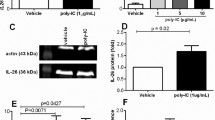
Abstract
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) is a superfamily of enzymes that may play a major role in airways inflammation. We investigated the effect of interferon-γ (IFN-γ) on the gene expression of 19 different PLA2 types in human monocyte-derived macrophages and nasal epithelial cells (RPMI 2650). The cells were stimulated with IFN-γ for different lengths of time (up to 48 h), and the mRNA levels of the different PLA2 types were determined by reverse transcriptase–PCR (RT-PCR) and normalized to those of the house-keeping gene, GAPDH. It appeared that IFN-γ clearly increased the expression of secretory PLA2 IID (but not IIA) in macrophages, while both PLA2 IID and IIA were upregulated in RPMI 2650 cells. Moreover, after 18 h, the mRNA levels of cytosolic PLA2 IVA were 2–3 times higher in IFN-γ-stimulated macrophages than controls, while there was no such effect of IFN-γ in RPMI 2650 cells. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) augmented the increased gene expression of PLA2 IVA but decreased both the basal and the IFN-γ-induced PLA2 IID mRNA expression in macrophages (but not in RPMI 2650 cells). The NF-κB inhibitor Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate (PDTC) and the phoshatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor wortmannin were employed to get an insight into the mechanism behind these observations. Incubation of macrophages with PDTC had no effect on the LPS impairment of PLA2 IID gene expression, but inhibited the LPS mediated activation of PLA2 IVA. No significant effect was noted of PDTC on IFN-γ stimulation, while PI3K had no effect at all on any of the stimuli used. Furthermore, LPS (but not IFN-γ) increased the mRNA levels of the nuclear factor (NF)-κB inhibitors α and ξ in macrophages, but not in RPMI 2650 cells. These findings indicate that (a) the gene expression of secretory types PLA2 IID and IIA in response to IFN-γ is much dependent on cell type, and (b) the regulation of PLA2 type IID in human macrophages is clearly different from that of PLA2 type IVA. (c) PLA2 IVA is probably under control of both NF-κB and IFN-γ-responsive elements (GRE) or IFN-γ-activating sites (GAS). The possibility that PLA2 IID is involved in cytokine-mediated inflammation in the nasal mucosa is inferred, as is the potential role of PLA2 IID in the host defense against LPS-containing bacteria.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes P. J., K. F. Chung, C. P. Page. 1998. Inflammatory mediators of asthma: an update. Pharmacol. Rev.50:515–596
Seilhamer J. J., T. L. Randall, M. Yamanaka, L. K. Johnson. 1986. Pancreatic phospholipase A2: isolation of the human gene and cDNAs from porcine pancreas and human lung. DNA 6: 519–527
Seilhamer J. J., W. Pruzanski, P. Vadas, S. Plant, J. A. Miller, J. Kloss, L. K. Johnson. 1989. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J. Biol. Chem. 264:5335–5338
Ishizaki J., N. Suzuki, K. Higashino, Y. Yokota, T. Ono, K. Kawamoto, N. Fujii, H. Arita, K. Hanasaki. 1999. Cloning and characterization of novel mouse and human secretory phospholipase A2s. J. Biol. Chem. 274:24973–24979
Suzuki N., J. Ishizaki, Y. Yokota, K. Higashino, T. Ono, M. Ikeda, Fujii N., Kawamoto K., Hanasako K. 2000. Structures, enzymatic properties and expression of novel human and mouse secretory phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 275:5785–5793
Valentin E., A. G. Singer, F. Ghomashchi, M. Lazdunski, M. H. Gelb, G. Lambeau. 2000. Cloning and recombinant expression of human group IIF-secreted phospholipase A2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 279:223–228
Valentin E., F. Ghomashchi, M. Gelb, M. Lazdunski, G. Lambeau. 2000. Novel human secreted phospholipase A2 with homology to the group III bee venom enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 275:7492–7496
Clark J. D., L. Lin, R. W. Kriz, C. S. Ramesha, L. A. Sultzman, A. Y. Lin, N. Milona, J. L. Knopf. 1991. A novel arachidonic acid-selective cytosolic PLA2 contains a Ca2+-dependent translocation domain with homology to PKC and GAP. Cell 65:1043–4051
