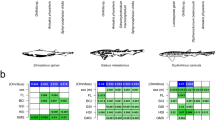
Abstract
The parasite communities of Scyliorhinus canicula and Galeus melastomus are studied for the first time in the Mediterranean. Their seasonal and geographical variations, and their relationship with environmental and fish biological data were tested. The parasite communities of both sharks were characterized by low richness and diversity, and high dominance. Infracommunity structure and composition differed between both species probably due to the consumption of different prey associated with their different bathymetric distributions. For G. melastomus, parasite infracommunity structure and the abundance of some parasites differed across seasons and/or localities due to different dynamics of intermediate hosts populations, in turn linked to different environmental conditions. While Ditrachybothridium macrocephalum was more abundant in juvenile specimens of G. melastomus as a result of ontogenic diet shifts, Grillotia sp. accumulated in adult hosts. The abundance of Proleptus obtusus was significantly higher in S. canicula, likely due to its shallower distribution coupled with higher consumption of reptantian decapods with respect to G. melastomus. Monogenean parasites were associated to high turbidity and temperature levels, which are known to enhance monogenean infection and reproductive success. Cestodes of G. melastomus were linked to high turbidity and O2 levels, which increase zooplankton biomass, favouring the transmission of heteroxenous parasites.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, M. J., R. N. Gorley & K. R. Clarke, 2008. PERMANOVA+ for PRIMER: Guide to Software and Statistical Methods. PRIMER-E, Plymouth.
Bagge, A. M., R. Poulin & E. T. Valtonen, 2004. Fish population size, and not density, as the determining factor of parasite infection: a case study. Parasitology 128: 305–313.
Beveridge, I. & R. A. Campbell, 2007. Revision of the Grillotia erinaceus (van Beneden, 1858) species complex (Cestoda: Trypanorhyncha), with the description of G. brayi n. sp. Systematic Parasitology 68: 1–31.
Bray, R. A. & P. D. Olson, 2004. The plerocercus of Ditrachybothridium macrocephalum Rees, 1959 from two deep-sea elasmobranchs, with a molecular analysis of its position within the order Diphyllidea and a checklist of the hosts of larval diphyllideans. Systematic Parasitology 59: 159–167.
Brazenor, A. K. & K. S. Hutson, 2015. Effects of temperature and salinity on the life cycle of Neobenedenia sp. (Monogenea: Capsalidae) infecting farmed barramundi (Lates calcarifer). Parasitology Research 114: 1875–1886.
Brinkmann Jr., A., 1988. Presence of Otodistomum sp. metacercariae in Norwegian marine fishes. Sarsia 73: 79–82.
Bush, A. O., K. D. Lafferty, J. M. Lotz, A. W. Shostak, et al., 1997. Parasitology meets ecology on its own terms: Margolis et al. revisited. Journal of Parasitology 83: 575–583.
Campbell, R. A., R. L. Haedrich & T. A. Munroe, 1980. Parasitism and ecological relationships among deep-sea benthic fishes. Marine Biology 57: 301–313.
Capapé, C. & J. Zaouali, 1977. Contribution a la biologie des Scyliorhinidae des cótes Tunisiennes. VI: Galeus melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 Répartition géographique et bathymetrique, sexualité, reproduction, fécondité. Cahiers de Biologie Marine 18: 449–463.
Carbonell, A., F. Alemany, P. Merella, A. Quetglas & E. Román, 2003. The by-catch of sharks in the western Mediterranean (Balearic Islands) trawl fishery. Fisheries Research 61: 7–18.
Carrassón, M., C. Stefanescu & J. E. Cartes, 1992. Diets and bathymetric distributions of two bathyal sharks of the Catalan Deep sea (Western Mediterranean). Marine Ecology Progress Series 82: 21–30.
Cartes, J. E., T. Madurell, E. Fanelli & J. L. López-Jurado, 2006. Dynamics of suprabenthos-zooplankton communities around the Balearic Islands (western Mediterranean): influence of environmental variables and effects on the biological cycle of Aristeus antennatus. Journal of Marine Systems 71: 316–335.
Cartes, J. E., F. Maynou, P. Abelló, M. Emelianov, L. Gil de Sola & M. Solé, 2011. Long-term changes in the abundance and deepening of the deep-sea shrimp Aristaeomorpha foliacea in the Balearic Basin: relationships with hydrographic changes at the Levantine Intermediate Water. Journal of Marine Systems 88: 516–525.
Cartes, J. E., E. Fanelli, C. López-Pérez & M. Lebrato, 2013. Deep-sea macroplankton distribution (at 400 to 2300 m) in the northwestern Mediterranean in relation to environmental factors. Journal of Marine Systems 113–114: 75–87.
