Abstract
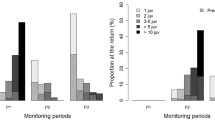
Redheads, Aythya americana, concentrate in large numbers annually in traditional wintering areas along the western and northern rim of the Gulf of Mexico. Two of these areas are the Laguna Madre of Texas and Chandeleur Sound of Louisiana. We collected data on 54,340 activities from 103 redhead flocks in Texas and 51,650 activities from 57 redhead flocks in Louisiana. Males and females fed similarly, differing neither in levels of feeding (percent of all birds in flock that were feeding) (p>0.90) nor in percentages of birds feeding by diving, tipping, dipping, or gleaning from the surface (p>0.10). The foraging level of redheads in the upper Laguna Madre region was relatively constant throughout two winters. Foraging of redheads in early winter in Louisiana was significantly greater than redhead foraging in the upper Laguna Madre, but by late winter, foraging by redheads in Louisiana had declined to the same level as that shown by redheads foraging in the upper Laguna Madre. The overall foraging level of redheads from Chandeleur Sound was greater (41%) than that of redheads in the upper Laguna Madre (26%), yet it was quite similar to the 46% foraging level reported for redheads from the lower Laguna Madre. Redheads in the upper Laguna Madre region of Texas fed more by diving than did those in the Chandeleur Sound and the lower Laguna Madre. Diving increased in frequency in late winter. Greater reliance by redheads on diving in January and February indicates that the birds altered their foraging to feed in deeper water, suggesting that the large concentrations of redheads staging at this time for spring migration may have displaced some birds to alternative foraging sites. Our results imply that the most likely period for food resources to become limiting for wintering redheads is when they are staging in late winter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adair, S. E., 1990. Factors influencing wintering diving duck use of coastal ponds in south Texas. Master of Science thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, U.S.A
S. E. Adair J. L. Moore W. H. Kiel SuffixJr. (1996) ArticleTitleWintering diving duck use of coastal ponds: an analysis of alternative hypotheses Journal of Wildlife Management 60 83–93
J. Altmann (1974) ArticleTitleObservational study of behavior: sampling methods Behaviour 49 227–267 Occurrence Handle4597405 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:CSuC28zhsFc%3D
F. C. Bellrose (1980) Ducks, Geese and Swans of North America Stackpole Books Harrisburg, Pennsylvania, U.S.A
J. F. Bergan L. M. Smith J. J. Mayer (1989) ArticleTitleTime-activity budgets of diving ducks wintering in South Carolina Journal of Wildlife Management 53 769–776
S. E. Cornelius (1977) ArticleTitleFood and resource utilization by wintering redheads on lower Laguna Madre Journal of Wildlife Management 41 374–385
S. E. Cornelius (1982) ArticleTitleWetland salinity and salt gland size in the Redhead Aythya americana Auk 99 774–778
R. B. Frederick E. E. Klaas (1982) ArticleTitleResource use and behavior of migrating snow geese Journal of Wildlife Management 46 601–614
J. W. Hedgpeth (1947) ArticleTitleThe Laguna Madre of Texas North American Wildlife Conference 12 364–380
G. R. Hepp (1985) ArticleTitleEffects of environmental parameters on the foraging behavior of three species of wintering dabbling ducks (Anatini) Canadian Journal of Zoology 63 289–294 Occurrence Handle10.1139/z85-044
H. D. Hoese R. S. Jones (1963) ArticleTitleSeasonality of larger animals in a Texas turtle grass community Publications of the Institute of Marine Science The University of Texas 9 37–47
W. N. Holmes J. G. Phillips (1985) ArticleTitleThe avian salt gland Biological Review 60 213–256
C. W. Jeske H. F. Percival (1995) ArticleTitleTime and energy budgets of wintering Ring-necked Ducks (Aythya collaris) in Florida, USA Wildfowl 46 109–118
D. G. Jorde G. L. Krapu R. D. Crawford (1983) ArticleTitleFeeding ecology of mallards wintering in Nebraska Journal of Wildlife Management 47 1044–1053