Pickard T. R., B. A. Strifler, R. M. Kramer, J. D. Sharp. 1999. Molecular cloning of two new human paralogs of 85-kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 274:8823–8831
Underwood K. W., C. Song, R. W. Kriz, X. J. Chang, J. L. Knopf, L.-L. Lin. 1998. A novel calcium-independent phospholipase A2, cPLA2-γ, that is prenylated and contains homology to cPLA2. J. Biol. Chem. 273:21926–21932
Chen J., S. J. Engle, J. J. Seilhamer, J. A. Tischfield. 1994. Cloning and recombinant expression of a novel human low molecular weight Ca2+-dependent phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 269:2365–2368
Larsson P. K. A., H. E. Claesson, B. P. Kennedy. 1998. Multiple splice variants of the human calcium-independent phospholipase A2 and their effect on enzyme activity. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 207–214
Mancuso D. J., C. M. Jenkins, R. W. Gross. 2000. The genomic organization, complete mRNA sequence, cloning, and expression of a novel human intracellular membrane-associated calcium-independent phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 275: 9937–9945
Tanaka H., R. Takeya, H. Sumimoto. 2000. A novel intracellular membrane-bound calcium-independent phospholipase A2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 272:320–326
Tjoelker L., C. Wilder, C. Eberhardt, D. Stafforini, G. Dietsch, B. Schimpf, S. Hooper, H. Trong, L. Cousens, G. Zimmerman, Y. Yamada, T. McIntyre, S. Prescott, P. Gray. 1995. Anti-inflammatory properties of a platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase. Nature 374:549–553
Tew D., C. Southan, S. Rice, M. Lawrence, H. Li, H. Boyd, K. Moores, I. Gloger, C. Macphee. 1996. Purification, properties, sequencing, and cloning of a lipoprotein-associated, serine-dependent phospholipase involved in the oxidative modification of low-density lipoproteins. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 16:591–599
Hattori K., H. Adachi, A. Matsuzawa, K. Yamomoto, M. Tsujimoto, J. Aoki, M. Hattori, H. Arai, K. Inoue. 1996. cDNA cloning and expression of intracellular platelet-activating factor (PAF) acetylhydrolase II. J. Biol. Chem. 271:33032–33038
Adachi H., M. Tsjuimoto, M. Hattori, H. Arai, K. Inoue. 1995. cDNA cloning of human cytosolic platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase γ-subunit and its mRNA expression in human tissues. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 214:180–187
Adachi H., M. Tsujimoto, M. Hattori, H. Arai, K. Inoue. 1997. Differential tissue distribution of the β- and γ-subunits of human cytosolic platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase (isoform I). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 233:10–13
Cupillard L., K. Koumanov, M. G. Mattéi, M. Lazdunski, G. Lambeau. 1997. Cloning, chromosomal mapping, and expression of a novel human secretory phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 272:15745–15752
Gelb M. H., E. Valentin, F. Ghomaschi, M. Lazdunski, G. Lambeau. 2000. Cloning and recombinant expression of a structurally novel human secreted phospholipase A2. J. Biol. Chem. 275:39823–39826
Rouault M., J. G. Bollinger, M. Lazdunski, M. H. Gelb, G. Lambeau. 2003. Novel mammalian group XII secreted phospholipase A2 lacking enzymatic activity. Biochemistry 42: 11494–11503
Dennis E. A. 1997. The growing phospholipase A2 superfamily of signal transduction enzymes. Trends Biochem. Sci. 22:1–2
Balsinde J., M. A. Balboa, P. A. Insel, E. A. Dennis. 1999. Regulation and inhibition of phospholipase A2. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 39:175–189
Wu T., S. J. Levine, M. Cowan, C. Logun, W. C. Angus, J. H. Shelhamer. 1997. Antisense inhibition of 85-kDa cPLA2 blocks arachidonic acid release from airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. 273:L331–L338
Wu T., S. J. Levine, M. G. Lawrence, C. Logun, W. Angus, J. H. Shelhamer. 1994. Interferon-γ induces the synthesis and activation of cytosolic phospholipase A2. J. Clin. Invest. 93:571–577
