Abstract
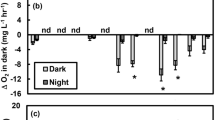
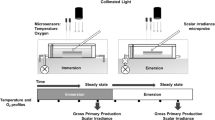
Oxygen flux between aquatic ecosystems and the water column is a measure of ecosystem metabolism. However, the oxygen flux varies during the day in a “hysteretic” pattern: there is higher net oxygen production at a given irradiance in the morning than in the afternoon. In this study, we investigated the mechanism responsible for the hysteresis in oxygen flux by measuring the daily pattern of oxygen flux, light, and temperature in a seagrass ecosystem (Zostera muelleri in Swansea Shoals, Australia) at three depths. We hypothesised that the oxygen flux pattern could be due to diel variations in either gross primary production or respiration in response to light history or temperature. Hysteresis in oxygen flux was clearly observed at all three depths. We compared this data to mathematical models, and found that the modification of ecosystem respiration by light history is the best explanation for the hysteresis in oxygen flux. Light history-dependent respiration might be due to diel variations in seagrass respiration or the dependence of bacterial production on dissolved organic carbon exudates. Our results indicate that the daily variation in respiration rate may be as important as the daily changes of photosynthetic characteristics in determining the metabolic status of aquatic ecosystems.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthony, K. R. N. & O. Hoegh-Guldberg, 2003. Kinetics of photoacclimation in corals. Oecologia 134: 23–31.
Barrón, C., N. Marbà, J. Terrados, H. Kennedy & C. M. Duarte, 2004. Community metabolism and carbon budget along a gradient of seagrass (Cymodocea nodosa) colonization. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 1642–1651.
Berg, P., M. H. Long, M. Huettel, J. E. Rheuban, K. J. McGlathery, R. W. Howarth, K. H. Foreman, A. E. Giblin & R. Marino, 2013. Eddy correlation measurements of oxygen fluxes in permeable sediments exposed to varying current flow and light. Limnology and Oceanography 58: 1329–1343.
Bernard, O., 2011. Hurdles and challenges for modelling and control of microalgae for CO2- mitigation and biofuel production. Journal of Process Control 21: 1378–1389.
Bertelli, C. M. & R. K. F. Unsworth, 2014. Protecting the hand that feeds us: Seagrass (Zostera marina) serves as commercial juvenile fish habitat. Marine Pollution Bulletin 83: 425–429.
Buapet, P., L. M. Rasmusson, M. Gullström & M. Björk, 2013. Photorespiration and carbon limitation determine productivity in temperate seagrasses. PLoS One 8: e83804.
Caffrey, J. M., 2004. Factors controlling net ecosystem metabolism in U.S. estuaries. Estuaries 27: 90–101.
Campbell, S., C. Miller, A. Steven & A. Stephens, 2003. Photosynthetic responses of two seagrasses across a water quality gradient using chlorophyll fluorescence. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 291: 57–78.
Campbell, S. J., L. J. McKenzie & S. P. Kerville, 2006. Photosynthetic responses of seven tropical seagrasses to elevated seawater temperature. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 330: 455–468.
Champenois, W. & A. V. Borges, 2012. Seasonal and interannual variations of community metabolism rates of a Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadow. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 347–361.
Cole, L. W. & K. J. McGlathery, 2012. Nitrogen fixation in restored eelgrass meadows. Marine Ecology Progress Series 448: 235–246.
Collier, C. J., S. Uthicke & M. Waycott, 2011. Thermal tolerance of two seagrass species at contrasting light levels: implications for future distribution in the Great Barrier Reef. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 2200–2210.
Duarte, C. M. & C. L. Chiscano, 1999. Seagrass biomass and production: a reassessment. Aquatic Botany 65: 159–174.
Duarte, C. M., N. Marbà, E. Gacia, J. W. Fourqurean, J. Beggins, C. Barrón & E. T. Apostolaki, 2010. Seagrass community metabolism: Assessing the carbon sink capacity of seagrass meadows. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 24: GB4032.
Dunton, K. H. & D. A. Tomasko, 1994. In situ photosynthesis in the seagrass Halodule wrightii in a hypersaline subtropical lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 107: 281–293.
Erftemeijer, P. L. A. & J. Stapel, 1999. Primary production of deep-water Halophila ovalis meadows. Aquatic Botany 65: 71–82.
Fourqurean, J. W., C. M. Duarte, H. Kennedy, N. Marbà, M. Holmer, M. A. Mateo, E. T. Apostolaki, G. A. Kendrick, D. Krause-Jensen, K. J. McGlathery & O. Serrano, 2012. Seagrass ecosystems as a globally significant carbon stock. Nature Geoscience 5: 505–509.
