Abstract
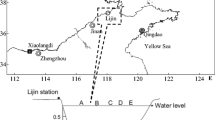
The Huanghe River (Yellow River) had been the second largest river in the world in terms of sediment load to the sea; however, the river water discharge and sediment flux to the sea and their seasonal variability have been significantly altered by the dam activities and recent water–sediment regulation. These changes are believed to have important impacts on the flux of phosphorus that is generally transported in particulate form. In this article, the samples of suspended particulate matter (SPM) were collected at the Lijin Station during two high-discharge events in 2005 and were separated by particle size. Sequential extractions were applied to determine the forms of P in different particle size fractions and to assess the potential bio-availability of particulate phosphorus (PP). Based on the in-laboratory measurement, the impacts of different hydrological regimes on the source of PP and its bio-availability were also analyzed. The results indicate that exchangeable, organic, authigenic, and refractory P were preferentially associated with clay, very fine, and fine silt fractions. Detrital P was mainly associated with the medium and coarse silt fractions. Detrital P and authigenic P (two forms of calcium bound phosphorus) were the dominant fractions in all samples. Thus, the potential bio-available PP (exchangeable P and organic P) was mainly associated with the finer particles, such as clay. Higher content of exchangeable, organic, authigenic, and residual P and lower content of detrital P were found during the period of rainstorm compared to that of WSR. P forms and partitioning of P forms among different particle size fractions were assumed to depend on the sources of SPM. It is likely that the pathways and fates of PP forms were controlled by damming and by the related changes of hydrological regime. Therefore, anthropogenic changes of hydrological regime and particle size dominanted the amount and distribution pattern of bio-available P transportation to the estuary and the adjacent sea, which will have profound impacts on the marine ecosystems at the Huanghe River Estuary and even the Bohai Sea.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrov, Y., J. B. Laronne & I. Reid, 2003. Suspended sediment transport in flash floods of the semiarid northern Negev, Israel. IAHS Publication 278: 346–352.
Andrieux-Loyer, F. & A. Aminot, 2001. Phosphorus forms related to sediment grain size and geochemical characteristics in French coastal areas. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science 52: 617–629.
Asselman, N., 1999. Suspended sediment dynamics in a large drainage basin: the river Rhine. Hydrological Processes 13: 1437–1450.
Benitez-Nelson, C. R., 2000. The biogeochemical cycling of phosphorus in marine systems. Earth-Science Review 51: 109–135.
Bergamaschi, B. A., E. Tsamakis, R. G. Keil, T. I. Eglinton, D. B. Montlucon & J. I. Hedges, 1997. The effect of grain size and surface area on organic mater, lignin and carbohydrate concentration, and molecular compositions in Peru margin sediments. Geochimica Cosmochimica Acta 61(6): 1247–1260.
Beusen, A. H. W., A. L. M. Dekkers, A. F. Bouwman, W. Ludwig & J. Harrison, 2005. Estimation of global river transport of sediments and associated particulate C, N, and P. Global Biogeochemical Cycles 19: GB4S05, doi:10.1029/2005GB002453.
Bowes, M. J., W. A. House & R. A. Hodgkinson, 2003. Phosphorus dynamics along a river continuum. The Science of the Total Environment 313: 199–212.
Cristian, T. & W. Bernhard, 2005. Retention of sediments and nutrients in the Iron Gate Reservoir on the Danube River. Biogeochemistry 76: 539–565.
Froelich, P. N., M. L. Bender, N. A. Luedtke, G. R. Heath & T. Devries, 1982. The marine phosphorus cycle. American Journal of Science 282: 474–511.
Garnier, J., B. Leporcq, N. Sanchez & X. Philippon, 1999. Biogeochemical mass-balance (C, N, P, Si) in three large reservoirs of the Seine Basin (France). Biogeochemistry 47: 119–146.
Gomez, B., J. D. Phillips, F. J. Magilligan & L. A. James, 1997. Floodplain sedimentation and sensivity: summer 1993 flood, Upper Mississippi River Valley. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms 22: 923–936.
Horowitz, A. J., 1991. A primer on sediment-trace element chemistry, 2nd ed. Lewis Publisher Inc, Chelsea MN.
Howarth, R. W., H. S. Jensen, R. Marino & H. Postma, 1995. Transport to and processing of P in nearshore and oceanic waters. In Tiessen, H. (ed.), Phosphorus in the Global Environment. Wiley, New York: 323–328.
Humborg, C., V. Ittekkot, A. Cociasu & B. v. Bodungen, 1997. Effect of Danube River dam on Black Sea biogeochemistry and ecosystem structure. Nature 386: 385–388.
Hudson, P. F., 2003. Event sequence and sediment exhaustion in the lower Panuco Basin, México. Catena 52: 57–76.
Jensen, H., T. Bendixen & F. Ø. Andersen, 2006. Transformation of particle-bound phosphorus at the land-sea interface in a Danish estuary. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 6(5–6): 547–555.
Jordan-Meille, L., J. M. Dorioz & N. Mathieu, 1998. An artificial flood to determine the hydrological network’s contribution to phosphorus exports in a small rural watershed. Water Research 32(6): 1801–1810.
