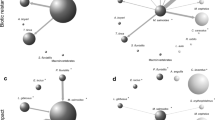
Abstract
Fish and invertebrates are introduced in freshwaters around the world for commercial purposes, despite widely known impacts on food webs and biological invasions. As a proxy for artificial environments, we modeled a typical reservoir in a Brazilian semiarid region using an ecosystem approach. We compared the role of native and non-native invasive species (NIS) in the food web, between dry and wet periods, and under the influence of an extreme drought period (from 2011 to 2015), simulating the variation in fish biomasses due to decreasing consumption. Key ecosystem groups were fishes (mainly NIS), birds, and insects. Nutrient cycling was dependent on invaders, while the trophic structure was detritus based during the drought. Biomass of detritivores was almost two times higher than herbivores, and native fish species decreased abruptly in response to invaders and volume variation. The dominance of low-trophic levels (TLII) and tilapia—Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus, 1758) and other tilapiines—resulted from interactions among invaders, feeding behavior on benthos, and environmental seasonality, tending toward biotic homogenization (“benthification”) at the ecosystem level. An increasing relevance of detritivores with cascading effects in ecosystems subject to drought, multiple introductions, and ubiquitous food sources has clear implications for the fisheries and the water quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agostinho, A. A., L. C. Gomes, N. C. L. Santos, J. C. G. Ortega & F. M. Pelicice, 2016. Fish assemblages in Neotropical reservoirs: colonization patterns, impacts and management. Fisheries Research 173: 26–36.
Ahrens, R. N. M., C. J. Walters & V. Christensen, 2012. Foraging arena theory. Fish and Fisheries 13: 41–59.
Angelini, R., N. N. Fabré & U. L. Silva-Júnior, 2006. Trophic analysis and fishing simulation of the biggest Amazonian catfish. Journal of Agricultural Research 1: 151–158.
Angelini, R., R. J. de Morais, A. C. Catella, E. K. Resende & S. Libralato, 2013. Aquatic food webs of the oxbow lakes in the Pantanal: a new site for fisheries guaranteed by alternated control? Ecological Modelling 253: 82–96.
Attayde, J. L., J. Brasil & R. A. Menescal, 2011. Impacts of introducing Nile tilapia on the fisheries of a tropical reservoir in North-eastern Brazil. Fisheries Management and Ecology 18: 437–443.
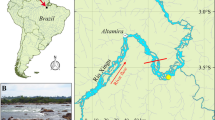
Barbosa, J. E. D. L., E. S. F. Medeiros, J. Brasil, R. D. S. Cordeiro, M. C. B. Crispim & G. H. G. Da Silva, 2012. Aquatic systems in semi-arid Brazil: limnology and management. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 24: 103–118.
Bezerra, L. A. V., W. D. Paulino, D. S. Garcez, H. Becker & J. I. Sánchez-Botero, 2014. Limnological characteristics of a reservoir in semiarid Northeastern Brazil subject to intensive tilapia farming (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus, 1758). Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 26: 47–59.
Blossey, B. & R. Notzold, 1995. Evolution of increased competitive ability in invasive nonindigenous plants—a hypothesis. Journal of Ecology 83: 887–889.
Brasil, J., J. L. Attayde, F. R. Vasconcelos, D. D. F. Dantas & V. L. M. Huszar, 2016. Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 770: 145–164.
Cai, Y., Y. Zhang, Z. Wu, Y. Chen, J. Xu & Z. Gong, 2017. Composition, diversity, and environmental correlates of benthic macroinvertebrate communities in the five largest freshwater lakes of China. Hydrobiologia 788: 85–98.
Chaparro, G., M. S. Fontanarrosa, D. Cataldo & I. O’Farrell, 2015. Hydrology driven factors might weaken fish predation effects on zooplankton structure in a vegetated warm temperate floodplain lake. Hydrobiologia 752: 187–202.
Christensen, V. & C. J. Walters, 2004. Ecopath with Ecosim: methods, capabilities and limitations. Ecological Modelling 172: 109–139.
Cirilo, J. A., S. M. G. L. Montenegro & J. N. B. Campos, 2017. The Issue of Water in the Brazilian Semi-Arid Region Waters of Brazil. Springer, Cham: 59–71.
Coll, M. & S. Libralato, 2012. Contributions of food web modelling to the ecosystem approach to marine resource management in the Mediterranean Sea. Fish and Fisheries 13: 60–88.
