Abstract
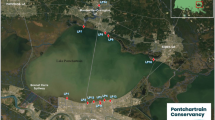
Laguna del Sauce is a eutrophic shallow lake and the second drinking water source in Uruguay. This ecosystem suffers recurrent blooms of potentially toxic nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria, mostly during summertime. Here we analyze environmental drivers and potential impacts of blooms of the toxic cyanobacteria Raphidiopsis raciborskii in Laguna del Sauce from 2003 to 2020, and assess its effects on governance and biomonitoring. We registered three blooms of R. raciborskii, in 2004, 2015, and 2020, the last two expressed saxitoxin (lack of toxicity information for 2004). The 2015 bloom occurred in autumn, reaching an absolute biovolume of 104 mm3 l−1, and had high saxitoxin concentrations (up to 9.8 μg l−1) which continued to be detected even after the bloom collapsed. This was the first saxitoxin register in this ecosystem and drastically affected the drinking water supply. After this massive bloom, a monitoring program was established which continues up to date. The 2020 bloom also occurred in autumn and lasted until winter; it was of lower magnitude (up to 6.3 mm3 l−1) and had lower saxitoxin concentration (up to 0.9 μg l−1) compared to the 2015 bloom. Blooms of R. raciborskii were associated with a combination of persistent low water level, low water color, and high water transparency, conditions that rarely coincide in this ecosystem. Hence, the programs which started after the 2015 bloom, allowed better characterizing the environmental drivers of R. raciborskii blooms in Laguna del Sauce. Furthermore, these implied adapting the ecosystem management and water treatment strategies, and strengthening of academia—stakeholders’ interactions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agawin, N. S. R., S. Rabouille, M. J. W. Veldhuis, S. Lidewij, S. Hol, H. M. J. van Overzee & J. Huisman, 2007. Competition and facilitation between unicellular nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria and non-nitrogen-fixing phytoplankton species. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 2233–2248.
Aguilera, A., E. B. Gómez, J. Kaštovský, R. O. Echenique & G. L. Salerno, 2018. The polyphasic analysis of two native Raphidiopsis isolates supports the unification of the genera Raphidiopsis and Cylindrospermopsis (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Phycologia 57(2): 130–146.
APHA, American Public Health Association, 1985. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. APHA/AWWA/WPCF, Washington D.C., USA.
Bakker, E. S. & S. Hilt, 2015. Impact of water-level fluctuations on cyanobacterial blooms: options for management. Aquatic Ecology 50: 485–498.
Biggs, R., M. Schlüter & M. L. Schoon (eds), 2015. Principles for building resilience. Sustaining ecosystem services in social-ecological systems. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Bonilla, S., 2009. Cianobacterias planctónicas del Uruguay. Manual para la identificación y medidas de monitoreo. Montevideo: UNESCO. PHI-VII (Documento técnico, 16).Bouvy, M., M. Pagano, & M.Troussellier, 2001. Effects of a cyanobacterial bloom (Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii) on bacteria and zooplankton communities in Ingazeira reservoir (northeast Brazil). Aquatic Microbial Ecology, 25(3):215–227.
Bonilla, S., L. Aubriot, M. C. Soares, M. González-Piana, A. Fabre, V. L. M. Huszar, M. Lürling, D. Antoniades, J. Padisák & C. Kruk, 2012. What drives the distribution of the bloom-forming cyanobacteria Planktothrix agardhii and Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii?, FEMS Microbiology Ecology, Volume 79, Issue 3, March 2012, Pages 594–607,
Brandenburg, K., L. Siebers, J. Keuskamp, T. G. Jephcott & D. B. Van de Waal, 2020. Effects of nutrient limitation on the synthesis of N-rich phytoplankton toxins: a meta-analysis. Toxins 12(4): 221.
Brasil, J., J. L. Attayde, F. R. Vasconcelos, D. D. F. Dantas & V. L. M. Huszar, 2016. Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 770: 145–164.
Briand, J. F., C. Leboulanger, J. F. Humbert, C. Bernard & P. Dufour, 2004. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) invasion at mid-latitudes: selection, wide physiological tolerance, or global warming Journal of Phycology 40(2): 231–238.
