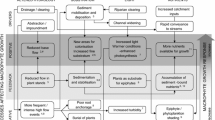
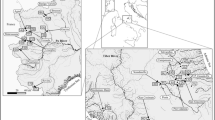
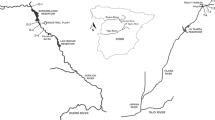
Abstract
The impact of altering hydro-morphology on three macrophyte community types was investigated at 107 European stream sites. Sites were surveyed using standard macrophyte and habitat survey techniques (Mean Trophic Rank Methodology and River Habitat Survey respectively). Principal Components Analysis shows the macrophyte community of upland streams live in a more structurally diverse physical habitat than lowland communities. Variables representing the homogeneity and diversity of the physical environment were used to successfully separate un-impacted from impacted sites, e.g. homogeneity of depth and substrate increased with decreasing quality class for lowland sites (ANOVA p < 0.05). Macrophyte attribute groups and structural metrics such as species richness were successfully linked to hydro-morphological variables indicative of impact. Most links were specific to each macrophyte community type, e.g., the attribute group liverworts, mosses and lichens decreased in abundance with increasing homogeneity of depth and decreasing substrate size at lowland sites but not at upland sites. Elodea canadensis, Sparganium emersum and Potamogeton crispus were indicative of impacted lowland sites. Many of the indicator species are also known to be tolerant to other forms of impact. The potential for a macrophyte tool indicative of hydro-morphological impact is discussed. It is concluded one could be constructed by combining indicator species and metrics such as species richness and evenness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Baattrup-Pedersen K. Szoszkiewicz R. Nijboer M. O’Hare T. Ferreira (2006) ArticleTitleMacrophyte communities in unimpacted European streams: variability in assemblage patterns, abundance and diversity Hydrobiologia 566 179–196
A. Baattrup-Pedersen S. E. Larsen T. Riis (2003) ArticleTitleComposition and richness of macrophyte communities in small Danish streams – influence of environmental factors and weed cutting Hydrobiologia 495 171–179 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1025442017837
A. Baattrup-Pedersen S. E. Larsen T. Riis (2002) ArticleTitleLong-term effects of stream management on plant communities in two Danish lowland streams Hydrobiologia 481 33–45 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1021296519187
A. Baattrup-Pedersen T. Riis (1999) ArticleTitleMacrophyte diversity and composition in relation to substratum characteristics in regulated and unregulated Danish streams Freshwater Biology 42 375–385 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.1999.444487.x
A. Brookes (1988) Channelized rivers: perspectives for environmental management John Wiley Chichester
P. A. Chambers E. E. Prepas H. R. Hamilton M. L. Bothwell (1991) ArticleTitleCurrent Velocity and Its Effect on Aquatic Macrophytes in Flowing Waters Ecological Applications 1 249–257 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1941754
F. H. Dawson P. J. Raven M. J. Gravelle (1999a) ArticleTitleDistribution of the morphological groups of aquatic plants for rivers in the U.K Hydrobiologia 415 123–130 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003859906618
F. H. Dawson J. R. Newman M. J. Gravelle K. J. Rouen P. Henville (1999b) Assessment of the Trophic Status of Rivers using Macrophytes: Evaluation of the Mean Trophic Rank R&D Technical Report E39, Environment Agency of England & Wales Bristol
Environment Agency, 2003. River Habitat Survey in Britain and Ireland. Field Survey Guidance Manual. Environment Agency
InstitutionalAuthorNameEuropean Commission (2000) Directive of the European Parliament and of the Council 2000/60/EC establishing a framework for Community action in the field of water policy European Commission PE-CONS 3639/1/00 REV 1 Luxembourg
A. M. Fox (1992) Macrophytes P. Calow G. E. Petts (Eds) The Rivers Handbook Hydrological and Ecological Principles Blackwell Scientific Publications Oxford 216–233
T. D. French P. A. Chambers (1996) ArticleTitleHabitat partitioning in riverine macrophyte communities Freshwater Biology 36 509–520 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.1996.00105.x