Keil, R. G., L. M. Mayer, P. D. Quay, J. E. Richey & J. I. Hedges, 1997. Loss of organic matter from riverine particles in deltas. Geochimica Cosmaochimica Acta 61(7): 1507–1511.
Kelly, V. J., 2001. Influence of reservoir solute transport: a regional-scale approach. Hydrological Processes 15: 1227–1249.
Koch, M. S., R. E. Benz & D. T. Rudnick, 2001. Solid-phase phosphorus pools in highly organic carbonate sediments of northeastern Florida Bay. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 52: 279–291.
Krein, A. & M. Schorer, 2000. Road runoff pollution by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and its contribution to river sediments. Water Research 34(16): 4110–4115.
Li, G. Y., 2002. The Yellow River water and sediment regulation. The Yellow River 24(11): 1–5. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Li, G. Y., 2006. Regulation of water and sediment for the Yellow River based on joint operation of reservoirs and artificial intervention. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering 37(12): 1439–1446. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Liu, S. M., J. Zhang & D. J. Li, 2004. Phosphorus cycling in sediments of the Bohai and Yellow Seas. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 59: 209–218.
Liu, L. F., L. Z. Zhang & X. S. Zhang, 2006. Particulate organic carbon content in size-fractioned total suspended solids at Lijin hydrographic station of the Huanghe River. Periodical of Ocean University of China 36(Suppl): 126–130. (in Chinese with English abstract).
Mossa, J., 1996. Sediment dynamics in the lowermost Mississippi River. Engineering Geology 45: 457–479.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica Chimica Acta 27: 31–36.
Nixon, S. W., 2003. Replacing the Nile: are anthropogenic nutrients proving the fertility once brought to the Mediterranean by a great river? Ambio 32(1): 30–39.
Nixon, S. W., 2004. The artificial Nile. American Scientist 92: 158–165.
Pacini, N. & R. Gächter, 1999. Speciation of riverine particulate phosphorus during rain events. Biogeochemistry 47: 87–109.
Rabalais, N. N., W. J. Wiseman, R. E. Turner, B. K. Sen Gupta & Q. Dortch, 1996. Nutrient changes in the Mississippi River and system responses on the adjacent continental shelf. Estuaries 19: 386–407.
Ruttenberg, K. C., 1992. Development of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 37(7): 1460–1480.
Sherman, B., P. Ford, P. Hatton, J. Whittington, D. Green, D. Baldwin, R. Oliver, R. Shiel, J. van Berkel, R. Beckett, L. Grey & B. Maher, 2001. The Chaffey Dam Story. Final Report for CRCFE Projects B.202 and B.203. Cooperative Research Centre for Freshwater Ecology, University of Canberra, ACT, Australia.
Steegen, A., G. Govers, J. Nachtergaele, I. Takken, L. Beuselinck & J. Poesen, 2000. Sediment export by water from an agricultural catchment in the Loam Belt of central Belgium. Geomorphology 33: 25–36.
Stone, M. & A. Mudroch, 1989. Effect of particle size, chemistry and mineralogy of river sediments on phosphate adsorption. Environmental Technology Letters 10(5): 501–510.
Stone, M. & M. C. English, 1993. Geochemical composition, phosphorus speciation and mass transport of fine-grained sediment in two lake Erie tributaries. Hydrobiologia 253(1–3): 17–29.
Udden, J. A., 1914. Mechanical composition of clastic sediments. Bulletin of the Geological Society of America 25: 655–744.
Vink, S., R. M. Chambers & S. V. Smith, 1997. Distribution of phosphorus in sediments from Tomales Bay, California. Marine Geology 139: 157–179.
Walling, D. E. & J. C. Woodward, 1993. Use of a field-based water elutriation system for monitoring the in situ particle size characteristics of fluvial suspended sediment. Water Research 23(9): 1413–1421.
Wang, H. J., Z. S. Yang, N. S. Bi & H. D. Li, 2005. Rapid shifts of the river plume pathway off the Huanghe (Yellow) River mouth in response to water-sediment regulation scheme in 2005. Chinese Science Bulletin 50(24): 2878–2884.
Wentworth, C. K., 1922. A scale of grade and class terms for clastic sediments. Journal of Geology 30: 377–392.
Xu, J. X., 2002. River sedimentation and channel adjustment of the lower Yellow River as influenced by low discharges and seasonal channel dry-up. Geomorphology 43: 151–164.
Yu, Z. G., T. Z. Mi, Q. Z. Yao, B. D. Xie & J. Zhang, 2001. Nutrients concentration and changes in decade-scale in the central Bohai Sea. Acta Oceanologica Sinica 20(1): 65–75.
Acknowledgments
This study was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40876038 and No. 40976044) and the National Basic Research Program of China (973) (2002CB12405). We thank Professor Xiuli Feng for the assistance in particle size analyses and Professor Houjie Wang for useful comments. The authors express their gratitude to Professor Pierluigi Viaroli, Professor Koen Martens, and anonymous reviewers for the critical comments, corrections, and suggestions, which helped improve the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Pierluigi Viaroli
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huijun, H., Zhigang, Y., Qingzheng, Y. et al. The hydrological regime and particulate size control phosphorus form in the suspended solid fraction in the dammed Huanghe (Yellow River). Hydrobiologia 638, 203–211 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0041-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-009-0041-1