Abstract
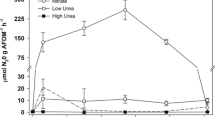
Changing environmental conditions and increased water consumption have transformed many historically perennial stream systems into intermittent systems. Multiple drying and wetting events throughout the year might impact many stream processes including nitrification and denitrification, key components of the nitrogen (N) cycle. During summer 2007, an experimental stream was used to dry and then rewet stream sediments to determine the effects of desiccation and rewetting of stream sediment on nitrification and denitrification potentials. Mean (±SE) nitrification and denitrification rates in sediment not dried (controls) were 0.431 ± 0.017 μg NO3 −–N/cm2/h and 0.016 ± 0.002 μg N2O–N/cm2/h, respectively. As sediment samples dried, nitrification rates decreased. Rates in sediments dried less than 7 d recovered to levels equal or greater than those in the controls within 1 d of being rewetted. Denitrification rates were not affected by 1 d of drying, but samples dried greater than 1 d experienced reduced rates of denitrification. Denitrification in sediments dried 7 d or less recovered by day seven of being rewetted. Nitrification and denitrification processes failed to fully recover in sediments dried more than 7 d. These results demonstrate that alterations in stream’s hydrology can significantly affect N-cycle processes.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander, R. B., R. A. Smith & G. E. Schwarz, 2000. Effect of stream channel size on the delivery of nitrogen to the Gulf of Mexico. Nature 403: 758–761.
Andersen, J. M., 1977. Rates of denitrification of undisturbed sediments of six lakes as a function of nitrate concentration, oxygen, and temperature. Archive fur Hydrobiologia 80: 147–159.
Angelo, R. T., 1994. Impacts of declining streamflow on surface water quality. 11th Annual Water and the Future of Kansas Conference Proceedings, Manhattan, KS: 1–2.
APHA (American Public Health Association), 2005. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC: 1368 pp.
Bernot, M. J. & W. K. Dodds, 2005. Nitrogen retention, removal, and saturation in lotic ecosystems. Ecosystems 8: 442–453.
Bothe, H., G. Jost, M. Schloter, B. B. Ward & K. P. Witzel, 2000. Molecular analysis of ammonia oxidation and denitrification in natural environments. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 24: 673–690.
Cavanaugh, J. C., W. B. Richardson, E. A. Strauss & L. A. Bartsch, 2006. Nitrogen dynamics in sediment during water level manipulation on the Upper Mississippi River. River Research Applications 22: 651–666.
Cross, F. B. & R. E. Moss, 1987. Historic changes in fish communities and aquatic habitats in plains streams of Kansas. In Matthews, W. J. & D. C. Heins (eds), Community Evolutionary Ecology of North American Stream Fishes. University of Oklahoma Press, Norman, OK: 155–165.
Davidson, E. A., M. K. Strand & L. F. Galloway, 1985. Evaluation of the most probable number method for enumerating denitrifying bacteria. Soil Science Society of American Journal 49: 642–645.
Dodds, W. K., K. Gido, M. R. Whiles, K. M. Fritz & W. J. Matthews, 2004. Life on the edge: the ecology of Great Plains prairie streams. BioScience 54: 205–216.
Duff, J. H., A. J. Tesoriero, W. B. Richardson, E. A. Strauss & M. D. Munn, 2008. Whole-stream response to nitrate loading in three streams draining agricultural landscapes. Journal of Environmental Quality 37: 1133–1144.
Eberle, M. E., T. L. Wenke & N. E. Mandrak, 1998. Assessment of the Solomon River, North Fork Solomon River, and South Fork Solomon River in Northwestern Kansas. Kansas Department of Wildlife and Parks and U.S. Bureau of Reclamation: 63.
Fierer, N. & J. P. Schimel, 2002. Effects of drying–rewetting frequency on soil carbon and nitrogen transformations. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 34: 777–787.
García-Ruiz, R., S. N. Pattinson & B. A. Whitton, 1998. Denitrification in river sediments: relationships between process rates and properties of water and sediment. Freshwater Biology 39: 467–476.
Gido, K. B., W. K. Dodds & M. E. Eberle, 2010. Retrospective analysis of fish community change during a half-century of land-use and streamflow changes. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 29: 970–987.
Groffman, P. M. & J. M. Tiedje, 1988. Denitrification hysteresis during wetting and drying cycles in soil. Soil Science of American Journal 52: 1626–1629.
