Abstract
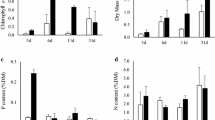
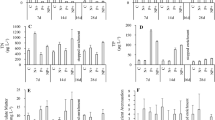
Periphyton development is generally negatively influenced by eutrophication in shallow lakes and reservoirs. To better understand the nutrient enrichment effect on the periphyton and how the changes in seston may interfere in community responses, we performed an experiment with combined and isolated N and P addition during the enrichment and no-enrichment period. Changes in biomass, nutrient content and N and P stoichiometry of periphyton and seston under enrichment were evaluated. Glass slides were used to assess periphyton responses in open-bottom mesocosms. Sampling was performed on the 7th, 14th and 28th day of experimental period. The isolated and combined P enrichment increased periphyton and seston chlorophyll-a on the 7th day, but only seston responded to isolated P addition on the 14th day. The isolated N addition had no significant effect on periphyton and seston chlorophyll-a. After interrupting the enrichment, there was high loss of biomass, changes in P content and a predominance of heterotrophic components in the periphyton. We conclude that periphyton responds rapidly to P enrichment, which has been identified as the primary limiting nutrient. However, periphyton was sensitive to changes in seston, which can interfere with nutrient availability, through nutrient interception, and light availability, through shading.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, J. M., 1976. An ignition method for determination of total phosphorus in lake sediments. Water Research 10: 329–331.
APHA, AWWA and WEF, 2012. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 22nd ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Bicudo, C. E. M., C. F. Carmo, D. C. Bicudo, R. Henry, A. C. S. Pião, C. M. Santos & M. R. M. Lopes, 2002. Morfologia e morfometria de três reservatórios do PEFI. In Bicudo, D. C., M. C. Forti & C. E. M. Bicudo (eds), Parque Estadual das Fontes do Ipiranga: unidade de conservação ameaçada pela urbanização de São Paulo. Editora Secretaria do Meio Ambiente do Estado de São Paulo, São Paulo: 141–158.
Borduqui, M. & C. Ferragut, 2012. Factors determining periphytic algae succession in a tropical hypereutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 683: 109–122.
Burkholder, J. M., 1996. Interactions of benthic algae with their substrata. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal Ecology: Freshwater Benthic Ecosystems. Academic, San Diego: 253–297.
Carlson, R. E., 1977. A trophic state index for lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 22: 361–369.
DeNicola, D. M. & M. Kelly, 2014. Role of periphyton in ecological assessment of lakes. Freshwater Science 33(2): 619–638.
Dodds, W. K., 2003. The role of periphyton in phosphorous retention in shallow freshwater aquatic systems. Journal of Phycology 39: 840–849.
Dunck, B., D. C. Amaral, U. L. Fernandes, N. F. Santana, T. M. Lopes & L. Rodrigues, 2018. Herbivory effects on the periphytic algal functional diversity in lake ecosystems: an experimental approach. Hydrobiologia 816: 231–241.
Engle, D. L. & J. M. Melack, 1993. Consequences of riverine flooding for seston and the periphyton of floating meadows in an Amazon floodplain lake. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 1500–1520.
Fanta, S. E., W. R. Hill, T. B. Smith & B. J. Roberts, 2010. Applying the light: nutrient hypothesis to stream periphyton. Freshwater Biology 55: 931–940.
Fermino, F. S., C. E. M. Bicudo & D. C. Bicudo, 2011. Seasonal influence of nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment on the floristic composition of the algal periphytic community in a shallow tropical, mesotrophic reservoir (São Paulo, Brazil). Oecologia Australis 15: 476–493.
Fonseca, B. M. & C. E. M. Bicudo, 2010. How important can the presence/absence of macrophytes be in determining phytoplankton strategies in two tropical shallow reservoirs with different trophic status? Journal of Plankton Research 32: 31–46.
Frost, P. C., H. Hillebrand & M. Kahlert, 2005. Low algal carbon content and its effect on the C:P stoichiometry of periphyton. Freshwater Biology 50: 1781–1785.