Chambers, C., 2008. Determining deep-sea fish community structure in the Arctic: using species assemblages, stomach contents, parasite infracommunities and stable isotopes to evaluate trophic interactions. PhD Thesis. University of Manitoba, Winnipeg.
Cheung, S. G., H. Y. Chan, C. C. Liu & P. K. Shin, 2008. Effect of prolonged hypoxia on food consumption, respiration, growth and reproduction in marine scavenging gastropod Nassarius festivus. Marine Pollution Bulletin 57: 280–286.
Compagno, L. J. V., 1984. FAO species catalogue. Sharks of the world. An annotated and illustrated catalogue of shark species known to date. Part 1. Hexanchiformes to Lamniformes, Vol. 4. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome.
Constenla, M., F. E. Montero, F. Padrós, J. E. Cartes, V. Papiol & M. Carrassón, 2015. Annual variation of parasite communities of deep-sea macrourid fishes from the western Mediterranean Sea and their relationship with fish diet and histopathological alterations. Deep-Sea Research I 104: 106–121.
Costa, G., M. Khadem, T. Dellinger, M. Biscoito & E. Melo-Moreira, 2016. Larval cestodes infecting the deep-water fish, Cataetyx laticeps (Pisces: Bythidae) from Madeira Archipelago, Atlantic Ocean. Acta Parasitologica 61: 187–190.
Dallarés, S., M. Constenla, F. Padrós, J. E. Cartes, M. Solé & M. Carrassón, 2014. Parasites of the deep-sea fish Mora moro (Risso, 1810) from the NW Mediterranean Sea and relationship with fish diet and enzymatic biomarkers. Deep-Sea Research I 92: 115–126.
Dallarés, S., A. Pérez-del-Olmo, M. Carrassón & R. Kuchta, 2015. Morphological and molecular characterisation of Ditrachybothridium macrocephalum Rees, 1959 (Cestoda: Diphyllidea) from Galeus melastomus Rafinesque in the Western Mediterranean. Systematic Parasitology 92: 45–55.
Dallarés, S., C. M. Moyà-Alcover, F. Padrós, J. E. Cartes, M. Solé, C. Castañeda & M. Carrassón, 2016. The parasite community of Phycis blennoides (Brünnich, 1768) from the Balearic Sea in relation to diet, biochemical markers, histopathology and environmental variables. Deep-Sea Research I 118: 84–100.
Dent, F. & S. Clarke, 2015. State of the global market for shark products. FAO Fisheries and Aquaculture Technical Paper 590.
Dimech, M., M. J. Kaiser, S. Ragonese & P. J. Schembri, 2012. Ecosystem effects of fishing on the continental slope in the Central Mediterranean Sea. Marine Ecology Progress Series 449: 41–54.
D’Onghia, G., C.-Y. Politou, A. Bozzano, D. Lloris, G. Rotllant, L. Sion & F. Mastrototaro, 2004. Deep-water fish assemblages in the Mediterranean Sea. Scientia Marina 68: 87–99.
Ebert, D. A., 1994. Diet of the sixgill shark Hexanchus griseus off southern Africa. South African Journal of Marine Science 14: 213–218.
Euzet, L., C. Combes & A. Caro, 1993. A Checklist of Monogenea and Mediterranean fish. Second international Symposium on Monogenea.
Gross, M., 2014. Learning to live with sharks. Current Biology 24: R341–R344.
Heins, D. C. & J. A. Baker, 2008. The stickleback-Schistocephalus host-parasite system as a model for understanding the effect of a macroparasite on host reproduction. Behaviour 145: 625–645.
Henderson, A. C. & J. J. Dunne, 1998. The metazoan parasites of the lesser-spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula (L.) from the Galway Bay area. The Irish Naturalists’ Journal 26: 104–107.
Henderson, A. C., K. Flannery & J. Dunne, 2002. An investigation into the metazoan parasites of the spiny dogfish (Squalus acanthias L.), off the west coast of Ireland. Journal of Natural History 36: 1747–1760.
Isbert, W., C. Rodríguez-Cabello, I. Frutos, I. Preciado, F. E. Montero & A. Pérez-del-Olmo, 2015. Metazoan parasite communities and diet of the velvet belly lantern shark Etmopterus spinax (Squaliformes: Etmopteridae): a comparison of two deep-sea ecosystems. Journal of Fish Biology 86: 687–706.
IUCN, 2016. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Version 2016.2 [available on internet at www.iucnredlist.org]. Downloaded on 13 October 2016.