Groffman, P. M., E. A. Holland, D. D. Myrold, G. P. Robertson & X. Zou, 1999. Denitrification. In Robertson, G. P., D. C. Coleman, C. S. Bledsoe & P. Sollins (eds), Standard Methods for Long-term Ecological Research. Oxford University Press, Oxford: 272–288.
Håkanson, L. & M. Jansson, 1983. Principles of Lake Sedimentology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin: 316 pp.
Hedin, L. O., J. C. Von Fischer, N. E. Ostrom, B. P. Kennedy, M. G. Brown & G. P. Robertson, 1998. Thermodynamic constrains on nitrogen transformations and other biogeochemical processes at soil stream interfaces. Ecology 79: 684–703.
Hermansson, A., J. S. K. Bäckman, B. H. Svensson & P.-E. Lindgren, 2004. Quantification of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria in limed and non-limed acidic coniferous forest soil using real-time PCR. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 36: 1935–1941.
IPCC, 2007. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Solomon, S., D. Qin, M. Manning, Z. Chen, M. Marquis, K. B. Averyt, M.Tignor, H. L. Miller (eds)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA.
Jones, J. G., 1979. Microbial nitrate reduction in freshwater sediments. Journal of General Microbiology 115: 27–35.
Kemp, M. J. & W. K. Dodds, 2001. Centimeter-scale patterns in dissolved oxygen and nitrification rates in a prairie stream. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 20: 347–357.
Kemp, M. J. & W. K. Dodds, 2002. Comparisons of nitrification and denitrification in prairie and agriculturally influenced streams. Ecological Applications 12: 998–1009.
Kern, J., A. Darwich, K. Furch & W. J. Junk, 1996. Seasonal denitrification in flooded and exposed sediments from the Amazon floodplain at Lago Camaleao. Microbial Ecology 32: 47–57.
Kieft, T. L., E. Soroker & M. K. Firestone, 1987. Microbial biomass response to a rapid increase in water potential when dry soil is wetted. Soil Biology and Biochemistry 19: 119–126.
Konhauser, K., 2007. Introduction to Geomicrobiology. Blackwell Science Ltd., Oxford: 440.
Mitchell, A. & D. S. Baldwin, 1998. Effects of desiccation/oxidation on the potential for bacterial mediated P release from sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 481–487.
Mitchell, A. & D. S. Baldwin, 1999. The effects of sediment desiccation on the potential for nitrification, denitrification, and methanogenesis in an Australian reservoir. Hydrobiologia 392: 3–11.
Modini, C., M. Contin, L. Leita & M. De Nobili, 2002. Response of microbial biomass to air-drying and rewetting in soils and compost. Geoderma 105: 111–124.
Mulholland, P. J., A. M. Helton, G. C. Poole, R. O. Hall Jr., S. K. Hamilton, B. J. Peterson, J. L. Tank, L. R. Ashkenas, L. W. Cooper, C. N. Dahm, W. K. Dodds, S. E. G. Findlay, S. V. Gregory, N. B. Grimm, S. L. Johnson, W. H. McDowell, J. L. Meyer, H. M. Valett, J. R. Webster, C. P. Arango, J. J. Beaulieu, M. J. Bernot, A. J. Burgin, C. C. Crenshaw, L. T. Johnson, B. R. Niederlehner, J. M. O’Brien, J. D. Potter, R. W. Sheibley, D. J. Sobota & S. M. Thomas, 2008. Stream denitrification across biomes and its response to anthropogenic nitrate loading. Nature 454: 202–206.
National Assessment Synthesis Team, 2001. Climate Change Impacts on the United States: The Potential Consequences of Climate Variability and Change. US Global Change Research Program, Washington, DC: 541.
Nielsen, L. P., P. B. Christensen, N. P. Revsbech & J. Sorensen, 1990. Denitrification and photosynthesis in stream sediment studied with microsensor and whole-core techniques. Limnology and Oceanography 35: 1135–1144.
Pattinson, S. N., R. García-Ruiz & B. A. Whitton, 1998. Spatial and seasonal variation in denitrification in Swale-Ouse system, a river continuum. The Science of the Total Environment 210(211): 289–305.
Peterson, B. J., W. M. Wollheim, P. J. Mullholland, J. R. Webster, J. L. Meyer, J. L. Tank, E. Marti, W. B. Bowden, H. M. Valett, A. E. Hershey, W. H. McDowell, W. K. Dodds, S. K. Hamilton, S. Gregory & D. D. Morall, 2002. Control of nitrogen export from watersheds by headwater streams. Science 292: 86–90.