Conley, D. J., H. W. Paerl, R. W. Howarth, D. F. Boesch, S. P. Seitzinger, K. E. Havens, C. Lancelot & G. E. Likens, 2009. Controlling eutrophication: nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 323: 1014–1015.
Cury, P., 2000. Small pelagics in upwelling systems: patterns of interaction and structural changes in “wasp-waist” ecosystems. ICES Journal of Marine Science 57: 603–618.
D’Alelio, D., S. Libralato, T. Wyatt & M. Ribera d’Alcalà, 2016. Ecological-network models link diversity, structure and function in the plankton food-web. Scientific Reports 6: 21806.
Daga, V. S., F. Skóra, A. A. Padial, V. Abilhoa, É. A. Gubiani & J. R. S. Vitule, 2015. Homogenization dynamics of the fish assemblages in Neotropical reservoirs: comparing the roles of introduced species and their vectors. Hydrobiologia 746: 327–347.
Elliott, J. A., 2012. Is the future blue-green? A review of the current model predictions of how climate change could affect pelagic freshwater cyanobacteria. Water Research 46: 1364–1371.
Estes, J. A., J. Terborgh, J. S. Brashares, M. E. Power, J. Berger, W. J. Bond, S. R. Carpenter, T. E. Essington, R. D. Holt, J. B. C. Jackson, R. J. Marquis, L. Oksanen, T. Oksanen, R. T. Paine, E. K. Pikitch, W. J. Ripple, S. A. Sandin, M. Scheffer, T. W. Schoener, J. B. Shurin, A. R. E. Sinclair, M. E. Soule, R. Virtanen & D. A. Wardle, 2011. Trophic downgrading of planet earth. Science 333: 301–306.
Feroz Khan, M. & P. Panikkar, 2009. Assessment of impacts of invasive fishes on the food web structure and ecosystem properties of a tropical reservoir in India. Ecological Modelling 220: 2281–2290.
Finn, J. T., 1976. Measures of ecosystem structure and function derived from analysis of flows. Journal of Theoretical Biology 56: 363–380.
Frau, D., Y. Battauz & R. Sinistro, 2017. Why predation is not a controlling factor of phytoplankton in a Neotropical shallow lake: a morpho-functional perspective. Hydrobiologia 788: 115–130.
Gascuel, D. & D. Pauly, 2009. EcoTroph: modelling marine ecosystem functioning and impact of fishing. Ecological Modelling 220: 2885–2898.
González-Bergonzoni, I., E. Jeppesen, N. Vidal, F. Teixeira-de Mello, G. Goyenola, A. López-Rodríguez & M. Meerhoff, 2016. Potential drivers of seasonal shifts in fish omnivory in a subtropical stream. Hydrobiologia 768: 183–196.
Gozlan, R. E., 2008. Introduction of non-native freshwater fish: is it all bad? Fish and Fisheries 9: 106–115.
Gurevitch, J., 2006. Commentary on Simberloff (2006): meltdowns, snowballs and positive feedbacks. Ecology Letters 9: 919–921.
Gurevitch, J., G. A. Fox, G. M. Wardle & D. Taub, 2011. Emergent insights from the synthesis of conceptual frameworks for biological invasions. Ecology Letters 14: 407–418.
Heymans, J. J., M. Coll, S. Libralato, L. Morissette & V. Christensen, 2014. Global patterns in ecological indicators of marine food webs: a modelling approach. PLoS ONE 9: e95845.
Higgins, S. N. & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2010. What a difference a species makes: a meta–analysis of dreissenid mussel impacts on freshwater ecosystems. Ecological Monographs 80: 179–196.
Hulme, P. E., 2015. Invasion pathways at a crossroad: policy and research challenges for managing alien species introductions. Journal of Applied Ecology 52: 1418–1424.
Johnson, P. T., J. D. Olden & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2008. Dam invaders: impoundments facilitate biological invasions into freshwaters. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 6: 357–363.
Johnson, P. T. J., J. D. Olden, C. T. Solomon & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2009. Interactions among invaders: community and ecosystem effects of multiple invasive species in an experimental aquatic system. Oecologia 159: 161–170.
Karatayev, A. Y., D. Boltovskoy, D. K. Padilla & L. E. Burlakova, 2007. The invasive bivalves Dreissena polymorpha and Limnoperna fortunei: parallels, contrasts, potential spread and invasion impacts. Journal of Shellfish Research 26: 205–213.
Keane, R. M. & M. J. Crawley, 2002. Exotic plant invasions and the enemy release hypothesis. Trends in Ecology & Evolution Elsevier 17: 164–170.
