Abstract
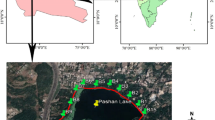
We examined the interaction between environmental variables measured at three different scales (i.e., landscape, lake, and in-lake) and fish assemblage descriptors across a range of over 50 floodplain lakes in the Mississippi Alluvial Valley of Mississippi and Arkansas. Our goal was to identify important local- and landscape-level determinants of fish assemblage structure. Relationships between fish assemblage structure and variables measured at broader scales (i.e., landscape-level and lake-level) were hypothesized to be stronger than relationships with variables measured at finer scales (i.e., in-lake variables). Results suggest that fish assemblage structure in floodplain lakes was influenced by variables operating on three different scales. However, and contrary to expectations, canonical correlations between in-lake environmental characteristics and fish assemblage structure were generally stronger than correlations between landscape-level and lake-level variables and fish assemblage structure, suggesting a hierarchy of influence. From a resource management perspective, our study suggests that landscape-level and lake-level variables may be manipulated for conservation or restoration purposes, and in-lake variables and fish assemblage structure may be used to monitor the success of such efforts.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The use of trade, product, industry, or firm names or products or software is for informative purposes and does not constitute an endorsement by the U.S. government or U.S. Geological Survey.
References
Allen, T. F. H. & T. B. Starr, 1982. Hierarchy: Perspectives for Ecological Complexity. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago, IL.
Amarasinghe, U. S. & R. L. Welcomme, 2002. An analysis of fish species richness in natural lakes. Environmental Biology of Fishes 65: 327–339.
Anderson, M. J., 2001. A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecology 26: 32–46.
Anderson, M. J. & J. Robinson, 2003. Generalized discriminant analysis based on distances. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Statistics 45: 301–318.
Anderson, M. J. & T. J. Willis, 2003. Canonical analysis of principal coordinates: a useful method of constrained ordination for ecology. Ecology 84: 511–525.
Baker, J. A., K. J. Killgore & R. L. Kasul, 1991. Aquatic habitats and fish communities in the Lower Mississippi River. Aquatic Sciences 3: 313–356.
Balon, E. K., 1990. Epigenesis of an epigeneticist: the development of some alternative concepts on the early ontogeny and evolution of fishes. Guelph Ichthyology Reviews 1: 1–42.
Biedenharn, D. S., C. R. Thorne & C. C. Watson, 2000. Recent morphological evolution of the lower Mississippi River. Geomorphology 34: 227–249.
Brind’Amour, A., D. Boisclair, P. Legendre & D. Borcard, 2005. Multiscale spatial distribution of a littoral fish community in relation to environmental variables. Limnology and Oceanography 50: 465–479.
Browne, R. A., 1981. Lakes as islands: biogeographic distribution, turnover rates, and species composition in the lakes of central New York. Journal of Biogeography 8: 75–83.
Brunton, M. N., 1985. The effects of suspensoids on fish. Hydrobiologia 125: 221–241.
Cao, Y., D. P. Larsen & R. S. Thorne, 2001. Rare species in multivariate analysis for bioassessment: some considerations. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20: 144–153.
Clarke, K. R. & R. N. Gorley, 2006. PRIMER v6: User Manual/Tutorial. PRIMER-E, Plymouth, UK.
Cooper, C. M. & J. R. McHenry, 1989. Sediment accumulation and its effects on a Mississippi River oxbow lake. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences 13: 33–37.
Dembkowski, D. J. & L. E. Miranda, 2011. Comparison of fish assemblages in two disjoined segment of an oxbow lake in relation to connectivity. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 140: 1060–1069.
Dembkowski, D. J. & L. E. Miranda, 2012. Hierarchy in factors affecting fish biodiversity in floodplain lakes of the Mississippi Alluvial Valley. Environmental Biology of Fishes 93: 357–368.
Dolan, C. R. & L. E. Miranda, 2003. Immobilization thresholds of electrofishing relative to fish size. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 132: 969–977.
Eadie, J. M., T. A. Hurly, R. D. Montgomerie & K. L. Teather, 1986. Lakes and rivers as islands: species–area relationships in the fish faunas of Ontario. Environmental Biology of Fishes 15: 81–89.
Foley, J. A., C. J. Kucharik, T. E. Twine, M. T. Coe & S. D. Donner, 2004. Land use, land cover, and climate change across the Mississippi Basin: impacts on selected land and water resources. In DeFries, R. S., G. P. Asner, & R. A. Houghton (eds), Ecosystems and Land Use Change. Geophysical Monograph Series, Vol. 153. American Geophysical Union, Washington, DC: 249–261.
GeoStor, 2009. Arkansas’ Official GIS Platform. Arkansas Geographic Information Office, Arkansas. http://www.geostor.arkansas.gov/G6/Home.html. Accessed October 2010.
Goldstein, R. M. & T. P. Simon, 1999. Toward a united definition of guild structure for feeding ecology of North American freshwater fishes. In Simon, T. P. (ed.), Assessing the Sustainability and Biological Integrity of Water Resources Using Fish Communities. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL.
