Abstract
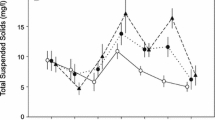
Shelter availability is one of the key features governing crayfish habitat quality. It can directly influence crayfish’s individual survival of by lowering the risk of predation, but the ecosystem-wide impacts of sheltering on water quality are largely unknown. To test the effects of shelter availability for Procambarus clarkii in clear-water macrophyte-dominated lakes, we performed a 24-day mesocosm experiment in 20 tanks (4 with one crayfish with and without shelters, 4 with two crayfish with and without shelters and 4 controls). The bottom of each tank was almost completely covered by the eelgrass Vallisneria denseserrulata. Compared with the treatments with shelters, more broken leaves occurred in the treatments without shelters at both crayfish densities at equivalent crayfish numbers, and total phosphorus was higher in the treatments without shelters. Total suspended solids and total nitrogen concentrations were higher in the treatments with two crayfish without shelters than in those with shelters, whilst these variables did not differ between treatments in the mesocosms with one crayfish only. Our results suggest that shelter availability reduces the activity of crayfish (e.g. movement and burrowing) and agonistic behaviour, thereby decreasing the negative effect of the invasive P. clarkii on water quality in V. denseserrulata-dominated clear-water lakes.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study are available in the supplementary material of this article.
References
Albertson, L. K. & M. D. Daniels, 2016. Effects of invasive crayfish on fine sediment accumulation, gravel movement, and macroinvertebrate communities. Freshwater Science 35(2): 644–653.
Alcorlo, P., M. Otero & W. Geiger, 2004. Feeding preferences and food selection of the red swamp crayfish, Procambarus clarkii, in habitats differing in food item diversity. Crustaceana 77: 435–453.
Angeler, D. G., S. Sanchez-Carrillo, G. Garcia & M. Alvarez-Cobelas, 2001. The influence of Procambarus clarkii (Cambaridae, Decapoda) on water quality and sediment characteristics in a Spanish floodplain wetland. Hydrobiologia 464: 89–98.
APHA, 1998. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. Americ Public Health Association, Washington DC.
Chambers, P. A., J. M. Hanson, J. M. Burke & E. E. Prepas, 1990. The impact of the crayfish Orconectes virilis on aquatic macrophytes. Freshwater Biology 24: 81–91.
Chen, L., Q. G. Ye, L. Z. Pan, L. M. Xu & W. Huang, 2008. Vallisneria species in lakes of the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River of China (in Chinese). Journal of Plant Ecology 32: 106–113.
China EPA, 2009. Water and wastewater monitoring and analysis methods, 4th ed. Chinese Environmental Science Press.
Cirujano, S., J. A. Camargo & C. Gómez-Cordovés, 2004. Feeding preference of the red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard) on living macrophytes in a Spanish wetland. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 19(2): 219–226.
Creed, R. P. & J. M. Reed, 2004. Ecosystem engineering by crayfish in a headwater stream community. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 23: 224–236.
Dai, A., 1983. Introduction of a kind of aquatic resource—Crayfish (in Chinese). Chinese Journal of Zoology 3: 51–53.
Figler, M. H., H. M. Cheverton & G. S. Blank, 1999. Shelter competition in juvenile red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii): the influences of sex differences, relative size, and prior residence. Aquaculture 178: 63–75.
Gao, J., C. Yang, Z. Zhang, Z. Liu & E. Jeppesen, 2021. Effects of co-occurrence of invading Procambarus clarkii and Pomacea canaliculata on Vallisneria denseserrulata-dominated clear-water ecosystems: a mesocosm approach. Knowledge & Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 422: 29.
Geiger, W., P. Alcorlo, A. Baltanas & C. Montes, 2005. Impact of an introduced crustacean on the trophic webs of Mediterranean wetlands. Biological Invasions 7: 49–73.
Gherardi, F., 2006. Crayfish invading Europe: the case study of Procambarus clarkii. Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology 39: 175–191.
Gherardi, F., 2007. Understanding the impact of invasive crayfish. In Gherardi, F. (ed), Biological Invaders in Inland Waters: Profiles, Distribution, and Threats Springer, Dordrecht: 507–542.
Gherardi, F. & A. Cioni, 2004. Agonism and interference competition in freshwater decapods. Behaviour 141: 1297–1324.
Gherardi, F. & P. Acquistapace, 2007. Invasive crayfish in Europe: the impact of Procambarus clarkii on the littoral community of a Mediterranean lake. Freshwater Biology 52: 1249–1259.
Gherardi, F., B. Renai & C. Corti, 2001. Crayfish predation on tadpoles: a comparison between a native (Austropotamobius pallipes) and an alien species (Procambarus clarkii). Knowledge Management of Aquatic Ecosystems 361: 659–668.
