects. In the present study, the pharmacological effects and underlying molecular mechanisms of CTS on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory responses were investigated. By enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, we observed that CTS reduced significantly the production of proinflammatory mediators (tumor necrosis factor-α and interleukin-6) induced by LPS in murine macrophage-like RAW264.7 cells. Mechanistically, CTS inhibited markedly the phosphorylation of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), including ERK1/2, p38MAPK, and JNK, which are crucially involved in regulation of proinflammatory mediator secretion. Moreover, immunofluorescence and western blot analysis indicated that CTS abolished completely LPS-triggered nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) activation. Taken together, these data implied that NF-κB and MAPKs might be the potential molecular targets for clarifying the protective effects of CTS on LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, S.Y., T.C. Moon, H.W. Chang, K.H. Son, S.S. Kang, and H.P. Kim. 2002. Effects of tanshinone I isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge on arachidonic acid metabolism and in vivo inflammatory responses. Phytotherapy Research 16: 616–620.
Ng, T.B., F. Liu, and Z.T. Wang. 2000. Antioxidative activity of natural products from plants. Life Sciences 66: 709–723.
Park, E.J., Y.Z. Zhao, Y.C. Kim, and D.H. Sohn. 2007. PF2401-SF, standardized fraction of Salvia miltiorrhiza and its constituents, tanshinone I, tanshinone IIA, and cryptotanshinone, protect primary cultured rat hepatocytes from bile acid-induced apoptosis by inhibiting JNK phosphorylation. Food and Chemical Toxicology 45: 1891–1898.
Zhou, L., Z. Zuo, and M.S. Chow. 2005. Danshen: An overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and clinical use. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 45: 1345–1359.
Adams, J.D., R. Wang, J. Yang, and E.J. Lien. 2006. Preclinical and clinical examinations of Salvia miltiorrhiza and its tanshinones in ischemic conditions. Chinese Medicine 1: 3.
Jung, H.W., U.K. Seo, J.H. Kim, K.H. Leem, and Y.K. Park. 2009. Flower extract of Panax notoginseng attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory response via blocking of NF-kappaB signaling pathway in murine macrophages. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 122: 313–319.
Choi, H.S., D.I. Cho, H.K. Choi, S.Y. Im, S.Y. Ryu, and K.M. Kim. 2004. Molecular mechanisms of inhibitory activities of tanshinones on lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide generation in RAW 264.7 cells. Archives of Pharmacal Research 27: 1233–1237.
van der Bruggen, T., S. Nijenhuis, E. van Raaij, J. Verhoef, and B.S. van Asbeck. 1999. Lipopolysaccharide-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha production by human monocytes involves the raf-1/MEK1-MEK2/ERK1-ERK2 pathway. Infection and Immunity 67: 3824–3829.
Andersson, K., and R. Sundler. 2000. Signalling to translational activation of tumour necrosis factor-alpha expression in human THP-1 cells. Cytokine 12: 1784–1787.
Fitzgerald, K.A., D.C. Rowe, and D.T. Golenbock. 2004. Endotoxin recognition and signal transduction by the TLR4/MD2-complex. Microbes and Infection 6: 1361–1367.
Kerfoot, S.M., and P. Kubes. 2005. Local coordination verses systemic disregulation: Complexities in leukocyte recruitment revealed by local and systemic activation of TLR4 in vivo. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 77: 862–867.
Beutler, B. 2000. Tlr4: Central component of the sole mammalian LPS sensor. Current Opinion in Immunology 12: 20–26.
Ghosh, S., M.J. May, and E.B. Kopp. 1998. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annual Review of Immunology 16: 225–260.
Dobrovolskaia, M.A., and S.N. Vogel. 2002. Toll receptors, CD14, and macrophage activation and deactivation by LPS. Microbes and Infection 4: 903–914.
Jeon, S.J., K.H. Son, Y.S. Kim, Y.H. Choi, and H.P. Kim. 2008. Inhibition of prostaglandin and nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells by tanshinones from the roots of Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge. Archives of Pharmacal Research 31: 758–763.
Lee, P., J. Hur, J. Lee, J. Kim, J. Jeong, I. Kang, S.Y. Kim, and H. Kim. 2006. 15, 16-dihydrotanshinone I suppresses the activation of BV-2 cell, a murine microglia cell line, by lipopolysaccharide. Neurochemistry International 48: 60–66.
Jin, D.Z., L.L. Yin, X.Q. Ji, and X.Z. Zhu. 2006. Cryptotanshinone inhibits cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme activity but not its expression. European Journal of Pharmacology 549: 166–172.
Baldwin, A.S., Jr. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: New discoveries and insights. Annual Review of Immunology 14: 649–683.
Suh, S.J., U.H. Jin, H.J. Choi, H.W. Chang, J.K. Son, S.H. Lee, S.J. Jeon, K.H. Son, Y.C. Chang, Y.C. Lee, and C.H. Kim. 2006. Cryptotanshinone from Salvia miltiorrhiza BUNGE has an inhibitory effect on TNF-alpha-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 production and HASMC migration via down-regulated NF-kappaB and AP-1. Biochemical Pharmacology 72: 1680–1689.
Cao, W., C. Bao, E. Padalko, and C.J. Lowenstein. 2008. Acetylation of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 inhibits Toll-like receptor signaling. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205: 1491–1503.
Wu, M.J., L. Wang, H.Y. Ding, C.Y. Weng, and J.H. Yen. 2004. Glossogyne tenuifolia acts to inhibit inflammatory mediator production in a macrophage cell line by downregulating LPS-induced NF-kappa B. Journal of Biomedical Science 11: 186–199.
Cheng, Y.W., C.Y. Chang, K.L. Lin, C.M. Hu, C.H. Lin, and J.J. Kang. 2008. Shikonin derivatives inhibited LPS-induced iNOS in RAW 264.7 cells via downregulation of MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 120: 264–271.
Chen, C.C., P.C. Tsai, B.L. Wei, and W.F. Chiou. 2008. 8-Prenylkaempferol suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase expression through interfering with JNK-mediated AP-1 pathway in murine macrophages. European Journal of Pharmacology 590: 430–436.
Jung, H.W., C.H. Yoon, Y.H. Kim, Y.C. Boo, K.M. Park, and Y.K. Park. 2007. Wen-Pi-Tang-Hab-Wu-Ling-San extract inhibits the release of inflammatory mediators from LPS-stimulated mouse macrophages. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 114: 439–445.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 30811120434, no. 30772576), the National Science and Technology Major Project of China “Key New Drug Creation and Manufacturing Program” [Grant 2009ZX09102-152, 2009ZX09303-007], Major Program in Key Field of People's Government of Guangdong Province (P. R. of China, no. 2003A30904), and the Key Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, People's Republic of China (no. 7117380).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, S., Shen, XY., Huang, HQ. et al. Cryptotanshinone Suppressed Inflammatory Cytokines Secretion in RAW264.7 Macrophages through Inhibition of the NF-κB and MAPK Signaling Pathways. Inflammation 34, 111–118 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9214-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9214-3