Burford, M. A., J. Beardall, A. Willis, P. T. Orr, V. F. Magalhaes, L. M. Rangel, S. Azevedo & B. A. Neilan, 2016. Understanding the winning strategies used by the bloom-forming cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Harmful Algae 54: 44–53.
Chapin, III F.S., C. Folke & G. P. Kofinas, 2009. A framework for Understanding Change. In: Chapin III F. S., C. Folke & G. P. Kofinas (eds), Principles of Ecosystem Stewardship, Resilience-Based Natural Resource Management in a Changing World. Springer, Berlin: 3–28.
Chonudomkul, D., W. Yongmanitchai, G. Theeragool, M. Kawachi, F. Kasai, K. Kaya & M. M. Watanabe, 2004. Morphology, genetic diversity, temperature tolerance and toxicity of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) strains from Thailand and Japan. FEMS Microbiology Ecology 48(3): 345–355.
Chorus, I. & J. Bartram, 1999. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring, and Management. World Health Organization. E & FN Spon, London
Chorus, I. & Welker, M., 2021. Toxic Cyanobacteria in Water: A Guide to Their Public Health Consequences, Monitoring and Management. Taylor & Francis, Milton Park: 858.
Costa, M. R. A., J. L. Attayde & V. Becker, 2016. Effects of water level reduction on the dynamics of phytoplankton functional groups in tropical semi-arid shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 778: 75–89.
Crisci, C., R. Terra, J. P. Pacheco, B. Ghattas, M. Bidegain, G. Goyenola, J. J. Lagomarsino, G. Méndez & N. Mazzeo, 2017a. Multi-model approach to predict phytoplankton biomass and composition dynamics in a eutrophic shallow lake governed by extreme meteorological events. Ecological Modelling 360: 80–93.
Crisci, C., G. Goyenola, R. Terra, J.J. Lagomarsino, JP Pacheco, I. Díaz, L. González-Madina, P. Levrini, G. Méndez, M. Bidegain, G. Ghattas & N. Mazzeo, 2017b. Dinámica ecosistémica y calidad de agua: estrategias de monitoreo para la gestión de servicios asociados a Laguna del Sauce (Maldonado, Uruguay). INNOTEC: 46–57.
Dolman, A.M., J. Rücker, F.R. Pick, J. Fastner, T. Rohrlack, U. Mischke & C. Widner, 2012. Cyanobacteria and Cyanotoxins: The Influence of Nitrogen versus Phosphorus. PLoS ONE 7: e38757
Fabre, A., C. Carballo, E. Hernandez, P. Piriz, L. Bergamino, L. Mello, S. González, G. Pérez, J. G. León, L. Aubriot, S. Bonilla & C. Kruk, 2010. El nitrógeno y la relación zona eufótica/zona de mezcla explican la presencia de cianobacterias en pequeños lagos subtropicales, artificiales de Uruguay. Pan-American Journal of Aquatic Sciences 5: 112–125.
Folke, C., 2016. Resilience (Republished). Ecology and Society 21(4): 44.
Gobler, C. J., J. M. Burkholder, T. W. Davis, M. J. Harke, T. Johengen, C. A. Stow & D. B. Van de Waal, 2016. The dual role of nitrogen supply in controlling the growth and toxicity of cyanobacterial blooms. Harmful Algae 54: 87–97.
González-Madina, L., J. P. Pacheco, N. Mazzeo, P. Levrini, J. M. Clemente, J. J. Lagomarsino & C. Fosalba, 2017. Factores ambientales controladores del fitoplancton con énfasis en las cianobacterias potencialmente tóxicas en un lago somero utilizado como fuente de agua para potabilización: Laguna del Sauce, Maldonado, Uruguay. INNOTEC 13: 26–35.
González-Madina, L., J. P. Pacheco, L. Yema, P. de Tezanos, P. Levrini, J. Clemente, C. Crisci, J. J. Lagomarsino, G. Méndez, C. Fosalba, G. Goyenola & N. Mazzeo, 2018. drivers of cyanobacteria dominance, composition and nitrogen fixing behavior in a shallow lake with alternative regimes in time and space, Laguna del Sauce (Maldonado, Uruguay). Hydrobiologia 829: 61–76.
Guillard, R. L., 1978. Counting slides. In Sournia, A. (ed), Phytoplankton manual UNESCO, Paris: 182–189.