Kovalenko, K. E., S. M. Thomaz & D. M. Warfe, 2012. Habitat complexity: approaches and future directions. Hydrobiologia 685: 1–17.
Lake, P. S., 2003. Ecological effects of perturbation by drought in flowing waters. Freshwater Biology 48: 1161–1172.
Leprieur, F., O. Beauchard, S. Blanchet, T. Oberdorff & S. Brosse, 2008. Fish Invasions in the world’s river systems: when natural processes are blurred by human activities. PLoS Biology 6: e28.
Letnic, M., J. K. Webb, T. S. Jessop, D. Florance & T. Dempster, 2014. Artificial water points facilitate the spread of an invasive vertebrate in arid Australia. Journal of Applied Ecology 51: 795–803.
Libralato, S., V. Christensen & D. Pauly, 2006. A method for identifying keystone species in food web models. Ecological Modelling 195: 153–171.
Lima, L. F. O., B. I. A. L. Brasil & M. J. Martins-Silva, 2013. Melanoides tuberculata (Müller, 1774): northeastern dispersal in the São Francisco Basin, Brazil. Check List 9: 162–164.
Mayer, C. M., L. E. Burlakova, P. Eklöv, D. Fitzgerald, A. Y. Karatayev, S. A. Ludsin, S. Millard, E. L. Mills, A. P. Ostapenya, L. G. Rudstam, B. Zhu & T. V. Zhukova, 2014. The benthification of freshwater lakes: exotic mussels turning ecosystems upside down. In Nalepa, T. F. & D. W. Schloesser (eds), Quagga and Zebra Mussels: Biology, Impacts, and Control, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Boca Raton: 575–586.
Mills, E. L., J. M. Casselman, R. Dermott, J. D. Fitzsimons, G. Gal, K. T. Holeck, J. A. Hoyle, O. E. Johannsson, B. F. Lantry, J. C. Makarewicz, E. S. Millard, I. F. Munawar, M. Munawar, R. O’Gorman, R. W. Owens, L. G. Rudstam, T. Schaner & T. J. Stewart, 2003. Lake Ontario: food web dynamics in a changing ecosystem (1970–2000). Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60: 471–490.
Molisani, M. M., H. D. S. Barroso, H. Becker, M. O. P. Moreira, C. A. G. Hijo, T. M. do Monte & G. H. Vasconcellos, 2010. Trophic state, phytoplankton assemblages and limnological diagnosis of the Castanhão Reservoir, CE, Brazil. Acta Limnologica Brasiliensia 22: 1–12.
Naylor, R. L., R. W. Hardy, D. P. Bureau, A. Chiu, M. Elliott, A. P. Farrell, I. Forster, D. M. Gatlin, R. J. Goldburg, K. Hua & P. D. Nichols, 2009. Feeding aquaculture in an era of finite resources. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106: 15103–15110.
Njiru, M., J. B. Okeyo-Owuor, M. Muchiri & I. G. Cowx, 2004. Shifts in the food of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in Lake Victoria, Kenya. African Journal of Ecology 42: 163–170.
Novaes, J. L. C., A. E. Freire, R. R. A. Amorim & R. S. Costa, 2015. Diagnosis of the artisanal fisheries in a brazilian semiarid reservoir [Diagnóstico da pesca artesanal em um reservatório do semiárido Brasileiro]. Boletim do Instituto de Pesca 41: 31–42.
Odum, E. P., 1969. The strategy of ecosystem development. Science 164: 262–270.
Ortega, J. C. G., H. F. Júlio, L. C. Gomes & A. A. Agostinho, 2015. Fish farming as the main driver of fish introductions in Neotropical reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 746: 147–158.
Padial, A. A., A. A. Agostinho, V. M. Azevedo-Santos, F. A. Frehse, D. P. Lima-Junior, A. L. B. Magalhães, R. P. Mormul, F. M. Pelicice, L. A. V. Bezerra, M. L. Orsi, M. Petrere-Junior & J. R. S. Vitule, 2017. The “Tilapia Law” encouraging non-native fish threatens Amazonian River basins. Biodiversity and Conservation 26: 243–246.
Paerl, H. W. & V. J. Paul, 2012. Climate change: links to global expansion of harmful cyanobacteria. Water Research 46: 1349–1363.
Paterson, G., S. A. Rush, M. T. Arts, K. G. Drouillard, G. D. Haffner, T. B. Johnson, B. F. Lantry, C. E. Hebert, D. J. McGoldrick, S. M. Backus & A. T. Fisk, 2014. Ecological tracers reveal resource convergence among prey fish species in a large lake ecosystem. Freshwater Biology 59: 2150–2161.