Gaiser, E. E., D. L. Childers, R. D. Jones, J. F. Richards, L. J. Scinto & J. C. Trexler, 2006. Periphyton responses to eutrophication in the Florida Everglades: cross-system patterns of structural and compositional change. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 617–630.
Golterman, H. L., R. S. Clymo & M. A. M. Ohmstad, 1978. Methods for Physical and Chemical Analysis of Freshwaters. International Biological Programmer. (Handbook, 8), 2ª ed. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford: 213p.
Guariento, R. D., L. S. Carneiro, A. Caliman, R. L. Bozelli & F. A. Esteves, 2011. How light and nutrients affect the relationship between autotrophic and heterotrophic biomass in a tropical black water periphyton community. Aquatic Ecology 45(4): 561–569.
Havens, K. E., T. L. East, R. H. Meeker & W. P. Davis, 1996. Phytoplankton and perifíton responses to in situ experimental nutrient enrichment in a shallow subtropical lake. Journal of Plankton Research 18(4): 551–556.
Hill, W. R., S. E. Fanta & B. J. Roberts, 2009. Quantifying phosphorus and light effects in stream algae. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 368–380.
Hill, W. R., B. J. Roberts, S. N. Francoeur & S. E. Fanta, 2011. Resource synergy in stream periphyton communities. Journal of Ecology 99: 454–463.
Hillebrand, H. & U. Sommer, 1999. The nutrient stoichiometry of benthic microalgal growth: Redfield proportions are optimal. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 440–446.
Hwang, S. J., K. E. Havens & A. D. Steinman, 1998. Phosphorus kinetics of planktonic and benthic assemblages in a shallow subtropical lake. Freshwater Biology 40(4): 729–745.
Jones, J. R., D. V. Obrecht, B. D. Perkins, M. F. Knowlton, A. P. Thorpe, S. Watanabe, & R. R. Bacon, 2008. Nutrients, seston, and transparency of Missouri reservoirs and oxbow lakes: an analysis of regional limnology. Lake and Reservoir Management 24: 155–180.
Kahlert, M. & K. Pettersson, 2002. The impact of substrate and lake trophy on the biomass and nutrient status of benthic algae. Hydrobiologia 486: 161–169.
Kahlert, M., A. T. Hasselrot, H. Hillebrand & K. Pettersson, 2002. Spatial and temporal variation in the biomass and nutrient status of epilithic algae in Lake Erken, Sweden. Freshwater Biology 47: 1–24.
Liboriussen, L. & E. Jeppesen, 2006. Structure, biomass, production and depth distribution of periphyton on artificial substratum in shallow lakes with contrasting nutrient concentrations. Freshwater Biology 51: 95–109.
Lock, M. A., R. R. Wallace, J. W. Costerton, R. M. Ventullo & S. E. Charlton, 1984. River epilithon: toward a structural–functional model. Oikos 42: 10–12.
Mackereth, F. J. H., J. Heron & J. F. Talling, 1978. Water Analysis: Some Revised Methods for Limnologists. Freshwater Biological Association, London: 121p.
Marker, A. F. H., H. Nusch, H. Rai & B. Riemann, 1980. The measurement of photosynthetic pigments in freshwaters and standardization of methods: conclusion and recommendations. Archiv für Hydrobiologie Beiheft Ergebnisse der Limnologie 14: 91–106.
Oliveira, D. E., C. Ferragut & D. C. Bicudo, 2010. Relationships between environmental factors, periphyton biomass and nutrient content in Garças Reservoir, a hypereutrophic tropical reservoir. Lakes and Reservoirs: Research and Management 15: 129–137.
Pellegrini, B. G., & C. Ferragut, 2018. Associations between epiphyton species composition and macrophyte diversity in a shallow tropical reservoir. Fundamental and Applied Limnology/Archiv für Hydrobiologie 191: 111–122.
Pompêo, M. L. M. & V. Moschini-Carlos, 2003. Macrófitas aquáticas e perifíton: aspectos ecológicos e metodológicos. RIMA/FAPESP, São Carlos.