Hall, R. I., P. R. Leavitt, R. Quinlan, A. S. Dixit & J. P. Smol, 1999. Effects of agriculture, urbanization, and climate on water quality in the northern Great Plains. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 739–756.
Hamilton, S. K. & W. H. Lewis, Jr., 1990. Basin morphology in relation to chemical and ecological characteristics of lakes on the Orinoco River floodplain, Venezuela. Hydrobiological Archives 119: 393–425.
Imhof, J. G., J. Fitzgibbon & W. K. Annable, 1996. A hierarchical evaluation system for characterizing watershed ecosystems for fish habitat. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 53: 312–326.
Johnson, D. E., 1998. Applied Multivariate Methods for Data Analysis. Duxbury Press, Pacific Grove, CA.
Junk, W. J., P. B. Bayley & R. E. Sparks, 1989. The flood pulse concept in river-floodplain systems. In Dodge, D. P. (ed.), Proceedings of the International Large River Symposium. Canadian Special Publication of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, Vol. 106. Department of Fisheries and Oceans, Ottawa: 110–127.
Killgore, K. J. & J. P. Hoover, 1992. A Guild for Monitoring and Evaluating Fish Communities in Bottomland Hardwood Wetlands. U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, Waterways Experiment Station, Wetlands Reserve Technical Note FW-EV-2.2, Vicksburg, MS.
Killgore, K. J., J. J. Hoover, J. P. Kirk, S. G. George, B. R. Lewis & C. E. Murphy, 2007. Age and growth of pallid sturgeon in the free-flowing Mississippi River. Journal of Applied Ichthyology 4: 452–456.
Legendre, P. & E. D. Gallagher, 2001. Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 129: 271–280.
Lubinski, B. J., J. R. Jackson & M. A. Eggleton, 2008. Relationships between floodplain lake fish communities and environmental variables in a large river-floodplain ecosystem. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 137: 895–908.
Lucas, G., 1985. Survey of the Fisheries of the Mississippi Delta. Freshwater Fisheries Report 46, Mississippi Department of Wildlife, Fisheries and Parks, Jackson, MS.
MacArthur, R. H. & E. O. Wilson, 1967. The Theory of Island Biogeography. Princeton University Press, Princeton, NJ.
Magnuson, J. J., L. B. Crowder & P. A. Medvick, 1979. Temperature as an ecological resource. American Zoologist 19: 331–343.
Magnuson, J. J., W. M. Tonn, A. Banerjee, J. Toivonen, O. Sanchez & M. Rask, 1998. Isolation vs. extinction in the assembly of fishes in small northern lakes. Ecology 79: 2941–2956.
MARIS (Mississippi Automated Resource Information System), 2003. Mississippi Automated Resource Information System. MARIS, Jackson, MS.
McCune, B. & J. B. Grace, 2002. Analysis of Ecological Communities. MjM Software, Gleneden Beach, OR.
McHenry, J. R., C. M. Cooper & J. C. Ritchie, 1982. Sedimentation of Wolf Lake, lower Yazoo River basin, Mississippi. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 1: 547–558.
Miranda, L. E., 2005. Fish assemblages in oxbow lakes relative to connectivity with the Mississippi River. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 134: 1480–1489.
Miranda, L. E., 2011. Depth as an organizer of fish assemblages in floodplain lakes. Aquatic Sciences 73: 211–221.
Miranda, L. E. & G. M. Lucas, 2004. Determinism in fish assemblages of floodplain lakes of the vastly disturbed Mississippi Alluvial Valley. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 133: 358–370.
Miyazono, S., J. N. Aycock, L. E. Miranda & T. E. Tietjen, 2010. Assemblage patterns of fish functional groups relative to habitat connectivity and conditions in floodplain lakes. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 19: 578–585.
Mormul, R. P., S. M. Thomaz, A. A. Agostinho, C. C. Bonecker & N. Mazzeo, 2012. Migratory benthic fishes may induce regime shifts in a tropical floodplain pond. Freshwater Biology 57: 1592–1602.
Nõges, T., 2009. Relationships between morphometry, geographic location and water quality parameters of European lakes. Hydrobiologia 633: 33–43.
Nunn, A. D., J. P. Harvey & I. G. Cowx, 2007. Benefits to 0+ fishes of connecting man-made waterbodies to the lower River Trent, England. River Research and Applications 23: 361–376.
Penczak, T., G. Zieba, H. Kozalinski & A. Kruk, 2003. The importance of oxbow lakes for fish recruitment in a river system. Hydrobiological Archives 158: 267–281.
Penczak, T., W. Galicka, Ł. Glowacki, H. Koszalinski, A. Kruk, G. Zieba, J. Kostrezwa & L. Marszal, 2004. Fish assemblage changes relative to environmental factors and time in the Warta River, Poland, and its oxbow lakes. Journal of Fish Biology 64: 483–501.
Rempel, R. S. & P. J. Colby, 1991. A statistically valid model of the morphoedaphic index. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 48: 1937–1943.
