Abstract
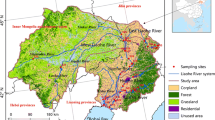
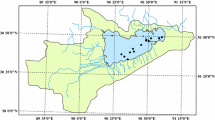
Absorptions by non-phytoplankton particles and phytoplankton, and chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) were measured at 50 sites in large, shallow, Lake Taihu in winter and summer 2006 to study their seasonal and spatial variations, and their relative contributions to total absorption. The CDOM absorption was significantly higher in winter than in summer, due to degradation and release of fixed carbon in phytoplankton and submerged aquatic vegetation (SAV). The hyperbolic model was used to model the spectral absorption of CDOM, and the mean spectral slope of 6.38 nm−1 was obtained. At most sites, the spectral absorption of non-phytoplankton particles was similar to that of the total particles, demonstrating that the absorption of the total particles is dominated by the absorption of non-phytoplankton particles. In summer, phytoplankton absorption increased markedly, due to frequent algal blooms especially in Meiliang Bay. In winter, the significant increase in non-phytoplankton particle absorption resulted from the increase of inorganic particulate matter caused by sediment resuspension. Strong linear relationships were found between a d(440) and total suspended matter (TSM), organic suspended matter (OSM), and inorganic suspended matter (ISM). Strong linear relationships were also found between a ph(440), a ph(675) and chlorophyll a (Chl-a) concentration. The total relative contributions of non-phytoplankton particles over the range of photosynthetically active radiation (PAR) (400–700 nm) were 48.4 and 79.9% in summer and winter respectively. Non-phytoplankton particle absorption dominated the total absorption, especially in winter, in Lake Taihu, due to frequent sediment resuspension in the large shallow lake as a result of strong windy conditions. The results indicate that strong absorption by CDOM and non-phytoplankton particles at the blue wavelength has an impact on the spectral availability, and acts as a selection factor for the composition of the phytoplankton community, with cyanobacteria being the dominate species in Lake Taihu.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a(λ), ap(λ), ad(λ), aph(λ), aCDOM(λ), aw(λ):
-
Spectral absorption coefficient of total, total particles, non-phytoplankton particles, phytoplankton, CDOM and pure water, respectively (m−1)
- Chl-a :
-
Chlorophyll a concentration (μg l−1)
- PAR:
-
Photosynthetically available radiation (400–700 nm)
- S, Sd:
-
The absorption spectral slope of CDOM and non-phytoplankton particles
- SAV:
-
Submerged aquatic vegetation
- TSM, OSM, ISM:
-
Total, organic and inorganic suspended matter concentration, respectively (mg l−1)
References
Babin, M., D. Stramski, G. M. Ferrari, H. Claustre, A. Bricaud, G. Obolensky & N. Hoepffner, 2003. Variations in the light absorption coefficients of phytoplankton, nonalgal particles, and dissolved organic matter in coastal waters around Europe. Journal of Geophysical Research 108: 1–20.
Bannister, T. T., 1974. Production equations in terms of chlorophyll concentration, quantum yield, and upper limit to production. Limnology and Oceanography 19: 1–12.
Bricaud, A., A. Morel & L. Prieur, 1981. Absorption by dissolved organic matter of the sea (yellow substance) in the UV and visible domain. Limnology and Oceanography 26: 43–53.
Bricaud, A., A. Morel, M. Babin, K. Allali & H. Claustre, 1998. Variations of light absorption by suspended particles with chlorophyll a concentration in oceanic (case 1) waters: analysis and implications for bio-optical models. Journal of Geophysical Research 103: 31033–31044.
Bricaud, A., M. Babin, A. Morel & H. Claustre, 1995. Variability in the chlorophyll-specific absorption coefficients of natural phytoplankton: analysis and parameterization. Journal of Geophysical Research 100: 13321–13332.
Cao, W. X., Y. Z. Yang, X. Q. Xu, L. M. Huang & J. L. Zhang, 2003. Regional patterns of particulate spectral absorption in the Pearl River estuary. Chinese Science Bulletin 48: 2344–2351.
Chen, Y. W., B. Q. Qin, K. Teubner & M. T. Dokulil, 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 445–453.