Gacia, E., H. Kennedy, C. M. Duarte, J. Terrados, N. Marbà, S. Papadimitriou & M. Fortes, 2005. Light-dependence of the metabolic balance of a highly productive Philippine seagrass community. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 316: 55–67.
Geertz-Hansen, O., C. Montes, C. M. Duarte, K. Sand-Jensen, N. Marbá & P. Grillas, 2011. Ecosystem metabolism in a temporary Mediterranean marsh (Doñana National Park, SW Spain). Biogeosciences 8: 963–971.
Glud, R. N., 2008. Oxygen dynamics of marine sediments. Marine Biology Research 4: 243–289.
Graf, A., A. Schlereth, M. Stitt & A. M. Smith, 2010. Circadian control of carbohydrate availability for growth in Arabidopsis plants at night. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107: 9458–9463.
Hennessey, T. L. & C. B. Field, 1991. Circadian rhythms in photosynthesis: oscillations in carbon assimilation and stomatal conductance under constant conditions. Plant Physiology 96: 831–836.
Hotchkiss, E. R. & R. O. Hall, 2014. High rates of daytime respiration in three streams: use of δ18O2 and O2 to model diel ecosystem metabolism. Limnology and Oceanography 59: 798–810.
Hume, A. C., P. Berg & K. J. McGlathery, 2011. Dissolved oxygen fluxes and ecosystem metabolism in an eelgrass (Zostera marina) meadow measured with the eddy correlation technique. Limnology and Oceanography 56: 86–96.
Jassby, A. D. & T. Platt, 1976. Mathematical formulation of the relationship between photosynthesis and light for phytoplankton. Limnology and Oceanography 21: 540–547.
Kaldy, J., 2012. Influence of light, temperature and salinity on dissolved organic carbon exudation rates in Zostera marina L. Aquatic Ecosystems 8: 19.
Kaldy, J. E., C. P. Onuf, P. M. Eldridge & L. A. Cifuentes, 2002. Carbon budget for a subtropical seagrass dominated coastal lagoon: how important are seagrasses to total ecosystem net primary production? Estuaries 25: 528–539.
Lee, K.-S., S. R. Park & Y. K. Kim, 2007. Effects of irradiance, temperature, and nutrients on growth dynamics of seagrasses: a review. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 350: 144–175.
Lindeboom, H. J. & A. J. J. Sandee, 1989. Production and consumption of tropical seagrass fields in eastern Indonesia measured with bell jars and microelectrodes. Netherlands Journal of Sea Research 23: 181–190.
Longstaff, B. J. & W. C. Dennison, 1999. Seagrass survival during pulsed turbidity events: the effects of light deprivation on the seagrasses Halodule pinifolia and Halophila ovalis. Aquatic Botany 65: 105–121.
Marra, J., 1978. Effect of short-term variations in light intensity on photosynthesis of a marine phytoplankter: a laboratory simulation study. Marine Biology 46: 191–202.
Martin, S., J. Clavier, J.-M. Guarini, L. Chauvaud, C. Hily, J. Grall, G. Thouzeau, F. Jean & J. Richard, 2005. Comparison of Zostera marina and maerl community metabolism. Aquatic Botany 83: 161–174.
Marsh, J. A., W. C. Dennison & R. S. Alberte, 1986. Effects of temperature on photosynthesis and respiration in eelgrass (Zostera marina L.). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 101: 257–267.
Mass, T., A. Genin, U. Shavit, M. Grinstein & D. Tchernov, 2010. Flow enhances photosynthesis in marine benthic autotrophs by increasing the efflux of oxygen from the organism to the water. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 107: 2527–2531.
Maxwell, P. S., K. A. Pitt, D. D. Burfeind, A. D. Olds, R. C. Babcock & R. M. Connolly, 2014. Phenotypic plasticity promotes persistence following severe events: physiological and morphological responses of seagrass to flooding. Journal of Ecology 102: 54–64.
McWatters, H. G. & P. F. Devlin, 2011. Timing in plants—A rhythmic arrangement. FEBS Letters 585: 1474–1484.
Miller, H. L., C. Meile & A. B. Burd, 2007. A novel 2D model of internal O2 dynamics and H2S intrusion in seagrasses. Ecological Modelling 205: 365–380.
Moncreiff, C. A., M. J. Sullivan & A. E. Daehnick, 1992. Primary production dynamics in seagrass beds of Mississippi Sound: the contributions of seagrass, epiphytic algae, sand microflora, and phytoplankton. Marine Ecology Progress Series 87: 161–171.
Moriarty, D. J. W., R. L. Iverson & P. C. Pollard, 1986. Exudation of organic carbon by the seagrass Halodule wrightii Aschers. and its effect on bacterial growth in the sediment. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 96: 115–126.
