Abstract
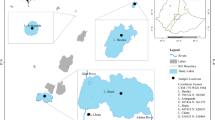
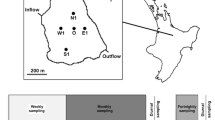
Chlorophyll a (Chl a) seasonality was investigated in four shallow eutrophic lakes located in north-central British Columbia (western Canada). Chlorophyll a concentration maxima in all four lakes occurred during the late summer/early autumn when near-surface total phosphorus ([Tot-P]) and total dissolved P concentrations, pH, and water temperature were highest. Mass balance and inferential analyses showed that bloom-triggering P loads came mostly from within-lake sources, but that mechanisms controlling internal loading in Charlie and Tabor (lakes having hypolimnetic oxygen deficits during summer) were fundamentally different than those in Nulki and Tachick (isothermal, well oxygenated lakes). Although the timing and intensity of major blooms were associated with late summer/early autumn P loads, average summer [Chl a] were predicted well by previously developed models based solely on spring overturn [Tot-P]. Instantaneous within-lake [Chl a] were best predicted by models incorporating both surface [Tot-P] and temperature (r 2 = 0.57–0.70). Moreover, [Tot-P] and temperature combined accounted for 57% of among-lake variations in instantaneous [Chl a]: log [Chl a] = 0.038 (°C) + 0.006 ([Tot-P]) + 0.203 (P < 0.001), where [Chl a] and [Tot-P] are in μg l−1. Positive associations between instantaneous [Chl a] and temperature support climate change models that forecast changes in phytoplankton productivity even if nutrient loading rates remain constant.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersen, J. M., 1974. Nitrogen and phosphorus budgets and the role of sediments in six shallow Danish lakes. Archiv fuer Hydrobiologie 74: 428–550.
Andersen, J. M., 1975. Influence of pH on release of phosphorus from lake sediments. Archiv fuer Hydrobiologie 76: 411–419.
Carignan, R. & D. R. S. Lean, 1991. Regeneration of dissolved substances in a seasonally anoxic lake: the relative importance of processes occurring in the water column and in the sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 36: 683–707.
Collos, Y., J. Husseini-Ratrema, B. Bec, A. Vaquer, T. Lam Hoai, C. Rougier, V. Pons & P. Souchu, 2005. Pheopigment dynamics, zooplankton grazing rates and the autumnal ammonium peak in a Mediterranean lagoon. Hydrobiologia 550: 83–93.
Cowan, J. L. W. & W. R. Boynton, 1996. Sediment-water oxygen and nutrient exchanges along the longitudinal axis of Chesapeake Bay: seasonal patterns, controlling factors and ecological significance. Estuaries 19: 562–580.
Dillon, P. J. & F. H. Rigler, 1974. The phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 19: 767–773.
Elliott, J. A., S. J. Thackeray, C. Huntingford & R. G. Jones, 2005. Combining a regional climate model with a phytoplankton community model to predict future changes in phytoplankton in lakes. Freshwater Biology 50: 1404–1411.
Farstad, L. & D. G. Laird, 1954. Soil survey of the Quesnel, Nechako Francois Lake and Bulkley-Terrace Areas in the central interior of British Columbia. Report No. 4 of the British Columbia Soil Survey.
Flanagan, K. M., E. McCauley, F. Wrona & T. Prowse, 2003. Climate change: the potential for latitudinal effects on algal biomass in aquatic ecosystem. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60: 635–639.
Glibert, P. M., J. H. Landsberg, J. J. Evans, M. A. Al-Sarawi, M. Faraj, M. A. Al-Jarallah, A. Haywood, S. Ibrahem, P. Klesius, C. Powell & C. Shoemaker, 2002. A fish kill of massive proportion in Kuwait Bay, Arabian Gulf, 2001: the roles of bacterial disease, harmful algae, and eutrophication. Harmful Algae 1: 215–231.
Gordon, N. D., T. A. McMahon & B. L. Finlayson, 1992. Stream hydrology, an introduction for ecologists. John Wiley & Sons, Toronto, ON, Canada, 529 pp.
Greenburg, L. S., L. S. Clescerti & A. D. Eaton (eds), 1992. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 18th edn. American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association and Water Environment Association, 1015 Fifteenth Street, NW, Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
Hecky, R. E., H. J. Kling & G. J. Brunskill, 1986. Seasonality of phytoplankton in relation to silicon cycling and interstitial water circulation in large, shallow lakes of central Canada. Hydrobiologia 138: 117–126.
Jacoby, J. M, D. D. Lynch, E. B. Welch & M. A. Perkins, 1982. Internal phosphorus loading in a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Research 16: 911–919.
Jensen, H. S. & F. Ø. Andersen, 1992. Importance of temperature, nitrate, and pH for phosphate release from aerobic sediments of four shallow, eutrophic lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 37: 577–589.
Johnson, P. T. J. & J. M. Chase, 2004. Parasites in the food web: linking amphibian malformations and aquatic eutrophication. Ecology Letters 7: 521–526.
Kamp-Nielsen, L., 1975. A kinetic approach to the aerobic sediment-water exchange of phosphorus in Lake Esrom. Ecological Modelling 1: 153–160.
Kenefick, S. L., S. E. Hrudey, E. E. Prepas, N. Motkosky & H. G. Peterson, 1992. Odorous substances and cyanobacterial toxins in prairie drinking water sources. Water Science & Technology 25: 147–154.
Koski-Vähälä, J., H. Hartikainen & P. Tallberg, 2001. Phosphorus mobilization from various sediment pools in response to increased pH and silicate concentration. Journal of Environmental Quality 30: 546–552.