Churilova, T. Y., 2001. Light absorption by phytoplankton and detritus in the Black Sea in spring. Oceanology, 41: 687–695.
Cleveland, J. S. & A. D. Weidemann, 1993. Quantifying absorption by aquatic particles: A multiple scattering correction for glass-fiber filters. Limnology and Oceanography 38: 1321–1327.
Cleveland, J. S., 1995. Regional models for phytoplankton absorption as a function of chlorophyll a concentration. Journal of Geophysical Research 100: 13333–13344.
Etheridge, S. M. & C. S. Roesler, 2004. Temporal variations in phytoplankton, particulates, and colored dissolved organic material based on optical properties during a Long Island brown tide compared to an adjacent embayment. Harmful Algae 3: 331–342.
Feng, S., Y. L. Zhang & B. Q. Qin, 2006. Photochemical degradation of chromophoric dissolved organic matter in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu. China Environmental Science, 26(4), 404–408 [In Chinese with English abstract].
Gallegos, C. L., 2005. Optical water quality of a blackwater river estuary: The Lower St. Johns River, Florida, USA. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 63: 57–72.
Green, S. & N. Blough, 1994. Optical absorption and fluorescence properties of chomophoric dissolved organic matter in natural waters. Limnology and Oceanography 39: 1903–1916.
Hoepffner, N. & S. Sathyendranath, 1993. Determination of the major groups of phytoplankton pigments from absorption spectra of total particulate matter. Journal of Geophysical Research 98: 22789–22803.
Hojerslev, N. K. & E. Aas, 2001. Spectral light absorption by yellow substance in the Kattegat- Skagerrak area. Oceanologia 43: 39–60.
Kirk, J. T. O., 1994. Light and photosynthesis in aquatic ecosystem. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, Britain.
Kishino, M., C. R. Booth & N. Okami, 1984. Underwater radiant energy absorbed by phytoplankton, detritus, dissolved organic matter, and pure water. Limnology and Oceanography, 29: 340–349.
Kishino, M., N. Okami, M. Takahashi & S. Ichimura, 1986. Light utilization efficiency and quantum yield of phytoplankton in a thermally stratified sea. Limnology and Oceanography 31: 557–566.
Kowalczuk, P., W. J. Cooper, R. F. Whitehead, M. J. Durako & W. Sheldon, 2003. Characterization of CDOM in an organic-rich river and surrounding coastal ocean in the South Atlantic Bight. Aquatic Science 65: 384–401.
Krause-Jensen, D. & K. Sand-Jensen, 1998. Light attenuation and photosynthesis of aquatic plant communities. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 396–407.
Magnusona, A., L.W. Harding Jr., M. E. Mallonees, J. E. Adolf, 2004. Bio-optical model for Chesapeake Bay and the Middle Atlantic Bight. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 61: 403–424.
Megard, R..O., W. S. Combs, P. D. Smith & A. S. Knoll, 1979. Attenuation of light and daily integral rates of photosynthesis attained by planktonic algae. Limnology and Oceanography 24: 1038–1050.
Mishra, A. K. & D. P. Rao, 2002. Relationship between sub-surface diffused reflectance and inherent optical properties in coastal waters. International Journal of Remote Sensing 23: 477–488.
Mitchell, B. G., 1990. Algorithms for determining the absorption coefficient of aquatic particulates using the quantitative filter technique (QFT). SPIE, 1302: 137–148.
Moran, M. A., W. M. Sheldon Jr & R. G. Zepp, 2000. Carbon loss and optical property changes during long-term photochemical and biological degradation of estuarine dissolved organic matter. Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1254–1264.
Pope, R. M. & E. S. Fry, 1997. Absorption spectrum (380–700 nm) of pure water. II. Integrating cavity measurements. Applied Optics 36: 8710–8723.
Qin, B. Q., W. P. Hu & W. M. Chen, 2004. Process and mechanism of environment changes of the Taihu Lake. Beijing, Science Press, 1–10 [In Chinese].
Roesler, C. S., 1998. Theoretical and experimental approaches to improve the accuracy of particulate absorption coefficients derived from the quantitative filter technique. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 1649–1660.