Murray, L. & R. L. Wetzel, 1987. Oxygen production and consumption associated with the major autotrophic components in two temperate seagrass communities. Marine Ecology Progress Series 38: 231–239.
O’Brien, K. R., M. A. Burford & J. D. Brookes, 2009. Effects of light history on primary productivity in a phytoplankton community dominated by the toxic cyanobacterium Cylindrospermopsis raciborskii. Freshwater Biology 54: 272–282.
Olivé, I., J. Silva, M. M. Costa & R. Santos, 2015. Estimating seagrass community metabolism using benthic chambers: the effect of incubation time. Estuaries and Coasts. doi:10.1007/s12237-015-9973-z.
Penhale, P. A. & W. O. Smith, 1977. Excretion of dissolved organic carbon by eelgrass (Zostera marina) and its epiphytes. Limnology and Oceanography 22: 400–407.
Plus, M., J.-M. Deslous-Paoli, I. Auby & F. Dagault, 2001. Factors influencing primary production of seagrass beds (Zostera noltii Hornem.) in the Thau lagoon (French Mediterranean coast). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 259: 63–84.
Post, A. F., Z. Dubinsky, K. Wyman & P. G. Falkowski, 1984. Kinetics of light-intensity adaptation in a marine planktonic diatom. Marine Biology 83: 231–238.
Ralph, P. J., 1998. Photosynthetic response of laboratory-cultured Halophila ovalis to thermal stress. Marine Ecology Progress Series 171: 123–130.
Ralph, P. J., S. M. Polk, K. A. Moore, R. J. Orth & W. O. Smith Jr, 2002. Operation of the xanthophyll cycle in the seagrass Zostera marina in response to variable irradiance. Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 271: 189–207.
Rheuban, J. E., P. Berg & K. J. McGlathery, 2014a. Multiple timescale processes drive ecosystem metabolism in eelgrass (Zostera marina) meadows. Marine Ecology Progress Series 507: 1–13.
Rheuban, J. E., P. Berg & K. J. McGlathery, 2014b. Ecosystem metabolism along a colonization gradient of eelgrass (Zostera marina) measured by eddy correlation. Limnology and Oceanography 59: 1376–1387.
Rice, E. W. & L. Bridgewater, 2012. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 22nd ed. American Public Health Association, Washington.
Silva, J. & R. Santos, 2003. Daily variation patterns in seagrass photosynthesis along a vertical gradient. Marine Ecology Progress Series 257: 37–44.
Spivak, A. C., E. A. Canuel, J. E. Duffy & J. P. Richardson, 2009. Nutrient enrichment and food web composition affect ecosystem metabolism in an experimental seagrass habitat. PLoS One 4: e7473.
Staehr, P. A. & J. Borum, 2011. Seasonal acclimation in metabolism reduces light requirements of eelgrass (Zostera marina). Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 407: 139–146.
Staehr, P. A., J. M. Testa, W. M. Kemp, J. J. Cole, K. Sand-Jensen & S. V. Smith, 2012. The metabolism of aquatic ecosystems: history, applications, and future challenges. Aquatic Sciences 74: 15–29.
Tobias, C. R., J. K. Böhlke & J. W. Harvey, 2007. The oxygen-18 isotope approach for measuring aquatic metabolism in high-productivity waters. Limnology and Oceanography 52: 1439–1453.
Vacchi, M., M. Montefalcone, C. F. Schiaffino, V. Parravicini, C. N. Bianchi, C. Morri & M. Ferrari, 2014. Towards a predictive model to assess the natural position of the Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows upper limit. Marine Pollution Bulletin 83: 458–466.
Valiela, I., 1995. Marine ecological processes, 2nd ed. Springer, New York.
Waycott, M., B. J. Longstaff & J. Mellors, 2005. Seagrass population dynamics and water quality in the Great Barrier Reef region: a review and future research directions. Marine Pollution Bulletin 51: 343–350.
Ziegler, S. & R. Benner, 1998. Ecosystem metabolism in a subtropical, seagrass-dominated lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 173: 1–12.
Ziegler, S. & R. Benner, 1999. Dissolved organic carbon cycling in a subtropical seagrass-dominated lagoon. Marine Ecology Progress Series 180: 149–160.
Acknowledgments
MPA’s contribution to this work was funded by a University of Queensland Engineering, Architecture and Information Technology (UQ EAIT) Strategic Fellowship. PSM was funded by the University of Queensland Collaboration and Industry Engagement Fund (UQ CIEF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: I.A. Nagelkerken
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adams, M.P., Ferguson, A.J.P., Maxwell, P.S. et al. Light history-dependent respiration explains the hysteresis in the daily ecosystem metabolism of seagrass. Hydrobiologia 766, 75–88 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2444-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2444-5