Redfield, A. C., 1958. The biological control of chemical factors in the environment. American Scientist 46: 205–221.
Sanches, L. F., R. D. Guariento, A. Caliman, R. L. Bozelli & F. A. Esteves, 2011. Effects of nutrients and light on periphytic biomass and nutrient stoichiometry in a tropical black-water aquatic ecosystem. Hydrobiologia 669: 35–44.
Santos, S. A. M., T. R. Santos, M. S. Furtado, R. Henry & C. Ferragut, 2017. Periphyton nutrient content, biomass and algal community on artificial substrate: response to experimental nutrient enrichment and the effect of its interruption in a tropical reservoir. Limnology 19: 209–218.
Sartory, D. P. & J. U. Grobbelaar, 1984. Extraction of chlorophyll a from freshwater phytoplankton for spectrophotometric analysis. Hydrobiologia 114: 177–187.
Sekar, R., V. P. Venugopalan, K. V. K. Nair & V. N. R. Rao, 2002. Nutrients dynamics and successional changes in a lentic freshwater biofilm. Freshwater Biology 47: 1893–1907.
Singer, G. A. & T. J. Battin, 2007. Anthropogenic subsidies alter consumer-resource stoichiometry, biodiversity, and food chains. Ecological Applications 17: 376–389.
Solorzano, L., 1969. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnology and Oceanography 14: 799–801.
Stelzer, R. S. & G. A. Lamberti, 2001. Effects of N:P ratio and total nutrient concentration on stream periphyton community structure, biomass, and elemental composition. Limnology and Oceanography 46(2): 356–367.
Sterner, R. W., J. J. Elser, E. J. Fee, S. J. Guildford & T. H. Chrzanowski, 1997. The light:nutrient ratio in lakes: the balance of energy and materials affects ecosystem structure and process. The American Naturalist 150: 663–684.
Stevenson, R. J., 1996. An introduction to algal ecology in freshwater benthic habits. In Stevenson, R. J., M. L. Bothwell & R. L. Lowe (eds), Algal ecology: freshwater benthic ecosystems. Academic, San Diego: 253–297.
Strickland, J. D. H. & T. R. Parsons, 1960. A manual of seawater analysis. Bulletin of Fisheries Research Board of Canada 125: 1–185.
Trochine, C., M. Guerrieri, L. Liboriussen, P. Willems, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Søndergaard & E. Jeppesen, 2017. Factors controlling the stable isotope composition and C:N ratio of seston and periphyton in shallow lake mesocosms with contrasting nutrient loadings and temperatures. Freshwater Biology 62: 1596–1613.
Umbreit, W. W., R. H. Burris & J. F. Stauffer, 1964. Manometric Methods Applicable to the Study of Tissue Metabolism. Burgess Publishing Company, Minneapolis.
Vadeboncoeur, Y., J. Kalff, K. Christoffersen & E. Jeppesen, 2006. Substratum as a driver of variation in periphyton chlorophyll and productivity in lakes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25(2): 379–392.
Valderrama, G. C., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 109–112.
Wetzel R. G. & G. E. Likens, 1991. Limnological analyses. Springer, New York.
Wu, Y., J. Liu, & E. R. Rene, 2018. Periphytic biofilms: a promising nutrient utilization regulator in wetlands. Bioresource Technology 248: 44–48.
Zhang, X., X. Mei, R. D. Gulati & Z. Liu, 2015. Effects of N and P enrichment on competition between phytoplankton and benthic algae in shallow lakes: a mesocosm study. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 22: 4418–4424.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the FAPESP (Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo) for financial support (Grant nº 2009/52253-4) and for a PhD Scholarship to RWL, DAT and TRS (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior - CAPES, FAPESP Grant nº 2013/03130-2, respectively). We are grateful to all the students and technicians involved in the laboratory and fieldwork.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Judit Padisák
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambrecht, R.W., Tavares, D.A., Santos, T.R. et al. Responses of periphyton biomass and nutrient status to experimental enrichment and its relationships with changes in seston nutrient content and chlorophyll-a. Hydrobiologia 836, 141–153 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-3947-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-019-3947-2