Abstract
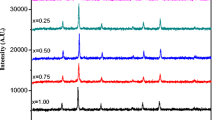
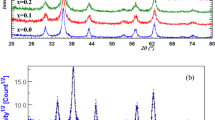
Nano size Mg x Co1 − x Fe2O4 (x = 0, 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8 and 1.0) ferrites have been prepared using sol gel method and characterized using i.r., TEM, XRD, magnetic and Mössbauer spectral studies. The particle size of as obtained samples was found to be ~6 nm, which increases up to ~80 nm after annealing at 1,000°C. The saturation magnetization decreases from 80.0–27.5 emu/g on increasing the Mg2 + ions after annealing at 1,000°C due to the diamagnetic behaviour of the Mg2 + ions. Room temperature (RT) Mössbauer spectra (MS) of as obtained samples exhibit a broad doublet, suggesting super paramagnetic nature of the sample. However, annealed samples exhibited a broad sextet, resolved into two sextets, corresponding to tetrahedrally and octahedrally coordinated Fe cations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Corless, L.M., Hasting, J.M.: A neutron diffraction study of magnesium ferrite. Phys. Rev. 90, 1013–1018 (1953)
Sagar, D.R., Parkash, C., Kishan, B.: Cation distribution in germanium substituted magnesium ferrites. Solid State Commun. 68, 193–195 (1988)
Kawade, V.B., Bichile, G.K., Jadhav, K.M.: X-ray and infrared studies of chromium substituted magnesium ferrite. Mater. Lett. 42, 33–37 (2000)
Berchmans, L.J., Selvan, R.K., Kumar, P.N.S., Augustin, C.O.: Structural and electrical properties of Ni1 − x Mg x Fe2O4 synthesized by citrate gel process. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 279, 103–110 (2004)
Pardeep, A., Chandrasekaran, G.: FTIR study of Ni, Cu and Zn substituted nano-particles of MgFe2O4. Mater. Lett. 60, 371–374 (2006)
Singhal, S., Garg, A.N., Chandra, K.: Evolution of the magnetic properties during the thermal treatment of nanosize BaMFe11O19 (M=Fe, Co, Ni and Al) obtained through aerosol route. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 285, 193–198 (2005)
Singhal, S., Barthwal, S.K., Chandra, K.: Preparation and characterization of nanosize nickel-substituted cobalt ferrites (Co1 − x Ni x Fe2O4). J. Solid State Chem. 178, 3183–3189 (2005)
Toledo, J.A., Valenzuela, M.A., Bosch, P., Armendariz, H., Montoya, A., Nava, N., Vazquez, A.: Effect of AI3 + introduction into hydrothermally prepared ZnFe2O4. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 198, 235–245 (2000)
Kools, F., Hanket, B.: Proc. ICF-5. 1, 417 (1989)
Verma, A., Goel, T.C., Mendiratta, R.G., Kishan, P.: Magnetic properties of nickel–zinc ferrites prepared by the citrate precursor method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 208, 13–19 (2000)
Ying, J.Y., Wang, G.H., Fuchs, H., Laschinsk, R., Gleiter, H.: STM/AFM study of grain boundary migration in nanostructured solids. Mater. Lett. 15, 180–185 (1992)
Dumesic, J.A., Topsoe, H.: Adv. Catal. 26, 121–246 (1977)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandra, K., Singhal, S. & Goyal, S. Magnetic and Mössbauer spectral studies of nano crystalline cobalt substituted magnesium ferrites (MgxCo1 − xFe2O4). Hyperfine Interact 183, 75–80 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-008-9761-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10751-008-9761-2