Kaiser E. 1999. Phospholipase A2: its usefulness in laboratory diagnostics. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 36:65–163
Peilot H., B. Rosengren, G. Bondjers, E. Hurt-Camejo. 2000. Interferon-gamma induces secretory group IIA phospholipase A2 in human arterial smooth muscle cells. Involvement of cell differentiation, STAT-3 activation, and modulation by other cytokines. J. Biol. Chem. 275:22895–22904
Lindbom J., A. G. Ljungman, M. Lindahl, C. Tagesson. 2002. Increased gene expression of novel cytosolic and secretory phospholipase A2 types in human airway epithelial cells induced by tumor necrosis factor-α and IFN-γ. J. Interferon. Cytokine. Res. 22:947–955
Van Cauwenberge P. B. 1997. Nasal sensitization. Allergy 52:7–9
Lindbom J., A. G. Ljungman, M. Lindahl, C. Tagesson. 2001. Expression of members of the phospholipase A2 family of enzymes in human nasal mucosa. Eur. Respir. J. 18:130–138
Gantner F., R. Kupferschmidt, C. Schudt, A. Wendel, A. Hatzelmann. 1997. In vitro differentiation of human monocytes to macrophages: change of PDE profile and its relationship to suppression of tumour necrosis factor-alpha release by PDE inhibitors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 121:221–231
Hammerstrom J. 1979. Human macrophage differentiation in vivo and in vitro. A comparison of human peritoneal macrophages and monocytes. Acta Pathol. Microbiol. Scand. C. 87: 113–120
Nii A., S. Sone, E. Orino, T. Ogura. 1993. Induction of a 26-kDa membrane-form tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in human alveolar macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 53:29–36
Murakami M., K. Yoshihara, S. Shimbara, M. Sawada, N. Inagaki, H. Nagai, M. Naito, T. Tsuruo, T. C. Moon, H. W. Chang, I. Kudo. 2002. Group IID heparin-binding secretory phospholipase A(2) is expressed in human colon carcinoma cells and human mast cells and up-regulated in mouse inflammatory tissues. Eur. J. Biochem. 269:2698–2707
Siebenlist U., G. Franzoso, K. Brown. 1994. Structure, regulation and function of NF-kappa B. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 10:405–455
Kumar A., J. Haque, J. Lacoste, J. Hiscott, B. R. Williams. 1994. Double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase activates transcription factor NF-kappa B by phosphorylating I kappa B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 91:6288–6292
Velasco M., M. J. Diaz-Guerra, P. Martin-Sanz, A. Alvarez, L. Bosca. 1997. Rapid up-regulation of IkappaBbeta and abrogation of NF-kappaB activity in peritoneal macrophages stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. J. Biol. Chem. 272:23025–23030
Yamazaki S., T. Muta, K. Takeshige. 2001. A novel IkappaB protein, IkappaB-zeta, induced by proinflammatory stimuli, negatively regulates nuclear factor-kappaB in the nuclei. J. Biol. Chem. 276:27657–27662
Muta T., S. Yamazaki, A. Eto, M. Motoyama, K. Takeshige. 2003. IkappaB-zeta, a new anti-inflammatory nuclear protein induced by lipopolysaccharide, is a negative regulator for nuclear factor-kappaB. J. Endotoxin. Res. 9:187–191
Murakami M., K. Yoshihara, S. Shimbara, M. Sawada, N. Inagaki, H. Nagai, M. Naito, T. Tsuruo, T. C. Moon, H. W. Chang, I. Kudo. 2002. Group IID heparin-binding secretory phospholipase A(2) is expressed in human colon carcinoma cells and human mast cells and up-regulated in mouse inflammatory tissues. Eur. J. Biochem. 269:2698–2707
Murakami M., R. S. Koduri, A. Enomoto, S. Shimbara, M. Seki, K. Yoshihara, A. Singer, E. Valentin, F. Ghomashchi, G. Lambeau, M. H. Gelb, I. Kudo. 2001. Distinct arachidonate-releasing functions of mammalian secreted phospholipase A2s in human embryonic kidney 293 and rat mastocytoma RBL-2H3 cells through heparan sulfate shuttling and external plasma membrane mechanisms. J. Biol. Chem. 276:10083–10096
Seeds M. C., D. L. Bowton, R. D. Hite, J. I. Gyves, D. A. Gyves. 2003. Human eosinophil group IID secretory phospholipase A2 causes surfactant dysfunction. Chest 123:376S–377S
Koduri R. S., J. O. Gronroos, V. J. Laine, C. Le Calvez, G. Lambeau, T. J. Nevalainen, M. H. Gelb. 2002. Bactericidal properties of human and murine groups I, II, V, X, and XII secreted phospholipases A(2). J. Biol. Chem. 277:5849–5857
