Abstract
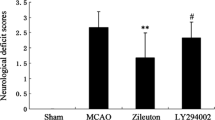
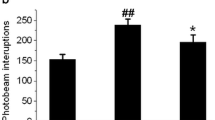
5-Lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton has been demonstrated to attenuate ischemic brain damage in rats of permanent focal cerebral ischemia in previous work. To further investigate the mechanism underlying zileuton's neuroprotection, adult male Sprague-Dawley rats underwent permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), then received treatment with zileuton or vehicle after the onset of ischemia. Neurological deficit, cerebral infarction, and morphological characteristic were measured 6 and 24 h after MCAO. The enzymatic activity of myeloperoxidase (MPO) was assessed 6 and 24 h after MCAO and the lipid peroxidation levels were evaluated by malondialdehyde assay. Expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) p65 in rat brain was detected by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in rat brain was determined by RT-PCR and Western blot. Nitric oxide production in rat brain was also measured 24 h after MCAO. The concentration of TNF-α and IL-1β in serum were detected by ELISA. Zileuton significantly reduced neurological deficit scores, cerebral infarct volume, MPO activity, and the lipid peroxidation levels. It also inhibited the expression of NF-κB and decreased the expression and activity of iNOS in rat brain. In addition, zileuton attenuated the release of TNF-α and IL-1β in serum. Our results suggest that zileuton reduces inflammatory reaction and brain damage in a rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia. The neuroprotective effect of zileuton in cerebral ischemia might be associated with the inhibition of inflammatory reaction.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dirnagl, U., C. Iadecola, and M.A. Moskowitz. 1999. Pathobiology of ischaemic stroke: an integrated view. Trends in Neurosciences 22: 391–397.
Durukan, A., and T. Tatlisumak. 2007. Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacology Biochemistry and Behavior 87: 179–197.
Lapchak, P.A., and D.M. Araujo. 2007. Advances in ischemic stroke treatment: neuroprotective and combination therapies. Expert Opinion Emerging Drugs 12: 97–112.
Huang, J., U.M. Upadhyay, and R.J. Tamargo. 2006. Inflammation in stroke and focal cerebral ischemia. Surgical Neurology 66: 232–245.
Mabuchi, T., K. Kitagawa, T. Ohtsuki, K. Kuwabara, Y. Yagita, T. Yanagihara, M. Hori, and M. Matsumoto. 2000. Contribution of microglia/macrophages to expansion of infarction and response of oligodendrocytes after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 31: 1735–1743.
Baskaya, M.K., Y. Hu, D. Donaldson, M. Maley, A.M. Rao, M.R. Prasad, and R.J. Dempsey. 1996. Protective effect of the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor AA-861 on cerebral edema after transient ischemia. Journal of Neurosurgery 85: 112–116.
Zhou, Y., E.Q. Wei, S.H. Fang, L.S. Chu, M.L. Wang, W.P. Zhang, G.L. Yu, Y.L. Ye, S.C. Lin, and Z. Chen. 2006. Spatio-temporal properties of 5-lipoxygenase expression and activation in the brain after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Life Sciences 79: 1645–1656.
Jatana, M., S. Giri, M.A. Ansari, C. Elango, A.K. Singh, I. Singh, and M. Khan. 2006. Inhibition of NF-kappaB activation by 5-lipoxygenase inhibitors protects brain against injury in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemia. Journal de Neuroinflammation 3: 12.
Bonizzi, G., J. Piette, S. Schoonbroodt, R. Greimers, L. Havard, M.P. Merville, and V. Bours. 1999. Reactive oxygen intermediate-dependent NF-kappaB activation by interleukin-1beta requires 5-lipoxygenase or NADPH oxidase activity. Molecular and Cellular Biology 19: 1950–1960.
Ridder, D.A., and M. Schwaninger. 2009. NF-kappaB signaling in cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 158: 995–1006.
Iadecola, C., F. Zhang, S. Xu, R. Casey, and M.E. Ross. 1995. Inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in brain following cerebral ischemia. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 15: 378–384.
Saito, K., K. Suyama, K. Nishida, Y. Sei, and A.S. Basile. 1996. Early increases in TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1 beta levels following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbil brain. Neuroscience Letters 206: 149–152.
Tu, X.K., W.Z. Yang, S.S. Shi, C.M. Chen, and C.H. Wang. 2009. 5-Lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton attenuates ischemic brain damage: involvement of matrix metalloproteinase 9. Neurological Research 31: 848–852.
