Abstract
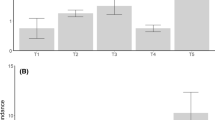
Although in situ sediment capping is frequently used to reduce internal loading of contaminants and nutrients, post-application assessment rarely includes the potential undesirable short-term effects on plankton species composition. We hypothesised that a modified zeolite (Z2G1) application as a sediment capping agent in Lake Okaro, New Zealand, could cause significant undesirable shifts in species composition of both zooplankton and phytoplankton due to burial of resting stages or interference with feeding for the zooplankton. Alternatively, we predicted that the capping agent might have no effect due to, for example, the coarse grain size of the material (1–3 mm). We used multidimensional scaling (MDS) and analysis of similarity (ANOSIM) to identify any adverse effects of Z2G1 on zooplankton and phytoplankton species composition (i.e. shifts in community structure, including species loss) by comparing the community structure before and after the Z2G1 application. We found no significant differences in species composition before and after the Z2G1 application at the depths investigated (surface and 9 m). However, all of the analyses showed statistically significant differences among seasons, indicating seasonal variations in plankton composition far outweigh those that may have resulted from the Z2G1 application. Coarse particle size, low dose rate and a restricted area where the sediment capping agent was applied were considered to be the factors limiting potential adverse effects on plankton species. Considerations of finer-grained material to increase coverage and efficacy of phosphorus adsorption require assessment for their effects on zooplankton, however, and a direct mode of application into the hypolimnion is recommended to minimise effects on zooplankton and phytoplankton communities.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey, S. A., I. C. Duggan, P. T. Jenkins & H. J. MacIsaac, 2005. Invertebrate resting stages in residual ballast sediment of transoceanic ships. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 1090–1103.
Baker, P. D. & L. D. Fabbro, 1999. A Guide to the Identification of Common Blue Green Algae (cyanoprokaryotes) in Australian Freshwaters. Co-operative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology, NSW, Australia: 42 pp.
Berg, U., T. Neumann, D. Donnert, R. Nüsch & D. Stüben, 2004. Sediment capping in eutrophic lakes – efficacy of undisturbed barriers to immobilize phosphorus. Applied Geochemistry 19: 1759–1771.
Burger, D. F., D. P. Hamilton, C. P. Pilditch & M. M. Gibbs, 2007. Benthic nutrient fluxes in a eutrophic, polymictic lake. Hydrobiologia 584: 13–25.
Chapman, M. A. & M. H. Lewis, 1976. An Introduction to the Freshwater Crustacea of New Zealand. Collins, Auckland: 261 pp.
Clarke, K. R. & R. M. Warwick, 2001. Changes in Marine Communities: An Approach to Statistical Analysis and Interpretation, 2nd ed. PRIMER-E, Plymouth.
Cooke, G. D., E. B. Welch, S. A. Peterson & P. R. Newroth, 1993. Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs, 2nd ed. CRC Press, Inc., Lewis Publishers, Boca Raton: 548 pp.
Cox, E. J., 1996. Identification of Freshwater Diatoms from Live Material. Chapman and Hall, London: 158 pp.
Duggan, I. C., J. D. Green & R. J. Shiel, 2002a. Distribution of rotifer assemblages in North Island, New Zealand, lakes: relationships to environmental and historical factors. Freshwater Biology 47: 195–206.
Duggan, I. C., J. D. Green & R. J. Shiel, 2002b. Rotifer resting egg densities in lakes of different trophic state, and their assessment using emergence and egg counts. Archiv für Hydrobiologie 153: 409–420.
Förstner, U. & S. E. Apitz, 2007. Sediment remediation: U.S. focus on capping and monitored natural recovery. Journal of Soils and Sediments 7: 351–358.
Forsyth, D. J., S. J. Dryden, M. R. James & W. F. Vincent, 1988. Lake Okaro ecosystem 1. Background limnology. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 49: 21–31.
Gensemer, R. W. & R. Playle, 1999. The bioavailability and toxicity of aluminium in aquatic environments. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology 29: 315–450.
Gulati, R. D. & W. R. Demott, 1997. The role of food quality for zooplankton: remarks on the state-of-the-art, perspectives and priorities. Freshwater Biology 38: 753–768.
Hamilton, D. P., 2005. Land use impacts on nutrient export in the Central Volcanic Plateau, North Island. New Zealand Journal of Forestry 49: 27–31.
Hart, R. C., 1986. Zooplankton abundance, community structure and dynamics in relation to inorganic turbidity, and their implications for a potential fishery in subtropical Lake le Roux, South Africa. Freshwater Biology 16: 351–371.
Hickey, C. W. & M. M. Gibbs, 2009. Lake sediment phosphorus release management – decision support and risk assessment framework. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 43: 819–856.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, K. E. Havens, O. Anneville, L. Carvalho, M. F. Coveney, R. Deneke, M. T. Dokulil, B. Foy, D. Gerdeux, S. E. Hampton, S. Hilt, K. L. Kangur, J. K. Hler, E. H. H. R. Lammens, T. L. Lauridsen, M. Manca, M. A. R. Miracle, B. Moss, P. N. Ges, G. Persson, G. Phillips, B. Portielje, S. Romo, C. L. Schelske, D. Straile, I. Tatrai, E. Wille & M. Winder, 2005. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading – an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshwater Biology 50: 1747–1771.