Peel, M. C., B. L. Finlayson & T. A. Mcmahon, 2007. Updated world map of the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. Hydrologycal Earth Systems Science Discussion 4: 439–473.
Pelicice, F. M., J. R. S. Vitule, D. P. Lima Junior, M. L. Orsi & A. A. Agostinho, 2014. A serious new threat to brazilian freshwater ecosystems: the naturalization of nonnative fish by decree. Conservation Letters 7: 55–60.
Pereira, L. S., L. F. C. Tencatt, R. M. Dias, A. G. de Oliveira & A. A. Agostinho, 2017. Effects of long and short flooding years on the feeding ecology of piscivorous fish in floodplain river systems. Hydrobiologia 795: 65–80.
Pinheiro, J., D. Bates, S. DebRoy, D. Sarkar, & The R Development Core Team, 2013. nlme: linear and nonlinear mixed effects models. R package version 3.1-113, 1–86.
Preston, D. L., J. S. Henderson & P. T. Johnson, 2012. Community ecology of invasions: direct and indirect effects of multiple invasive species on aquatic communities. Ecology 93: 1254–1261.
Radeloff, V. C., J. W. Williams, B. L. Bateman, K. D. Burke, S. K. Carter, E. S. Childress, K. J. Cromwell, C. Gratton, A. O. Hasley, B. M. Kraemer, A. W. Latzka, E. Marin-Spiotta, C. D. Meine, S. E. Munoz, T. M. Neeson, A. M. Pidgeon, A. R. Rissman, R. J. Rivera, L. M. Szymanski & J. Usinowicz, 2015. The rise of novelty in ecosystems. Ecological Applications 25: 2051–2068.
Rahel, F. J., 2007. Biogeographic barriers, connectivity and homogenization of freshwater faunas: it’s a small world after all. Freshwater Biology 52: 696–710.
Rodrigues-Filho, C. A. D. S., R. C. Gurgel-Lourenço, L. A. V. Bezerra, W. A. de Sousa, D. S. Garcez, S. M. Q. Lima, T. P. A. Ramos & J. I. Sánchez-Botero, 2016. Ichthyofauna of the humid forest enclaves in the tablelands of Ibiapaba and Araripe. Northeastern Brazil. Biota Neotropica 16: e20160273.
Saul, W.-C. & J. M. Jeschke, 2015. Eco-evolutionary experience in novel species interactions. Ecology Letters 18: 236–245.
Schwalb, A. N., D. Bouffard, L. Boegman, L. Leon, J. G. Winter, L. A. Molot & R. E. H. Smith, 2014. 3D modelling of dreissenid mussel impacts on phytoplankton in a large lake supports the nearshore shunt hypothesis and the importance of wind-driven hydrodynamics. Aquatic Sciences 77: 95–114.
Sena, A., C. Barcellos, C. Freitas & C. Corvalan, 2014. Managing the health impacts of drought in Brazil. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 11: 10737–10751.
Sih, A., D. I. Bolnick, B. Luttbeg, J. L. Orrock, S. D. Peacor, L. M. Pintor, E. Preisser, J. S. Rehage & J. R. Vonesh, 2010. Predator-prey naïveté, antipredator behavior, and the ecology of predator invasions. Oikos 119: 610–621.
Simberloff, D., 2006. Invasional meltdown 6 years later: important phenomenon, unfortunate metaphor, or both? Ecology Letters 9: 912–919.
Simberloff, D., 2011. How common are invasion-induced ecosystem impacts? Biological Invasions 13: 1255–1268.
Simberloff, D., 2015. Non-native invasive species and novel ecosystems. F1000prime Reports 7: 47.
Simberloff, D. & J. R. S. Vitule, 2014. A call for an end to calls for the end of invasion biology. Oikos 123: 408–413.
Spencer, C. N., B. R. McClelland & J. A. Stanford, 1991. Shrimp stocking, salmon collapse, and eagle displacement. BioScience 41: 14–21.
Thomaz, S. M., K. E. Kovalenko, J. E. Havel & L. B. Kats, 2015. Aquatic invasive species: general trends in the literature and introduction to the special issue. Hydrobiologia 746: 1–12.
Torchin, M. E., K. D. Lafferty, A. P. Dobson, V. J. McKenzie & A. M. Kuris, 2003. Introduced species and their missing parasites. Nature 421: 628–630.
