Abstract
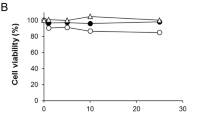
Radix Isatidis is the dried root of the plant Isatidis indigotica Fort (family Cruciferae) and traditionally used as an anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-endotoxic, and immune regulatory agent in the folk medicine of Korea and China. The aim of the present study was to determine the anti-inflammatory effects of methanolic extracts of Radix Isatidis (RIME) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated murine macrophages and in a TPA-induced ear edema animal model. Anti-inflammatory effects of RIME were examined in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages. In order to investigate the effects of RIME in vivo, activation of myeloperoxidase, and histological assessment were examined in the 12-O-tetradecanoyl-phorbol-13-acetate (TPA)-induced mouse ear edema model. RIME significantly inhibited the release from macrophages of inflammatory mediators such as nitric oxide, prostaglandin E2, and pro-inflammatory cytokines. Topical administration of RIME at 1–5 mg/ear resulted in reduction of ear inflammation in mice. Thus, our results indicate that the anti-inflammatory effects of RIME involve decreased production of inflammatory mediators, which suggests that RIME may have therapeutic potential in a variety of inflammation-related diseases.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Baeuerle, P.A. and T. Henkel. 1994. Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annual Review of Immunology 12: 141–179.
Lawrence, T., D.A. Willoughby, and D.W. Gilroy. 2002. Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators and insights into the resolution of inflammation. Annual Review of Immunology 2: 787–795.
Kaplanski, G., V. Marin, F. Montero-Julian, A. Mantovani, and C. Farnarier. 2003. IL-6: a regulator of the transition from neutrophil to monocyte recruitment during inflammation. Trends in Immunology 24: 25–29.
Iontcheva, I., S. Amar, K.H. Zawawi, A. Kantarci, and T.E. Van Dyke. 2004. Role for moesin in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated signal transduction. Infection and immunity 72: 2312–2320.
Dai, Q., J. Zhang, and S.B. Pruett. 2005. Ethanol alters cellular activation and CD14 partitioning in lipid rafts. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 332: 37–42.
Akira, S. and K. Takeda. 2004. Toll-like receptor signaling. Nature Reviews Immunology 4: 499–511.
Berg, D.J., J. Zhang, J.V. Weinstock, H.F. Ismail, K.A. Earle, H. Alila, R. Pamukcu, S. Moore, and R.G. Lynch. 2002. Rapid development of colitis in NSAID-treated IL-10-deficient mice. Gastroenterology 123: 1527–1542.
Rose, J.W., K.E. Hill, H.E. Watt, and N.G. Carlson. 2004. Inflammatory cell expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in the multiple sclerosis lesion. Journal of Neuroimmunology 149: 40–49.
Gomez, P.F., M.H. Pillinger, M. Attur, N. Marjanovic, M. Dave, J. Park, C.O. Bingham, H. Al-Mussawir, and S.B. Abramson. 2005. Resolution of inflammation: prostaglandin E2 dissociates nuclear trafficking of individual NF-kappaB subunits (p65, p50) in stimulated rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts. Journal of Neuroimmunology 175: 6924–6930.
Kwon, K.H., A. Murakami, R. Hayashi, and H. Ohigashi. 2005. Interleukin-1beta targets interleukin-6 in progressing dextran sulfate sodium-induced experimental colitis. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 337: 647–654.
Karin, M. and Y. Ben-Neriah. 2000. Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-κB activity. Annual Review of Immunology 18: 621–663.
Giuliani, C., G. Napolitano, I. Bucci, V. Montani, and F. Monaco. 2001. NF-κB transcription factor: role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory, autoimmune, and neoplastic diseases and therapy implications. La Clinica Terapeutica 152: 249–253.
Li, Q. and I.M. Verma. 2002. NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nature Reviews Immunology 2: 725–734.
Chen, Z.W., L.W. Wu, S.T. Liu, C.P. Cai, P.F. Rao, and L.J. Ke. 2006. Mechanism study of anti-influenza effects of Radix Isatidis water extract by red blood cells capillary electrophoresis. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 20: 1715–1719.