Schreck R., B. Meier, D. N. Mannel, W. Droge, P. A. Baeuerle. 1992. Dithiocarbamates as potent inhibitors of nuclear factor kappa B activation in intact cells. J. Exp. Med. 175:1181–1194
Schreck R., R. Grassmann, B. Fleckenstein, P. A. Baeuerle. 1992. Antioxidants selectively suppress activation of NF-kappa B by human T-cell leukemia virus type I Tax protein. J. Virol. 66:6288–6293
Guha M., N. Mackman. 2002. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase–Akt pathway limits lipopolysaccharide activation of signaling pathways and expression of inflammatory mediators in human monocytic cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277:32124–32132
Rosenberger C. M., B. B. Finlay. 2003. Phagocyte sabotage: disruption of macrophage signaling by bacterial pathogens. Nat. Rev., Mol. Cell Biol. 4:385–396
Wu T., T. Ikezono, C. W. Angus, J. H. Shelhamer. 1994. Characterization of the promoter for the human 85 kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 22:5093–5098
Morri H., M. Ozaki, Y. Watanabe. 1994. 5′-Flanking region surrounding a human cytosolic phospholipase A2 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 205:6–11
Ikezono T., T. Wu, X. L. Yao, S. Levine, C. Logun, W. C. Angus, J. H. Shelhamer. 1997. Leukemia inhibitory factor induces the 85-kDa cytosolic phospholipase A2 gene expression in cultured human bronchial epithelial cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1355:121–130
Dolan-O'Keefe M., V. Chow, J. Monnier, G. A. Visner, H. S. Nick. 2000. Transcriptional regulation and structural organization of the human cytosolic phospholipase A(2) gene. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 278:L649–L657
Blaine S. A., M. Wick, C. Dessev, R. A. Nemenoff. 2001. Induction of cPLA2 in lung epithelial cells and non-small cell lung cancer is mediated by Sp1 and c-Jun. J. Biol. Chem. 276:42737–42743
Gutcher I., P. R. Webb, N. G. Anderson. 2003. The isoform-specific regulation of apoptosis by protein kinase C. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 60:1061–1070
Matte C., G. Maion, W. Maurad, M. Olivier. 2001. Leishmania donovani-induced macrophages cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin E2 synthesis. Parasite Immunol. 23:177–184
Rao K. M. 2001. MAP kinase activation in macrophages. J. Leukoc. Biol. 69:3–10
Wright S. D., R. A. Ramos, P. S. Tobias, R. J. Ulevitch, J. C. Mathison. 1990. CD14, a receptor for complexes of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and LPS binding protein. Science 249:1431–1433
Hoshino K., O. Takeuchi, T. Kawai, H. Sanjo, T. Ogawa, Y. Takeda, K. Takeda, S. Akira. 1999. Cutting edge: Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-deficient mice are hyporesponsive to lipopolysaccharide: evidence for TLR4 as the LPS gene product. J. Immunol. 162:3749–3752
Andreani M., J. L. Olivier, F. Berenbaum, M. Raymondjean, G. Bereziat. 2000. Transcriptional regulation of inflammatory secreted phospholipases A(2). Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1488: 149–158
Roy S. K., S. J. Wachira, X. Weihua, J. Hu, D. V. Kalvakolanu. 2000. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-beta regulates interferon-induced transcription through a novel element. J. Biol. Chem. 275:12626–12632
Salmenpera P., S. Hamalainen, M. Hukkanen, E. Kankuri. 2003. Interferon-gamma induces C/EBP beta expression and activity through MEK/ERK and p38 in T84 colon epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 284:C1133–C1139
Gillies S. D., S. L. Morrison, V. T. Oi, S. Tonegawa. 1983. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell 33:717–728
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindbom, J., Ljungman, A.G. & Tagesson, C. Interferon γ-Induced Gene Expression of the Novel Secretory Phospholipase A2 Type IID in Human Monocyte-Derived Macrophages is Inhibited by Lipopolysaccharide. Inflammation 29, 108–117 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-006-9007-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-006-9007-x