Toussaint, A., O. Beauchard, T. Oberdorff, S. Brosse & S. Villéger, 2016. Worldwide freshwater fish homogenization is driven by a few widespread non-native species. Biological Invasions 18: 1295–1304.
Twardochleb, L. A. & J. D. Olden, 2016. Non-native Chinese mystery snail (Bellamya chinensis) supports consumers in urban lake food webs. Ecosphere 7: e01293.
Ulanowicz, R. E., S. J. Goerner, B. Lietaer & R. Gomez, 2009. Quantifying sustainability: resilience, efficiency and the return of information theory. Ecological Complexity 6: 27–36.
Vitule, J. R. S., C. A. Freire & D. Simberloff, 2009. Introduction of non-native freshwater fish can certainly be bad. Fish and Fisheries 10: 98–108.
Vitule, J. R. S., F. Skóra & V. Abilhoa, 2012. Homogenization of freshwater fish faunas after the elimination of a natural barrier by a dam in Neotropics. Diversity and Distributions 18: 111–120.
Vitule, J. R. S., A. P. L. da Costa, F. A. Frehse, L. A. V. Bezerra, T. V. T. Occhi, V. S. Daga & A. A. Padial, 2017. Comment on fish biodiversity and conservation in South America by Reis et al. (2016). Journal of Fish Biology 90: 1182–1190.
Walters, C. J. & S. J. D. Martell, 2004. Fisheries Ecology and Management. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
Walters, C. J., C. Villy & D. Pauly, 1997. Structuring dynamic models of exploited ecosystems from trophic mass-balance assessments. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 7: 139–172.
Weyl, O. L. F., 2008. Rapid invasion of a subtropical lake fishery in central Mozambique by Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (Pisces: Cichlidae). Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 18: 839–851.
Winemiller, K. O., P. B. McIntyre, L. Castello, E. Fluet-Chouinard, T. Giarrizzo, S. Nam, I. G. Baird, W. Darwall, N. K. Lujan, I. Harrison, M. L. J. Stiassny, R. A. M. Silvano, D. B. Fitzgerald, F. M. Pelicice, A. A. Agostinho, L. C. Gomes, J. S. Albert, E. Baran, M. Petrere, C. Zarfl, M. Mulligan, J. P. Sullivan, C. C. Arantes, L. M. Sousa, A. A. Koning, D. J. Hoeinghaus, M. Sabaj, J. G. Lundberg, J. Armbruster, M. L. Thieme, P. Petry, J. Zuanon, G. T. Vilara, J. Snoeks, C. Ou, W. Rainboth, C. S. Pavanelli, A. Akama, A. V. Soesbergen & L. Saenz, 2016. Balancing hydropower and biodiversity in the Amazon, Congo, and Mekong. Science 351: 128–129.
Yu, J., Z. Liu, H. He, W. Zhen, B. Guan, F. Chen, K. Li, P. Zhong, F. Teixeira-de Mello & E. Jeppesen, 2016. Submerged macrophytes facilitate dominance of omnivorous fish in a subtropical shallow lake: implications for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 775: 1–11.
Zuur, A. F., E. N. Ieno, N. J. Walker, A. A. Saveliev, G. M. Smith & Ebooks Corporation, 2009. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R. Statistics for Biology and Health. Springer, New York.
Acknowledgements
We are thankful to the Fundação Cearense de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (FUNCAP, AE1-0052-00044.01.00/11 SPU nº: 11295057-4) for the funding to this project. Coordenadoria de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) for granting the first author with scholarships and funding M. Coll (PVE A063-2013), and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for the funding to JRS Vitule (310850/2012-6 and 303776/2015-3). Thanks also to Sr. Walt Disney Paulino, to Sr. Deílton Holanda and to other technicians from the Companhia de Gestão do Recursos Hídricos (COGERH, Ceará, Brazil), as well as the staff of the Laboratório de Ecologia Aquática (LEA), from the Universidade Federal do Ceará, for sampling support and post processing, and the ornithologists Caio Brito, Lucas Barros e Bruno Martins for the identification of birds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: John E. Havel, Sidinei M. Thomaz, Lee B. Kats, Katya E. Kovalenko, & Luciano N. Santos / Aquatic Invasive Species II
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bezerra, L.A.V., Angelini, R., Vitule, J.R.S. et al. Food web changes associated with drought and invasive species in a tropical semiarid reservoir. Hydrobiologia 817, 475–489 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3432-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3432-8