John, D. M., B. A. Whitton & A. J. Brook, 2003. The Freshwater Algal Flora of the British Isles: An Identification Guide to Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 702 pp.
Jolly, V. H., 1977. The comparative limnology of some New Zealand lakes. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 11: 307–340.
Kirk, K. L., 1991. Inorganic particles alter competition in grazing plankton: the role of selective feeding. Ecology 72: 915–923.
Klapper, H., 2003. Technologies for lake restoration. Journal of Limnology 62: 73–90.
Lamb, D. S. & G. C. Bailey, 1981. Acute and chronic effects of alum to midge larva (Diptera: Chironomidae). Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 27: 59–67.
Lloyd, E. F., 1959. The hot springs and hydrothermal eruptions of Waiotapu. New Zealand Journal of Geology and Geography 2: 141–176.
McColl, R. H. S. & H. R. Hughes, 1981. The Effects of Land Use on Water Quality – a Review. Water and Soil Miscellaneous Publication 23. Ministry of Works and Development, Wellington: 59 p.
Paul, W. J., D. P. Hamilton & M. M. Gibbs, 2008. Low-dose alum application trialled as a management tool for internal nutrient loads in Lake Okaro, New Zealand. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 42: 207–217.
Pilgrim, M. P., B. J. Huser & P. L. Brezonik, 2007. A method for comparative evaluation of whole-lake and inflow alum treatment. Water Research 41: 1215–1224.
Prescott, G. W., 1978. How to Know Freshwater Algae, 3rd ed. Wm. C. Brown Publishers, Iowa: 293 pp.
Randall, S., D. Harper & B. Brierley, 1999. Ecological and ecophysiological impacts of ferric dosing in reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 395/396: 355–364.
Reynolds, C. S., 1998. What factors influence the species composition of phytoplankton in lakes of different trophic status? Hydrobiologia 369/370: 11–26.
Robb, M., B. Greenop, Z. Goss, G. Douglas & J. A. Adeney, 2003. Application of Phoslock™, an innovative phosphorus binding clay, to two Western Australian waterways: preliminary findings. Hydrobiologia 494: 237–243.
Ryan, E. F., I. C. Duggan, D. P. Hamilton & D. F. Burger, 2006. Phytoplankton assemblages in North Island lakes of New Zealand: is trophic state, mixing, or light climate more important? Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 40: 389–398.
Rydin, E., B. Huser & E. B. Welch, 2000. Amount of phosphorus inactivated by alum treatments in Washington Lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 226–230.
Schumaker, R. J., W. H. Funk & B. C. Moore, 1993. Zooplankton responses to aluminum sulphate treatment of Newman Lake, Washington. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 8: 375–387.
Shiel, R. J., 1995. A Guide to the Identification Of Rotifers, Cladocerans and Copepods from Australian Inland Waters. Co-operative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology, Murray-Darling Freshwater Research Centre, Albury, NSW: 144 pp.
Søndergaard, M., J. P. Jensen & E. Jeppesen, 2003. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 506: 135–145.
Tanner, C. C., K. Caldwell, D. Ray & J. McIntosh, 2007. Constructing wetlands to treat nutrient-rich inflow to Lake Okaro, Rotorua. Proceedings of Stormwater 2007: 5th South Pacific Stormwater Conference, 16–18th May, Auckland, New Zealand.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Toward the improvement of the qualitative phytoplankton method. Mitteilungen. Internationale Vereinigung für Limnologie 9: 1–38.
Vandekerkhove, J., B. Niessen, S. Declerck, E. Jeppesen, J. M. C. Porcuna, L. Brendonck & L. De Meester, 2004. Hatching rate and hatching success with and without isolation of zooplankton resting stages. Hydrobiologia 526: 235–241.
Vincent, W. F. (ed.), 1987. Forum on cyanobacterial dominance. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 21: 361–542.
White, E., B. J. Don, M. T. Downes, L. J. Kemp, A. L. MacKenzie & G. W. Payne, 1978. Sediments of Lake Rotorua as sources and sinks for plant nutrients. New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 12: 121–130.
Yamada, H., M. Kayama, K. Saito & M. Hara, 1987. Suppression of phosphate liberation from sediment by using iron slag. Water Research 21: 325–333.
Acknowledgements
The first author was funded with a Ph.D. scholarship within the Lake Biodiversity Restoration program funded by the N.Z. Foundation of Research, Science and Technology (Contract UOWX 0505). We thank Britta Deichmann for assistance with phytoplankton identifications and Michael Landman at Scion Research for helpful comments on this article. We gratefully acknowledge Environment Bay of Plenty and Scion for funding assistance. We are grateful to the two anonymous referees whose comments greatly improved the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: D. P. Hamilton, M. J. Landman / Lake Restoration: An Experimental Ecosystem Approach for Eutrophication Control
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkundakci, D., Duggan, I.C. & Hamilton, D.P. Does sediment capping have post-application effects on zooplankton and phytoplankton?. Hydrobiologia 661, 55–64 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9938-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-9938-y