Hammer, Ø. & D. A. T. Harper, 2006. Paleontological Data Analysis. Blackwell, Oxford
Hillebrand, H., C. D. Durselen, D. Kirschtel, U. Pollingher & T. Zohary, 1999. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. Journal of Phycology 35: 403–424.
Inda, H. & M. Steffen, 2010. Bases técnicas para el manejo integrado de Laguna del Sauce y cuenca asociada.Universidad de la República y South American Institute for resilience and Sustainability Studies, Uruguay. ISBN 978-9974-0-0694-2.
INE 2011. Censo poblacional del Instituto Nacional de Estadística. http://www.ine.gub.uy/web/guest/censos-2011
Izaguirre, I., M. L. Sánchez, M. R. Schiaffino, I. O´Farrel, P. Huber. N. Ferrer. J. Zunino, L. Lagomarsino & M. Mancini, 2015. Which environmental factors trigger the dominance of phytoplankton species across a moisture gradient of shallow lakes? Hydrobiologia 752: 47–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-014-2007-1.
Jacobsen, B. A. & P. Simonsen, 1993. Disturbance events affecting phytoplankton biomass, composition and species diversity in a shallow, eutrophic, temperate lake. Hydrobiologia 249(1): 9–14.
Jespersen, A. M. & K. Christoffersen, 1987. Measurements of chlorophyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie 109(3): 445–454.
Khan, F. A. & A. A. Ansari, 2005. Eutrophication: an ecological vision. The Botanical Review 71(4): 449–482.
Koroleff, F., 1970. Direct determination of ammonia in natural water as indophenol-blue. International Conference in the Exploration of the Sea. C.M 1969/C9. ICES. Information on techniques and methods for sea water analysis. Interlab Reports 3: 19–22.
Litchman, E., P. de Tezanos Pinto, C. A. Klausmeier, M. K. Thomas & K. Yoshiyama, 2010. Linking traits to species diversity and community structure in phytoplankton. Hydrobiologia 653: 15–38.
Lund, J., C. Kipling & E. Le Cren, 1958. The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and statistical basis of estimating by counting. Hydrobiologia 11: 143–170.
Lürling, M., F. Eshetu, E. J. Faassen, S. Kosten & V. L. Huszar, 2013. Comparison of cyanobacterial and green algal growth rates at different temperatures. Freshwater Biology 58(3): 552–559.
Margalef, R., 1978. Life forms of phytoplankton as survival alternatives in an unstableenvironment. Oceanologica Acta 1: 493–509.
Mazzeo, N., F. García-Rodríguez, A. Rodríguez, G. Méndez, C. Iglesias, H. Inda, G. Goyenola, S. García, C. Fosalba, S. Marroni, C. Crisci, L. Del Puerto, J. M. Clemente, J. P. Pacheco, C. Carballo, A. Kroeger, M. Vianna, M. Meerhoff, M. Steffen, J. J. Lagomarsino, M. Masdeu, N. Vidal, F. Texeira de Mello, I. González & D. Larrea, (2010). Estado trófico de Laguna del Sauce y respuestas asociadas. In Inda, H. & M. Steffen (eds), Bases técnicas para el manejo integrado de Laguna del Sauce y cuenca asociada. Montevideo, Uruguay: 31–49. ISBN 978–9974–0–0694–2.
Mazzeo, N., M. Trimble, L. Garrido, P. De Tezanos, R. Terra, C. Zurbriggen, H. Inda, C. Crisci, J.P Pacheco, L. González-Madina, P. Levrini, I. Gadino, M. Steffen & P. Bianchi, 2018. Aportes al Plan Director de Agua y Saneamiento de OSE para el departamento de Maldonado, Uruguay. Reporte Técnico en el marco del Convenio de Cooperación OSE-SARAS, Maldonado.
Mazzeo, N., C. Zurbriggen, M. Steffen, J. Barquín, I. Gadino, I. Díaz, A.L Ciganda, G. Goyenola & M. Trimble, 2019. Descentralización y centralización en la gestión del agua en Uruguay. In: Descentralización en Uruguay. Propuestas para avanzar en la agenda. Cardarello A & Ferla P (coordinadores). Konrad-Adenauer-Stiftung e.V. Fundación Konrad- Adenauer Oficina Uruguay. pp: 59–72.