Bederson, J.B., L.H. Pitts, M. Tsuji, M.C. Nishimura, R.L. Davis, and H. Bartkowski. 1986. Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17: 472–476.
Lin, T.N., Y.Y. He, G. Wu, M. Khan, and C.Y. Hsu. 1993. Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral ischemia model in rats. Stroke 24: 117–121.
Iadecola, C., and M. Alexander. 2001. Cerebral ischemia and inflammation. Current Opinion in Neurology 14: 89–94.
Martel-Pelletier, J., D. Lajeunesse, P. Reboul, and J.P. Pelletier. 2003. Therapeutic role of dual inhibitors of 5-LOX and COX, selective and non-selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 62: 501–509.
Bell, R.L., P.R. Young, D. Albert, C. Lanni, J.B. Summers, D.W. Brooks, P. Rubin, and G.W. Carter. 1992. The discovery and development of zileuton: an orally active 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor. International Journal of Immunopharmacology 14: 505–510.
Patel, N.S., S. Cuzzocrea, P.K. Chatterjee, R. Di Paola, L. Sautebin, D. Britti, and C. Thiemermann. 2004. Reduction of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury in 5-lipoxygenase knockout mice and by the 5-lipoxygenase inhibitor zileuton. Molecular Pharmacology 66: 220–227.
Lerouet, D., V. Beray-Berthat, B. Palmier, M. Plotkine, and I. Margaill. 2002. Changes in oxidative stress, iNOS activity and neutrophil infiltration in severe transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Brain Research 958: 166–175.
Weston, R.M., N.M. Jones, B. Jarrott, and J.K. Callaway. 2007. Inflammatory cell infiltration after endothelin-1-induced cerebral ischemia: histochemical and myeloperoxidase correlation with temporal changes in brain injury. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism 27: 100–114.
Beray-Berthat, V., N. Croci, M. Plotkine, and I. Margaill. 2003. Polymorphonuclear neutrophils contribute to infarction and oxidative stress in the cortex but not in the striatum after ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Research 987: 32–38.
Genovese, T., A. Rossi, E. Mazzon, R.D. Paola, C. Muia, R. Caminiti, P. Bramanti, L. Sautebin, and S. Cuzzocrea. 2008. Effects of zileuton and montelukast in mouse experimental spinal cord injury. British Journal of Pharmacology 153: 568–582.
Nurmi, A., P.J. Lindsberg, M. Koistinaho, W. Zhang, E. Juettler, M.L. Karjalainen-Lindsberg, F. Weih, N. Frank, M. Schwaninger, and J. Koistinaho. 2004. Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to infarction after permanent focal ischemia. Stroke 35: 987–991.
Schneider, A., A. Martin-Villalba, F. Weih, J. Vogel, T. Wirth, and M. Schwaninger. 1999. NF-kappaB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Natural Medicines 5: 554–559.
Tu, X.K., W.Z. Yang, S.S. Shi, C.H. Wang, and C.M. Chen. 2009. Neuroprotective effect of baicalin in a rat model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia. Neurochemical Research 34: 1626–1634.
Yang, Y., X. Xia, Y. Zhang, Q. Wang, L. Li, G. Luo, and Y. Xia. 2009. Delta–opioid receptor activation attenuates oxidative injury in the ischemic rat brain. BMC Biology 7: 55.
Cassatella, M.A. 1995. The production of cytokines by polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Immunology Today 16: 21–26.
Barone, F.C., B. Arvin, R.F. White, A. Miller, C.L. Webb, R.N. Willette, P.G. Lysko, and G.Z. Feuerstein. 1997. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha. A mediator of focal ischemic brain injury. Stroke 28: 1233–1244.
Boutin, H., R.A. LeFeuvre, R. Horai, M. Asano, Y. Iwakura, and N.J. Rothwell. 2001. Role of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in ischemic brain damage. Journal of Neuroscience 21: 5528–5534.
Acknowledgements
The key laboratory (Neurosurgical Department) funding from the Affiliated Union Hospital of Fujian Medical University, and the Professor Academic Development Fund of Fujian Medical University (JS0610), supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tu, Xk., Yang, Wz., Wang, Ch. et al. Zileuton Reduces Inflammatory Reaction and Brain Damage Following Permanent Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Inflammation 33, 344–352 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9191-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-010-9191-6