Kong, W., Y. Zhao, L. Shan, X. Xiao, and W. Guo. 2008. Thermochemical studies on the quantity-antibacterial effect relationship of four organic acids from Radix Isatidis on Escherichia coli growth. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin 31: 1301–1305.
Wang, W., J. Fang, Y. Liu, and W. Xie. 2006. Screening of anti-endotoxin components from Radix isatidis. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Medical sciences 26: 261–264.
Zhao, Y.L., J.B. Wang, L.M. Shan, C. Jin, L. Ma, and X.H. Xiao. 2008. Effect of Radix isatidis polysaccharides on immunological function and expression of immune related cytokines in mice. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 14: 207–211.
Gordon, J.S., P.M. Wolanin, A.V. Gonzalez, D.A. Fela, G. Sarngadharan, K. Rouzard, E. Perez, J.B. Stock, and M.B. Stock. 2008. Topical N-acetyl-S-farnesyl-L-cysteine inhibits mouse skin inflammation, and unlike dexamethasone, its effects are restricted to the application site. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 128: 643–654.
Sato, H., Y. Nakayama, C. Yamashita, and H. Uno. 2004. Anti-inflammatory effects of tacalcitol (1, 24(R)(OH)2D3, TV-02) in the skin of TPA-treated hairless mice. Journal of Dermatology 31: 200–217.
Xue, J., Y. Xu, L. Jin, G. Liu, Y. Sun, S. Li, and J. Zhang. 2008. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine on immune responses in abalone, Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Fish and Shellfish Immunology 24: 752–758.
Fang, J.G., Y.H. Liu, W.Q. Wang, W. Xie, S.X. Fang, and H.G. Han. 2005. The anti-endotoxic effect of o-aminobenzoic acid from Radix Isatidis. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 26: 593–597.
Du, P., S. Zhu, and P. Lü. 2001. Antibacterial activity of 20 kinds of Chinese medicinal materials for Helicobacter pylori in vitro. Zhong Yao Cai 24: 188–189.
Nathan, C. and Q.W. Xie. 1994. Nitric oxide synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell 78: 915–918.
Kamimura, D., K. Ishihara, and T. Hirano. 2003. IL-6 signal transduction and its physiological roles: the signal orchestration model. Reviews of Physiology, Biochemistry and Pharmacology 149: 1–38.
O’Shea, J.J. and P.J. Murray. 2008. Cytokine signaling modules in inflammatory responses. Immunity 28: 477–487.
Baldwin Jr., A.S. 1996. The NF-kappa B and I kappa B proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annual Review of Immunology 14: 649–683.
Ghosh, S., M.J. May, and E.B. Kopp. 1998. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annual Review of Immunology 16: 225–260.
Janssen-Heininger, Y.M., M.E. Poynter, and P.A. Baeuerle. 2000. Recent advances towards understanding redox mechanisms in the activation of nuclear factor kappaB. Free Radical Biology & Medicine 28: 1317–1327.
Jaulmes, A., B. Janvier, M. Andreani, and M. Raymondjean. 2005. Autocrine and paracrine transcriptional regulation of type II A secretory phospholipase A2 gene in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 25: 1161–1167.
An, Y.Q., X.B. Jia, H.J. Yuan, E. Sun, and Z.Z. Xu. 2008. Content determination of epigoitrin in Radix Isatidis and its preparation by RP-HPLC. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 33: 2074–2076.
Liu, Y., J. Fang, T. Lei, W. Wang, and A. Lin. 2003. Anti-endotoxic effects of syringic acid of Radix Isatidis. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology. Medical sciences 23: 206–208.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Regional Innovation Center (RIC) program of the Ministry of Knowledge Economy, Republic of Korea and Korea Association of Small Business Innovation Research (S6070031210), Republic of Korea. The authors greatly appreciate Dr. Jae-In Park (Department of Animal products and Food Science, Kangwon National University, Republic of Korea) for preparation of RIME.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, E.K., Kim, D.H., Lim, H. et al. The Anti-Inflammatory Effects of a Methanolic Extract from Radix Isatidis in Murine Macrophages and Mice. Inflammation 33, 110–118 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-009-9164-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-009-9164-9