Sasaki, H., S. I. Saitoh & M. Kishino, 2001. Bio-optical properties of seawater in the western subarctic Gyre and Alaskan Gyre in the subarctic north Pacific and the southern Bering sea. Journal of Oceanography 57: 275–284.
Sasaki, H., T. Miyamura, S. Saitoh & J. Ishizaka, 2005. Seasonal variation of absorption by particles and colored dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Funka Bay, southwestern Hokkaido, Japan. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 64: 447–458.
Scheffer, M., S. H. Hosper, M. L. Meijer, B. Moss & E. Jeppesen, 1993. Alternative equilibria in shallow lakes. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 8: 275–279.
Strömbeck, N. & D. C. Pierson, 2001. The effects of variability in the inherent optical roperties on estimations of chlorophyll a by remote ensing in Swedish freshwaters. The Science of the Total Environment 268: 123–37.
Tilstone, G. H., T. J. Smyth, R. J. Gowen, V. Martinez-Vicente & S. B. Groom, 2005. Inherent optical properties of the Irish Sea and their effect on satellite primary production algorithms. Journal of Plankton Research 27: 1–22.
Twardowski, M. S. & P. L. Donaghay, 2002. Photobleaching of aquatic dissolved materials: absorption removal, spectral alteration, and their interrelationship. Journal of Geophysical Research 107: 6.1–6.12.
Twardowski, M. S., E. Boss, J. M. Sullivan & P. L. Donaghay, 2004. Modeling the spectral shape of absorption by chromophoric dissolved organic matter. Marine Chemistry 89: 69–88.
Vähätalo, A. V., M. Salkinoja-Salonen, P. Taalas & K. Salonen, 2000. Spectrum of the quantum yield for photochemical mineralization of dissolved organic carbon in a humic lake. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 664–676.
Vähätalo, A. V., R. G. Wetzel & H. W. Paerl, 2005. Light absorption by phytoplankton and chromophoric dissolved organic matter in the drainage basin and estuary of the Neuse River, North Carolina (U.S.A.). Freshwater Biology 50: 477–493.
Van Dijk, G. M. & E. P. Achterberg, 1992. Light climate in the water column of a shallow eutrophic lake (Lake Veluwe) in the Netherlands. Archiv für Hydrobiologie, 125: 257–278.
Vodacek, A., N. V. Bloughl, M. D. DeGrandpre, E. T. Peltzer & R. K. Nelson, 1997. Seasonal variation of CDOM and DOC in the Middle Atlantic Bight: Terrestrial inputs and photooxidation. Limnology and Oceanography 42: 674–686.
Whitehead, R. F., S. De Mora, S. Demers, M. Gosselin, P. Monfort & B. Mostajir, 2000. Interactions of ultraviolet-B radiation, mixing, and biological activity on photobleaching of natural chromophoric dissolved organic matter: a mesocosm study. Limnology and Oceanography 45: 278–291.
Zhang, Y. L., B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu, G. Gao, L. C. Luo & W. M. Chen, 2006. Effect of sediment resuspension on underwater light field in shallow lakes in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River: A case study in Longgan Lake and Taihu Lake. Science in China Series D-Earth Science 49(Supp I): 114–125.
Zhang, Y. L., B. Q. Qin, W. M. Chen & G. W. Zhu, 2005. A preliminary study of chromophoric dissolved organic matter (CDOM) in Lake Taihu, a shallow subtropical lake in China. Acta Hydrochimica Et Hydrobiologica 33(4): 315–323.
Zhu, J. H. & T. J. Li, 2004. Spectral mode research about absorption coefficient of the de-pigment particles and yellow substance in Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Ocean Technology, 23: 7–13 (In Chinese with English Abstract).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences entitled “Key technology research on hyperspectral remote sensing of three typical water quality parameters in inland waters” (KZCX3-SW-350). We would like to express our deep thanks to Dr. Poynton S. L. for checking the English language and two anonymous reviewers for their useful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: L. Naselli-Flores
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, B., Wang, X. et al. A study of absorption characteristics of chromophoric dissolved organic matter and particles in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 592, 105–120 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0724-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-007-0724-4