Harper, D. M., A. C. Smart, S. Coley, S. Schmitz, A. G. de Beauregard, R. North, C. Adams, P. Obade & M. Kamau, 2002. Distribution and abundance of the Louisiana red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii Girard at Lake Naivasha, Kenya between 1987 and 1999. Hydrobiologia 488: 143–151.
Haubrock, P. J., A. F. Inghilesi, G. Mazza, M. Bendoni, L. Solari & E. Tricarico, 2019. Burrowing activity of Procambarus clarkii on levees: analysing behaviour and burrow structure. Wetlands Ecology and Management 27: 497–511.
Hill, A. M. & D. M. Lodge, 1994. Diel changes in resource demand: competition and predation in species replacement among crayfishes. Ecology 75(7): 2118–2126.
Issa, F. A., D. J. Adamson & D. H. Edwards, 1999. Dominance hierarchy formation in juvenile crayfish Procambarus clarkii. Journal of Experimental Biology 202(24): 3497–3506.
Jiang, S., L. Pang & C. Huang, 2007. Hazards and control of exotic species, Procambarus clarkii (in Chinese). Bulletin of Biology 42(5): 15–16.
Kawai, T. & Y. Kobayashi, 2005. Origin and current distribution of the alien crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Girard, 1852) in Japan. Crustaceana 78(9): 1143–1149.
Korschgen, C. E., W. L. Green & K. P. Kenow, 1997. Effects of irradiance on growth and winter bud production by Vallisneria americana and consequences to its abundance and distribution. Aquatic Botany 58: 1–9.
Li, Z. Q., Y. Dan & M. H. Tu, 2005. Seed germination of three species of Vallisneria (Hydrocharitaceae), and the effects of freshwater microalgae. Hydrobiologia 544: 11–18.
Liu, Z. W., J. R. Hu, P. Zhong, X. F. Zhang, J. J. Ning, S. E. Larsen, D. Y. Chen, Y. M. Gao, H. Hu & E. Jeppesen, 2018. Successful restoration of a tropical shallow eutrophic lake: strong bottom-up but weak top-down effects recorded. Water Research 146: 88–97.
Lodge, D. M. & J. G. Lorman, 1987. Reductions in submersed macrophyte biomass and species richness by the crayfish Orconectes rusticus. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 44: 591–597.
Lowery, R. S. & A. J. Mendes, 1977. Procambarus clarkii in Lake Naivasha, Kenya, and its effects on established and potential fisheries. Aquaculture 11(2): 111–121.
Martin, A. L., III. & P. A. Moore, 2010. Field observations of agonism in the crayfish, Orconectes rusticus: Shelter Use in a Natural Environment. Ethology 113(12): 1192–1201.
Mason, J. C., 1979. Effects of temperature, photoperiod, substrate and shelter on survival, growth and biomass accumulation of juvenile Pacifastacus leniusculus culture. Freshwater Crayfish 4: 73–82.
Matsuzaki, S. S., N. Usio, N. Takamura & I. Washitani, 2009. Contrasting impacts of invasive engineers on freshwater ecosystems: an experiment and meta-analysis. Oecologia 158(4): 673–686.
Moore, P. A., 2007. Agonistic behavior in freshwater crayfish: the influence of intrinsic and extrinsic factors on aggressive behavior and dominance. In Duffy, J. E. & M. Thiel (eds), Evolutionary Ecology of Social and Sexual Systems: Crustacea as Model Organisms Oxford University Press, Oxford: 90–114.
Nyström, P., O. Svensson, B. Lardner, C. Brönmark & W. Granéli, 2001. The influence of multiple introduced predators on a littoral pond community. Ecology 82: 1023–1039.
Oficialdegui, F. J., M. I. Sánchez & M. Clavero, 2020. One century away from home: how the red swamp crayfish took over the world. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 30: 121–135.
Ottolenghi, F., J. G. Qin & L. Mittiga, 2002. Enhancement of phosphorus release from lake sediments by aeration and crayfish activity. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 17(4): 635–640.
Parkyn, S. M., C. F. Rabeni & K. J. Collier, 1997. Effects of crayfish (Paranephrops planifrons parastacidae) on in-stream processes and benthic faunas: a density manipulation experiment. New Zealand Journal of Marine Freshwater Research 31: 685–692.
Penn, G. H., Jr., 1954. Introduction of American crawfishes into foreign lands. Ecology 35(2): 296.
Petrović, T. G., T. Z. Vŭcić, S. Z. Nikolić, J. P. Gavrić, S. G. Despotović, B. R. Gavrilović, T. B. Radovanović, C. Faggio & M. D. Prokić, 2020. The effect of shelter on oxidative stress and aggressive behavior in crested newt larvae (Triturus spp.). Animals 10(4): 603.
Rice, S. P., M. F. Johnson & I. Reid, 2012. Animals and the geomorphology of gravel-bed rivers. In Church, M., P. Biron & A. G. Roy (eds), Gravel-Bed Rivers: Processes, Tools, Environments Wiley, Chichester: 225–241.