Mehnert, G., F. Leunert, S. Cires, K. D. Johnk & J. Rucker, 2010. Competitiveness of invasive and native cyanobacteria from temperate freshwaters under various light and temperature conditions. Journal of Plankton Research 32: 1009–1021.
Miller, R., R. Poli, P. Rossel, & N. Simard, 2018. Transforming the Future, Anticipation in the 21st Century. Routledge-UNESCO Co-publication.
Moss, B., 2008. Water pollution by agriculture. Philosophical Transaction of Real Society: Series B 363: 659–666.
Moss, B., S. Kosten, M. Meerhoff, R. W. Battarbee, E. Jeppesen, N. Mazzeo, C. Havens, G. Lacerot, Z. Liu, L. De Meester, H. Paerl & M. Scheffer, 2011. Allied attack: climate change and eutrophication. Inland Waters 1: 101–105.
Müller, R. & O. Wiedemann, 1955. Die Bestimmung des Nitrations in Wasser. Von Wasser 22: 247–271.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Rilley, 1962. A modified single-solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Nusch, E. A., 1980. Comparison of methods of chlorophyll and phaeopigment determination. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 14: 14–36.
O'Farrell, I., M. L. Sánchez, M. R. Schiaffino, I. Izaguirre, P. Huber, L. Lagomarsino & L. Yema, 2021. Human impacted shallow lakes in the Pampean plain are ideal hosts for cyanobacterial harmful blooms. Environmental Pollution. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2021.117747.
O’Neil, J. M., T. W. Davis, M. A. Burford & C. J. Gobler, 2012. The rise of harmful cyanobacteria blooms: the potential roles of eutrophication and climate change. Harmful Algae 14: 313–334.
Pacheco, J. P., C. Iglesias, M. Meerhoff, C. Fosalba, G. Goyenola, F. Teixeira-de Mello, S. García, M. Gelós & F. García-Rodríguez, 2010. Phytoplankton community structure in five subtropical shallow lakes with different trophic status (Uruguay): a morphology-based approach. Hydrobiologia 646(1): 187–197.
Paerl, H. W. & J. Huisman, 2009. Climate change: a catalyst for global expansion of harmful cyanobacterial blooms. Environmental Microbiology Reports 1: 27–37.
Paerl, H. W., W. S. Gardner, K. E. Havens, A. R. Joyner, M. J. McCarthy, S. E. Newell & J. T. Scott, 2016. Mitigating cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms in aquatic ecosystems impacted by climate change and anthropogenic nutrients. Harmful Algae 54: 213–222.
Paerl, H. W., K. E. Havens, N. S. Hall, T. G. Otten, M. Zhu, H. Xu, G. Zhu & B. Qin, 2019. Mitigating a global expansion of toxic cyanobacterial blooms: confounding effects and challenges posed by climate change. Marine and Freshwater Research. https://doi.org/10.1071/MF18392.
Padisak, J., 1997. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Woloszyska) Seenayya et Subba Raju, an expanding, highly adaptive Cyanobacterium: worldwide distribution and review of its ecology. Archiv Für Hydrobiologie Supp 107: 563–593.
Padisák, J. & V. Istvánovics, 1997. Differential response of blue-green algal groups to phosphorus load reduction in a large shallow lake: Balaton, Hungary. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol. 26: 574–580.
Pahl-Wostl, C. 2015. Water Governance. Concepts, Methods, and Practice. Springer, Switzerland
Piccini, C., L. Aubriot, A. Fabre, V. Amaral, M. González-Piana, A. Gianni, C. C. Figueredo, L. Vidal, C. Kruk & S. Bonilla, 2011. Genetic and eco-physiological differences of South American Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii isolates support the hypothesis of multiple ecotypes. Harmful Algae 10: 644–653.
R Core Team. 2013. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria.
Recknagel, F., P. T. Orr & H. Cao, 2014. Inductive reasoning and forecasting of population dynamics of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in three sub-tropical reservoirs by evolutionary computation. Harmful Algae 31: 26–34.
Reynolds, C. S., 2006. Ecology of phytoplankton, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Rockström, J., W.S..Noone, A. Persson, F.S. Chapin III, E. Lambin, T.M. Lenton, M. Scheffer, C. Folke, H.J. Schellnhuber & B. Nykvist,2009. Planetary boundaries: exploring the safe operating space for humanity. Ecology and Society 14(2).