Furse, M., D. Hering, O. Moog, P. Verdonschot, R. K. Johnson, K. Brabec, K. Gritzalis, A. Buffagni, P. Pinto, N. Friberg, J. Murray-Bligh, J. Kokes, R. Alber, P. Usseglio-Polatera, P. Haase, R. Sweeting, B. Bis, K. Szoszkiewicz, H. Soszka, G. Springe, F. Sporka & I. Krno, 2006. The STAR project: context, objectives and approaches. Hydrobiologia 566: 3–29
S. M. Haslam (1978) River Plants: The macrophytic vegetation of watercourses Cambridge University Press Cambridge
K. Irvine (2004) ArticleTitleClassifying ecological status under the European Water Framework Directive: the need for monitoring to account for natural variability Aquatic conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 14 107–112 Occurrence Handle10.1002/aqc.622
R. H. G. Jongman C. J. F. Ter Braak O. F. R. Tongeren ParticleVan (1987) Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology Cambridge University Press Cambridge
P. Logan M. Furse (2002) ArticleTitlePreparing for the European Water Framework Directive - making the links between habitat and aquatic biota Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 12 425–437 Occurrence Handle10.1002/aqc.535
Minitab, 2004. Minitab 14.12.0 Release 14 Statistical software. Minitab Inc
G. E. Petts (1984a) The quality of reservoir releases G.E. Petts (Eds) Impounded Rivers: Perspectives for Ecological Management John Wiley & Sons Chichester 54–83
G. E. Petts (1984b) Vegetation reaction and structure G.E. Petts (Eds) Impounded Rivers: Perspectives for Ecological Management John Wiley & Sons Chichester 150–173
P. Pollard M. Huxham (1998) ArticleTitleThe European Water Framework Directive: a new era in the management of aquatic ecosystem health? Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Research 8 773–792 Occurrence Handle10.1002/(SICI)1099-0755(1998110)8:6<773::AID-AQC313>3.0.CO;2-R
P. J. Raven P. Fox M. Everard H. T. H. Holmes F. H. Dawson (1997) River Habitat Survey: a new system to classify rivers according to their habitat quality P. J. Boon (Eds) Freshwater Quality: Defining the Indefinable Scottish Natural Heritage, HMSO London 215–234
P. Scarlett M. T. O’Hare (2006) ArticleTitleCommunity structure of in-stream bryophytes in English and Welsh rivers Hydrobiologia 553 143–152 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-005-1078-4
S. Schneider A. Melzer (2003) ArticleTitleThe Trophic Index of Macrophytes (TIM) – A new tool for indicating the trophic status of running waters International Revue Hydrobiologie 88 49–67 Occurrence Handle10.1002/iroh.200390005
C. D. Sculthorpe (1967) The salient features of aquatic vascular plants C. D. Sculthorpe (Eds) The Biology of Aquatic Vascular Plants Spottiswode, Ballantyne London
A. M. Suren M. J. Duncan (1999) ArticleTitleRolling stones and mosses: effect of substrate stability on bryophyte communities in streams Journal of the North American Benthological Society 18 457–467 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1468378
Szoszkiewicz, K., T. Ferreira, T. Korte, A. Baattrup-Pedersen, J. Davy-Bowker & M. O’Hare, 2006. European river plant communities: the importance of organic pollution and the usefulness of existing macrophyte metrics. Hydrobiologia 566: 211–234
C. J. F. ter Braak P. Smilauer (1998) Canoco for Windows Microcomputer Power Ithaca
M. R. Vinson C. P. Hawkins (1998) ArticleTitleBiodiversity of stream insects: Variation at local, basin, and regional scales Annual Review of Entomology 43 271–293 Occurrence Handle15012391 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXktlagsw%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1146/annurev.ento.43.1.271
D. F. Westlake (1975) Macrophytes B. A. Whitton (Eds) River Ecology Blackwell Scientific Publications Oxford
J. F. Wright R. T. Clarke R. J. M. Gunn J. M. Winder N. T. Kneebone J. Davy-Bowker (2003) ArticleTitleResponse of the flora and macroinvertebrate fauna of a chalk stream site to changes in management Freshwater Biology 48 894–911 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2003.01058.x
J. F. Wright P. D. Hiley S. F. Ham A. D. Berrie (1981) ArticleTitleComparision of three mapping procedures developed for river macrophytes Freshwater Biology 11 369–379 Occurrence Handle10.1111/j.1365-2427.1981.tb01268.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
O’Hare, M.T., Baattrup-Pedersen, A., Nijboer, R. et al. Macrophyte communities of European streams with altered physical habitat. Hydrobiologia 566, 197–210 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0095-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0095-2