Rodríguez, C. F., E. Bécares & M. Fernández-Alὰez, 2003. Shift from clear to turbid phase in Lake Chozas (NW Spain) due to the introduction of American red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii). Hydrobiologia 506: 421–426.
Roessink, I., R. Gylstra, P. Heuts & B. Specken, 2017. Impact of invasive crayfish on water quality and aquatic macrophytes in the Netherlands. Aquatic Invasions 12(3): 397–404.
Souty-Grosset, C., P. M. Anastacio, L. Aquiloni, F. Banha, J. Choquer, C. Chucholl & E. Tricarico, 2016. The red swamp crayfish Procambarus clarkii in Europe: impacts on aquatic ecosystems and human well-being. Limnologica 58: 78–93.
Statzner, B. & O. Peltret, 2006. Assessing potential abiotic and biotic complications of crayfish-induced gravel transport in experimental streams. Geomorphology 74: 245–256.
Statzner, B., E. Fièvet, J.-Y. Champagne, R. Morel & E. Herouin, 2000. Crayfish as geomorphic agents and ecosystem engineers: biological behavior affects sand and gravel erosion in experimental streams. Limnology and Oceanography 45(5): 1030–1040.
Statzner, B., O. Peltret & S. Tomanova, 2003. Crayfish as geomorphic agents and ecosystem engineers: effect of a biomass gradient on baseflow and flood-induced transport of gravel and sand in experimental streams. Freshwater Biology 48: 147–163.
Van der Wal, J. E. M., 2011. Effects of crayfish on the establishment of macrophytes in a shallow peat lake. Wageningen UR.
Van der Wal, J. E. M., M. Dorenbosch, A. K. Immers, C. V. Forteza, J. J. M. Geurts, E. T. H. M. Peeters, B. Koese & E. S. Bakker, 2013. Invasive crayfish threaten the development of submerged macrophytes in lake restoration. PLoS ONE 8: e78579.
Wang, W. M., 1999. The exploitation and utilization of red swamp crayfish in China (in Chinese). Acta Hydrobiologica Sinica 23(4): 375–381.
Wang, Q. F., Y. H. Guo, R. R. Haynes & C. B. Hellquist, 2010. Hydrocharitaceae. In Wu, Z. Y. & P. Raven (eds), Flora of China, Vol. 23. Science Press, Beijing: 91–102.
Watanabe, R. & S. Ohba, 2022. Comparison of the community composition of aquatic insects between wetlands with and without the presence of Procambarus clarkii: a case study from Japanese wetlands. Biological Invasions 24(4): 1033–1047.
Zeng, Z., H. Wu, Y. Jiang & G. Peng, 2013. Dynamics and impacts of invasion by exotic species to Poyang Lake national nature reserve (in Chinese). Energy Research and Management 4: 15–18.
Zhan, A., P. Ni, W. Xiong, Y. Chen, Y. Lin & X. Huang, 2016. Biological invasions in aquatic ecosystems in China. Chapter 4. In Wan, F. et al. (eds) Biological Invasions and its Management in China, Invading Nature Springer Series in Invasion Ecology, Vol. 11: 67–96.
Zhang, X. M., W. Zhen, H. S. Jensen, K. Reitzel, E. Jeppesen & Z. W. Liu, 2021. The combined effects of macrophytes (Vallisneria denseserrulata) and a lanthanum-modified bentonite on water quality of shallow eutrophic lakes: A mesocosm study. Environmental Pollution 277: 116720.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Anne Mette Poulsen and EditSprings for language assistance. This study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2020CFB537), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32170383), key scientific research project funding from the Hubei Provincial Water Resources Bureau (HBSLKY202014) and preliminary hydraulic research and consulting work of Hubei Water Resources Research Institute (P21800600002). EJ was supported by AQUACOSMplus (Network of Leading European AQUAtic MesoCOSM Facilities Connecting Mountains to Oceans from the Arctic to the Mediterranean), AnaEE Denmark (anaee.dk) and the TÜBITAK program BIDEB 2232 (project 118C250).
Funding
Jian Gao was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Hubei Province (2020CFB537), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32170383), key scientific research project funding from the Hubei Provincial Water Resources Bureau (HBSLKY202014) and preliminary hydraulic research and consulting work of Hubei Water Resources Research Institute (P21800600002). Erik Jeppesen was supported by AQUACOSMplus (Network of Leading European AQUAtic MesoCOSM Facilities Connecting Mountains to Oceans from the Arctic to the Mediterranean), AnaEE Denmark (anaee.dk) and the TÜBITAK program BIDEB 2232 (project 118C250).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Dani Boix
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, J., Hu, S., Yang, C. et al. Shelter availability reduces the effects of the invasive Red Swamp Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii) on eelgrass-dominated clear-water lakes: a mesocosm approach. Hydrobiologia 849, 3597–3606 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-04969-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-022-04969-8