Rodríguez, A., G. Méndez, S. Kausas, J. M. Clemente, A. Kroger & N. Mazzeo, 2010. Importancia de la carga externa e interna de nutrientes en el estado trófico de la Laguna del Sauce. In Inda, H. & M. Steffen (eds), Bases técnicas para el manejo integrado de Laguna del Sauce y cuenca asociada. Montevideo, Uruguay: 53–61.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Schindler, D. W., 2006. Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 356–363.
Schwaderer, A. S., K. Yoshiyama, P. de. Tezanos Pinto, N. G. Swenson, C. A. Klausmeier & E. Litchman, 2011. Eco-evolutionary patterns in light utilization traits and distributions of freshwater phytoplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 589–598.
Sinha, R., L. A. Pearson, T. W. Davis, M. A. Burford, P. T. Orr & B. A. Neilan, 2012. Increased incidence of Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii in temperate zones–is climate change responsible? Water Research 46(5): 1408–1419.
Somma, A. 2014. El papel de la luz y la temperatura en la dinámica de cianobacterias en un lago de uso recreativo. Tesis de grado. Universidad de la República (Uruguay). Facultad de Ciencias.
Trimble, M. & N. Mazzeo, 2020. Water governance for adaptation and resilience in the Anthropocene. In: Torres, P. H., P. R. Jacobi, F. Barbi & L. R. Gonçalves (eds).,Adaptation and public policies in the Sao Paulo macro metropolis: a science-policy approach. São Paulo: IEE-USP pp: 29–33
Trimble, M., P. Jacobi, T. Olivier, M. Pascual, C. Zurbriggen, L. Garrido & N. Mazzeo, 2021. Reconfiguring water governance for resilient social-ecological systems in South America. In: Plummer, R. & J. Baird (eds), Water Resilience. Management and Governance in Times of Change. Springer, Switzerland: 113–135.
Uhelinger, V., 1964. Étude statistique des méthodes de dénobrement planctonique. Archive De Science 17: 121–223.
Utermöhl, H., 1985. Zur Vervolkommung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Mitteilungen Der Internationale Vereiningung Fuer Theoretische and Angewandte Limnologie 9: 1–38.
Valderrama, J. C., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total N and total P in natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 1009–1022.
Vidal, L. & C. Kruk, 2008. Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii (Cyanobacteria) extends its distribution to Latitude 34°53’S: taxonomical and ecological features in Uruguayan eutrophic lakes. Panamerican Jorunal of Aquatic Science 3: 142–151.
Wurtsbaugh, W.A., H.W. Paerl & W.K. Dodds, 2019. Nutrients, eutrophication and harmful algal blooms along the freshwater to marine continuum. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews. https://doi.org/10.1002/wat2.1373
Yema, L., E. Litchman & P. de Tezanos Pinto, 2016. The role of heterocysts in the physiology and ecology of bloom forming harmful cyanobacteria. Harmful Algae 60: 131–138.
Acknowledgements
This contribution is the result of multiple research projects financed by the CSIC-Udelar and the ANII, as well as agreements between the CURE- Udelar and public institutions such as OSE-UGD, OSE and the Ministry of the Environment. In the article, contributions have been incorporated in two projects in full development: Process of construction of the integrated management of water resources in Uruguay, status of situation and controversies financed by the Global Water Partnership (GWP); Transforming water governance in South America: from reaction to adaptation and anticipation funded by the Inter-American Institute for Global Change Research (IAI) SGP-HW 056; Bases for the design of a national water resources monitoring system from the perspective of virtual basins (FSDA 1 2018 1 154610). LGM and PL were supported by postgraduate grants from ANII and CSIC-Udelar, respectively. NM is a member of the National System of Researchers (ANII).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Guest editors: José L. Attayde, Renata F. Panosso, Vanessa Becker, Juliana D. Dias & Erik Jeppesen / Advances in the Ecology of Shallow Lakes
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
González-Madina, L., Levrini, P., de Tezanos Pinto, P. et al. Blooms of toxic Raphidiopsis raciborskii in Laguna del Sauce (Uruguay): environmental drivers and impacts. Hydrobiologia 849, 4041–4058 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04783-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04783-8