Kotak, B. G., S. L. Kenefick, D. L. Fritz, C. G. Rousseaux, E. E. Prepas & S. E. Hrudey, 1993. Occurrence and toxicological evaluation of cyanobacterial toxins in Alberta lakes and farm dugouts. Water Research 27: 495–506.
Larson, D. P., D. W. Schults & K. W. Malueg, 1981. Summer internal phosphorus supplies in Shagawa Lake, Minnesota. Limnology and Oceanography 26: 740–753.
Lehman, J. T., 1980. Nutrient recycling as an interface between algae and grazers in freshwater communities. Special Symposium of the American Society of Limnology and Oceanography 3: 251–263 (New England). In Lehman, J.T. 1988. Hypolimnetic metabolism in Lake Washington: relative effects of nutrient load and food web structure on lake productivity. Limnology and Oceanography 33: 1334–1347.
Lund, J. W. G., 1955. Further observations on the seasonal cycle of Melosira italica (Ehr.) Kutz. subsp. subarctica o Mull. Journal of Ecology 43: 90–102.
Macedo, M. F., P. Duarte, P. Mendes & J. G. Ferreira, 2001. Annual variation of environmental variables, phytoplankton species composition and photosynthetic parameters in a coastal lagoon. Journal of Plankton Research 23: 719–732.
Markager, S., W. F. Vincent & E. P. Y. Tang, 1999. Carbon fixation by phytoplankton in high Arctic lakes: implications for low temperature for photosynthesis. Limnology and Oceanography 44: 597–607.
Megard, R. O. & P. D. Smith, 1974. Mechanisms that regulate growth rates of phytoplankton in Shagawa Lake, Minnesota. Limnology and Oceanography 19: 279–296.
Mortimer, C. H., 1971. Chemical exchanges between sediments and water in the Great Lakes – speculations on probable regulatory mechanisms. Limnology and Oceanography 16: 387–404.
Munawar, M & I. F. Munawar, 1986. The seasonality of phytoplankton in the North American Great lakes, a comparative synthesis. Hydrobiologia. 138: 85–115.
Nguyen, V. V. & E. F. Wood, 1979. On the morphology of summer algae dynamics in non-stratified lakes. Ecological Modelling 6: 117–131.
Nürnberg, G. K., 1984. The prediction of internal phosphorus load in lakes with anoxic hypolimnia. Limnology and Oceanography 29: 111–124.
Olila, O. G. & K. R. Reddy, 1995. Influence of pH on phosphorus retention in oxidized lake sediments. Soil Science Society of America Journal 59: 946–959.
Ostrofsky, M. L. & F. H. Rigler, 1987. Chlorophyll-phosphorus relationships for subarctic lakes in western Canada. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 44: 775–781.
Perkins, R. G. & G. J. C. Underwood, 2002. Partial recovery of a eutrophic reservoir through managed phosphorus limitation and unmanaged macrophyte growth. Hydrobiologia 481: 75–87.
Petticrew, E. L. & J. M. Arocena, 2001. Evaluation of iron-phosphate as a source of internal lake phosphorus loadings. Science of the Total Environment 266: 87–93.
Prepas, E. E. & D. O. Trew, 1983. Evaluation of the phosphorus-chlorophyll relationship for lakes off the Precambrian Shield in western Canada. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 40: 27–35.
Riley, E. T. & E. E. Prepas, 1984. Role of internal phosphorus loading in two shallow, productive lakes in Alberta, Canada. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 41: 845–855.
Schindler, D. W., 1977. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 195: 260–262.
Schindler, D. E. & M. D. Scheuerell, 2002. Habitat coupling in lake ecosystems. Oikos 98: 177–189.
Shaw, R. D., A. M. Trimbee, A. Minty, H. Fricker & E. E. Prepas, 1989. Atmospheric deposition of phosphorus and nitrogen in central Alberta with emphasis on Narrow Lake. Water, Air, and Soil Pollution 43: 119–134.
Simmons, S., 1997. Quantifying the major sinks and sources of phosphorus in Tabor Lake: implications for management and remediation. Master of Science Thesis, University of Northern British Columbia, Prince George, B.C., Canada, 157 pp.
Søndergaard, M., 1988. Seasonal variations in the loosely sorbed phosphorus fractions of the sediment of a shallow and hypereutrophic lake. Environmental Geology and Water Sciences 11: 115–121.
Vadeboncoeur, Y., E. Jeppesen, M. J. Vander Zanden, H. H. Schierup, K. Christofferson & D. M. Lodge, 2003. From Greenland to green lakes: cultural eutrophication and the loss of benthic pathways in lakes. Limnology and Oceanography 48: 1408–1418.
Wetzel, R. G. & G. E. Likens 1990 Limnological analyses. 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York, NY, USA, 391 pp.
Acknowledgements
Pacific Environmental Sciences Centre and Zenon Environmental Laboratories provided quality analytical services. Randy Tancock and Gregory Warren (B.C. Ministry of Environment, MoE) assisted with the sampling of Charlie Lake, Scott McIntosh (Saik’uz First Nation) assisted with Nulki–Tachick sampling, and Glen Blair (Tabor Lake Cleanup Society) coordinated Tabor Lake sampling. Dr. Frede Andersen (University of Southern Denmark), Dr. Stephanie Guildford (University of Waterloo), Bruce Carmichael (MoE), and an anonymous reviewer provided valued comments on drafts. Funding was provided by MoE and Forest Renewal B.C.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: D. Hamilton
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
French, T.D., Petticrew, E.L. Chlorophyll a seasonality in four shallow eutrophic lakes (northern British Columbia, Canada) and the critical roles of internal phosphorus loading and temperature. Hydrobiologia 575, 285–299 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0377-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0377-8