Qiu, S. & A. J. McComb, 1994. Effects of oxygen concentration on phosphorus release from reflooded, air-dried wetland sediments. Australian Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 45: 1319–1328.
Qiu, S. & A. J. McComb, 1995. Planktonic and microbial contributions to phosphorus release from fresh and air-dried sediments. Marine & Freshwater Research 46: 1039–1045.
Qiu, S. & A. J. McComb, 1996. Drying-induced stimulation of ammonium release and nitrification in reflooded lake sediment. Marine Freshwater Research 47: 531–536.
Richardson, W. B., E. A. Strauss, L. A. Bartsch, E. M. Monroe, J. C. Cavanaugh, L. Vingum & D. M. Soballe, 2004. Denitrification in the Upper Mississippi River: rates, controls, and contribution to nitrate flux. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 61: 1102–1112.
Rigobelo, E. C. & E. Nahas, 2004. Seasonal fluctuations of bacterial populations and microbial activity in soils cultivated with Eucalyptus and Pinus. Science and Agriculture 61: 88–93.
Smith, M. S. & L. L. Parsons, 1985. Persistence of denitrifying enzyme activity in dried soils. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 49: 316–320.
Solorzano, L., 1969. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnology and Oceanography 14: 799–801.
Sophocleuous, M., 2000. From safe yield to sustainable development of water resources—the Kansas experience. Journal of Hydrology 235: 27–43.
Sorensen, J., 1978. Capacity for denitrification and reduction of nitrate to ammonia in coastal marine sediment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 35: 301–305.
Starry, O. S., H. M. Valett & M. E. Schreiber, 2005. Nitrification rates in a headwater stream: influences of seasonal variation in C and N supply. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 24: 753–768.
Strauss, E. A. & W. K. Dodds, 1997. Influence of protozoa and nutrient availability on nitrification rates in subsurface sediments. Microbial Ecology 34: 155–165.
Strauss, E. A. & G. A. Lamberti, 2000. Regulation of nitrification in aquatic sediments by organic carbon. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 1854–1859.
Strauss, E. A., N. L. Mitchell & G. A. Lamberti, 2002. Factors regulating nitrification in aquatic sediments: effects of organic carbon, nitrogen availability, and pH. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 59: 554–563.
Strauss, E. A., W. B. Richardson, L. A. Bartsch, J. C. Cavanaugh, D. A. Brusewitz, H. Imker, J. A. Heinz & D. M. Soballe, 2004. Nitrification in the Upper Mississippi River: patterns, controls, and contribution to the nitrate budget. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 23: 1–14.
Strauss, E. A., W. B. Richardson, J. C. Cavanaugh, L. A. Bartsch, R. M. Kreiling & A. J. Standorf, 2006. Variability and regulation of denitrification in an Upper Mississippi River backwater. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 25: 596–606.
Tiedje, J. M., 1988. Ecology of denitrification and dissimilatory nitrate reduction to ammonium. In Zehnder, A. J. B. (ed.), Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms. John Wiley and Sons, New York, NY: 179–244.
Triska, F. J., J. H. Duff & R. J. Avanzino, 1990. Influence of exchange flow between the channel and hyporheic zone on nitrate production in a small mountain stream. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 47: 2099–2111.
Wall, L. G., J. L. Tank, T. V. Royer & M. J. Bernot, 2005. Spatial and temporal variability in sediment denitrification within an agriculturally influenced reservoir. Biogeochemistry 76: 85–111.
Zaman, M. & S. X. Chang, 2004. Substrate type, temperature, and moisture content affect gross N mineralization and nitrification rates in agroforestry systems. Biology and Fertility of Soils 39: 269–279.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kathryn Sjoholm, Ryan Heffel, and Denise Gibbens for assistance in collection and processing of samples; The Evans-White lab at the University of Arkansas for their thoughtful comments and suggestions during the editing process; The FHSU Department of Agriculture for land access; and the Western Kansas Center for Biotechnology and Bioinformatics for use of lab equipment and space. This study was funded by NSF EPSCoR Grant # EPS-0553722.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Deanne Drake
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Austin, B.J., Strauss, E.A. Nitrification and denitrification response to varying periods of desiccation and inundation in a western Kansas stream. Hydrobiologia 658, 183–195 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0462-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-010-0462-x