Klimpel, S., H. W. Palm & A. Seehagen, 2003. Metazoan parasites and food composition of juvenile Etmopterus spinax (L., 1758) (Dalatiidae, Squaliformes) from the Norwegian Deep. Parasitology Research 89: 245–251.
Klimpel, S., M. W. Busch, E. Kellermanns, S. Kleinertz & H. W. Palm, 2009. Metazoan Deep-Sea Fish Parasites. Verlag Natur & Wissenschaft, Solingen.
Macquart-Moulin, C. & G. Patriti, 1996. Accumulation of migratory micronekton crustaceans over the upper slope and submarine canyons of the northwestern Mediterranean. Deep-Sea Research I 43: 579–601.
Madi, R. R. & M. T. Ueta, 2009. O papel de Ancyrocephalinae (Monogenea: Dactylogyridae), parasito de Geophagus brasiliensis (Pisces: Cichlidae), como indicador ambiental. Revista Brasileira de Parasitologia Veterinaria 18: 38–41.
Massutí, E. & J. Moranta, 2003. Demersal assemblages and depth distribution of elasmobranchs from the continental shelf and slope off the Balearic Islands (Western Mediterranean). ICES Journal of Marine Science 60: 753–766.
Matallanas, J., 1982. Feeding-habits of Scymnorhinus licha in catalan waters. Journal of Fish Biology 20: 155–163.
Mateu, P., F. E. Montero & M. Carrassón, 2014. Geographical variation in metazoan parasites of the deep-sea fish Bathypterois mediterraneus Bauchot, 1962 (Osteichthyes: Ipnopidae) from the Western Mediterranean. Deep-Sea Research I 87: 24–29.
Mattiucci, S., A. Garcia, P. Cipriani, M. Neves Santos, G. Nascetti & R. Cimmaruta, 2014. Metazoan parasite infection in the swordfish, Xiphias gladius, from the Mediterranean Sea and comparison with Atlantic populations: implications for its stock characterization. Parasite 21: 35.
Mnrasi, N., O. el Kamel, M. Boumaïza, C. Reynaud & C. Capapé, 2012. Food and feeding habits of the small-spotted catshark, Scyliorhinus canicula (Chontrichthyes: Scyliorhinidae) from the northern coast of Tunisia (central Mediterranean). Cahiers de Biologie Marine 53: 139–150.
Moon, S. Y., H. S. Yoon, H. Y. Soh & S. D. Choi, 2006. Environmental factors and variation characteristics of zooplankton communities in Gamak Bay. Ocean Polar Research 28: 79–94.
Moore, A. B. M., 2001. Metazoan parasites of the lesser-spotted dogfish Scyliorhinus canicula and their potential as stock discrimination tools. Journal of the Marine Biology Association of the UK 81: 1009–1013.
Monni, G. & A. M. Cognetti-Varriale, 2002. Antigenicity of Pseudodactylogyrus anguillae and P-bini (Monogenea) in the European eel (Anguilla anguilla, L.) under different oxygenation conditions. Fish and Shellfish Immunology 13: 125–131.
Moravec, F., Jo G. Van As & I. Dyková, 2002. Proleptus obtusus Dujardin, 1845 (Nematoda: Physalopteridae) from the puffader shyshark Haploblepharus edwardsii (Scyliorhynidae) from off South Africa. Systematic Parasitology 53: 169–173.
Moravec, F., 2007. Some aspects of the taxonomy and biology of adult spirurine nematodes parasitic in fishes: a review. Folia Parasitologica 54: 239–257.
Morris, T., A. Avenant-Oldewage, S. Lamberth & C. Reed, 2016. Shark parasites as bio-indicators of metals in two South African embayments. Marine Pollution Bulletin 104: 221–228.
Palm, H. W., 2004. The Trypanorhyncha Diesing, 1863. PKSPL-IPB Press, Bogor.
Palm, H. W. & P. Schröder, 2001. Cestode parasites from the elasmobranchs Heptranchias perlo and Deania from the Great Meteor Bank, central East Atlantic. Aquatic Living Resources 14: 137–144.
Pérez-del-Olmo, A., M. Fernández, J. A. Raga, A. Kostadinova & S. Morand, 2009. Not everything is everywhere: the distance decay of similarity in a marine host-parasite system. Journal of Biogeography 36: 200–209.
Pérez-i-García, D., M. Constenla, F. Padrós, A. Soler-Membrives, M. Solé & M. Carrassón, 2015. Parasite communities of the deep-sea fish Alepocephalus rostratus Risso, 1820 in the Balearic Sea (NW Mediterranean) along the slope and relationships with enzymatic biomarkers and health indicators. Deep-Sea Research I 99: 65–74.