Reynolds, J. B., 1996. Electrofishing. In Murphy, B. R. & D. W. Willis (eds), Fisheries Techniques, 2nd ed. American Fisheries Society, Bethesda, MD: 221–254.
Ritchie, J. C., 1972. Sediment, fish, and fish habitat. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 27: 124–125.
Rodríguez, M. A. & W. M. Lewis, Jr., 1997. Structure of fish assemblages along environmental gradients in floodplain lakes of the Orinoco River. Ecological Monographs 67: 109–128.
Roozen, F. M., G. J. van Geest, B. W. Ibelings, R. M. Roijackers, M. Scheffer & A. D. Buijse, 2003. Lake age and water level affect the turbidity of floodplain lakes along the lower Rhine. Freshwater Biology 48: 519–531.
Ross, S. T., 2001. Inland Fishes of Mississippi. University Press of Mississippi, Jackson, MS.
Ryder, R. A., 1982. The morphoedaphic index – use, abuse, and fundamental concepts. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 111: 154–164.
Sabo, M. J. & W. E. Kelso, 1991. Relationship between morphometry of excavated floodplain ponds along the Mississippi River and their use as fish nurseries. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 120: 552–561.
Scheffer, M., 2004. The Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Kluwer, Dordrecht.
Shields, F. D., Jr., S. S. Knight, R. E. Lizotte & D. G. Wren, 2010. Floodplain river backwater restoration: a case study. In Proceedings of the 9th Federal Interagency Sedimentation Conference. Joint Federal Interagency Conference Organizing Committee, Washington, DC, CD-ROM.
Shoup, D. E. & D. H. Wahl, 2009. Fish diversity and abundance in relation to interannual and lake-specific variation in abiotic characteristics of floodplain lakes of the Lower Kaskaskia River, Illinois. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 138: 1076–1092.
Shuter, B. J., J. A. MacLean, F. E. J. Fry & H. A. Regier, 1980. Stochastic simulation of temperature effects on first-year survival of smallmouth bass. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 109: 1–34.
Syms, C., 1995. Multi-scale analysis of habitat association in a guild of blennioid fishes. Marine Ecology Progress Series 125: 31–43.
Tales, E. & R. Berrebi, 2007. Controls of local young-of-the-year fish species richness in flood plain water bodies: potential effects of habitat heterogeneity, productivity and colonization-extinction events. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 16: 144–154.
Tebo, L. B. Jr., 1955. Effects of siltation, resulting from improper logging, on the bottom fauna of a small trout stream in the southern Appalachians. The Progressive Fish Culturist 17: 64–70.
Tejerina-Garro, F. L., R. Fortin & M. A. Rodríguez, 1998. Fish community structure in relation to environmental variation in floodplain lakes of the Araguaia River, Amazon Basin. Environmental Biology Fish 51: 399–410.
Tonn, W. M., 1990. Climate change and fish communities: a conceptual approach. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 119: 337–352.
Tonn, W. M., J. J. Magnuson, M. Rask & J. Toivonen, 1990. Intercontinental comparison of small-lake fish assemblages: the balance between local and regional processes. American Naturalist 136: 345–375.
Walser, C. A. & H. L. Bart, Jr., 1999. Influence of agriculture on in-stream habitat and fish community structure in Piedmont watersheds of the Chattahoochie River System. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 8: 237–246.
Welcomme, R. L., 1979. Fisheries Ecology of Floodplain Rivers. Langdon, London: 317 pp.
Winemiller, K. O., S. Tarim, D. Shorman & J. B. Cotner, 2000. Fish assemblage structure in relation to environmental variation among Brazos River oxbow lakes. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 129: 451–468.
Wootton, R. J., 1992. Fish Ecology. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Wren, D. G., G. R. Davidson, W. G. Walker & S. J. Galicki, 2008. The evolution of an oxbow lake in the Mississippi alluvial floodplain. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation 63: 129–135.
Zalewski, M. & R. J. Naiman, 1984. The regulation of riverine fish communities by a continuum of abiotic–biotic factors. In Alabaster, J. S. (ed.), Habitat Modification and Freshwater Fisheries. Batterworth Scientific, London.
Zeug, S. C., K. O. Winemiller & S. Tarim, 2005. Response of Brazos River oxbow fish assemblages to patterns of hydrologic connectivity and environmental variability. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 134: 1389–1399.
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Vicksburg District of the Army Corps of Engineers through K.J. Killgore, by Mississippi State University, and by the U.S. Geological Survey. The authors thank T. Alfermann, N. Aycock, J. Dagel, R. Krogman, S. Miyazono, and S. Wigen for assistance with fieldwork; and J. Breeggemann, D. Deslauriers, C.A. Hayer, M. Kaemingk, T. Rapp, and M. Wagner for helpful reviews of earlier drafts of the manuscript. (Any use of trade, firm, or product names is for descriptive purposes only and does not constitute endorsement by the U.S. Government).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Koen Martens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dembkowski, D.J., Miranda, L.E. Environmental variables measured at multiple spatial scales exert uneven influence on fish assemblages of floodplain lakes. Hydrobiologia 721, 129–144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1655-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1655-x