Pintner, T., 1899. Die Rhynchodäaldrüsen der Tetrarhynchen. Arbeiten aus den Zoologischen Instituten Universität Wien Tom. XII, Hft 1: 1–24.
Pintner, T., 1930. Wenigbekanntes und Unbekanntes von Rüsselband würmern. Sitzungsberichten der Kaiserlichen Akademie der Wissenschaften in Wien, Mathematisch-Naturwissenschaftiche Klasse 139: 445–537.
Polunin, N. V. C., B. Morales-Nin, W. E. Pawsey, J. E. Cartes, J. K. Pinnegar & J. Moranta, 2001. Feeding relationships in Mediterranean bathyal assemblages elucidated by stable nitrogen and carbon isotope data. Marine Ecology Progress Series 220: 13–23.
Raibaut, A., C. Combes & F. Benoit, 1998. Analysis of the parasitic copepod species richness among Mediterranean fish. Journal of Marine Systems 15: 185–206.
Raymond, K. M. N., L. L. Chapman & C. A. Lanciani, 2006. Host, macrohabitat, and microhabitat specificity in the gill parasite Afrodiplozoon polycotyleus (Monogenea). Journal of Parasitology 92: 1211–1217.
Rees, G., 1959. Ditrachybothridium macrocephalum gen. nov., sp. nov., a cestode from some elasmobranch fishes. Parasitology 49: 191–209.
Ruiz, D. J., S. Banks & M. Wolff, 2016. Elucidating fishing effects in a large-predator dominated system: the case of Darwin and Wolf Islands (Galápagos). Journal of Sea Research 107: 1–11.
Rumolo, P., J. E. Cartes, E. Fanelli, V. Papiol, M. Sprovieri, S. Mirto, S. Gherardi & A. Bonanno, 2015. Seasonal variations in the source of sea bottom organic matter off Catalonia coasts (Western Mediterranean): links with hydrography and biological response. Journal of Oceanography 71: 325–343.
Sardou, J., M. Etienne & V. Andersen, 1996. Seasonal abundance and vertical distributions of macroplankton and micronekton in the Northwestern Mediterranean Sea. Oceanologica Acta 19: 645–656.
Sasal, P., S. Morand & J.-F. Guégan, 1997. Determinants of parasite species richness in Mediterranean marine fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 149: 61–71.
Skinner, R. H., 1982. The interrelation of water quality, gill parasites, and gill pathology of some fishes from south Biscayne Bay, Florida. Fishery Bulletin 80: 269–280.
Sproston, N., 1946. A synopsis of the monogenetic trematodes. Transactions of the Zoological Society of London 25: 185–600.
Stevens, J. D., R. Bonfil, N. K. Dulvy & P. A. Walker, 2000. The effects of fishing on sharks, rays and chimaeras (chondrichthyans), and the implications for marine ecosystems. ICES Journal of Marine Science 57: 476–494.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1986. Canonical correspondence analyses a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67: 1167–1179.
Tyler, G. A., 2006. Tapeworms of elasmobranchs (Part II). A monograph on the Diphyllidea (Platyhelminthes, Cestoda). Bulletin of the University of Nebraska State Museum 20: 1–142.
Valls, M., A. Quetglas, F. Ordines & J. Moranta, 2011. Feeding ecology of demersal elasmobranchs from the shelf and slope off the Balearic Sea (Western Mediterranean). Scientia Marina 75: 633–639.
Willams, H. H., K. MacKenzie & A. M. McCarthy, 1992. Parasites as biological indicators of the population biology, migrations, diet and phylogenetics of fish. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 2: 144–176.
Acknowledgements
We thank two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments on the manuscript. We are grateful to Mar Costa for her collaboration in the dissection of some specimens of S. canicula and in the identification of their parasites. This study was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (MICYT) project BIOMARE (CTM2006–13508–C02–01MAR). S. Dallarés benefits of a PIF Ph.D. student Grant from the Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona (UAB) (Grant Number PIF2012–53296).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Vasilis Valavanis
Sara Dallarés and Ana Pérez-del-Olmo contributed equally towards this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dallarés, S., Pérez-del-Olmo, A., Montero, F.E. et al. Composition and seasonal dynamics of the parasite communities of Scyliorhinus canicula (L., 1758) and Galeus melastomus Rafinesque, 1810 (Elasmobranchii) from the NW Mediterranean Sea in relation to host biology and ecological features. Hydrobiologia 799, 275–291 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3226-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-017-3226-z