D. G. Jorde G. L. Krapu R. D. Crawford M. A. Hay (1984) ArticleTitleEffects of weather on habitat selection and behavior of mallards wintering in Nebraska Condor 86 258–265
D. G. Jorde R. B. Owen SuffixJr. (1988) The need for nocturnal activity and energy budgets of waterfowl M. W. Weller (Eds) Waterfowl in Winter University of Minnesota Press Minneapolis, MN, U.S.A
J. R. Lovvorn D. R. Jones (1991) ArticleTitleEffects of body size, body fat, and change in pressure with depth on buoyancy and costs of diving ducks (Aythya spp.) Canadian Journal of Zoology 69 2879–2887
J. B. Low (1945) ArticleTitleEcology and management of the Redhead, Nyroca americana, in Iowa Ecological Monographs 15 35–69 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1943294
C. A. McMahan (1970) ArticleTitleFood habits of ducks wintering on Laguna Madre, Texas Journal of Wildlife Management 34 946–949
Michot, T. C., 1997. Carrying capacity of seagrass beds predicted for Redheads wintering in Chandeleur Sound, Louisiana, USA. In Goss-Custard, J., R. Rufino & A. Luis (eds), Effect of Habitat Loss and Change on Waterbirds. Institute of Terrestrial Ecology Symposium no. 30, Wetlands International Publication no. 42: 93–102
Michot, T. C., 2000. Comparison of wintering Redhead populations in four Gulf of Mexico seagrass beds. In Comín, F. A., J. A. Herrera & J. Ramírez-Ramírez (eds), Limnology and Aquatic Birds: Monitoring, Modeling and Management. Second International Symposium on Limnology and Aquatic Birds: 243–260
T. C. Michot E. B. Moser W. Norling (1994) ArticleTitleEffect of weather and tides on feeding and flock positions of redheads wintering at the Chandeleur Islands, Louisiana Hydrobiologia 279/280 263–278 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00027860
T. C. Michot A. J. Nault (1993) ArticleTitleDiet differences in redheads from nearshore and offshore zones in Louisiana Journal of Wildlife Management 57 38–244
T. C. Michot M. C. Woodin S. E. Adair E. B. Moser (2006) ArticleTitleDiurnal time activity budgets of redheads (Aythya americana) wintering in seagrass beds and coastal ponds in Louisiana and Texas Hydrobiologia 567 113–128 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s10750-006-0058-7
R. Migoya G. A. Baldassarre M. P. Losito (1994) ArticleTitleDiurnal activity budgets and habitat functions of Northern Pintail (Anas acuta) wintering in Sinaloa, Mexico Wildfowl 45 134–146
M. R. Miller (1985) ArticleTitleTime budgets of northern pintails wintering in the Sacramento Valley, California Wildfowl 36 53–64
C. A. Mitchell (1992) ArticleTitleWater depth predicts redhead distribution in the lower Laguna Madre, Texas Wildlife Society Bulletin 20 420–424
C. A. Mitchell T. W. Custer P. J. Zwank (1992) ArticleTitleRedhead duck behavior on lower Laguna Madre and adjacent ponds of southern Texas Southwestern Naturalist 37 65–72
C. A. Mitchell T. W. Custer P. J. Zwank (1994) ArticleTitleHerbivory on shoalgrass by wintering Redheads in Texas Journal of Wildlife Management 58 131–141
Moore, J. L., 1991. Habitat-related activities and body mass of wintering Redhead Ducks on coastal ponds in south Texas. Master of Science thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, U.S.A
J. M. Morton A. C. Fowler R. L. Kirkpatrick (1989) ArticleTitleTime and energy budgets of American black ducks in winter Journal of Wildlife Management 53 401–410
S. L. Paulus (1984) ArticleTitleActivity budgets of nonbreeding gadwalls in Louisiana Journal of Wildlife Management 48 371–380
S. L. Paulus (1988a) Time-activity budgets of nonbreeding Anatidae: a review M. W. Weller (Eds) Waterfowl in Winter University of Minnesota Press Minneapolis, MN, U.S.A
S. L. Paulus (1988b) ArticleTitleTime-activity budgets of mottled ducks in Louisiana in winter Journal of Wildlife Management 52 711–718
H. Pöysä (1986) ArticleTitleSpecies composition and size of dabbling duck (Anas spp.) feeding groups; are foraging interactions important determinants? Ornis Fennica 63 33–41
Pulich, W. Jr., 1980. Ecology of a hypersaline lagoon: the Laguna Madre. In: Fore, P. L & R. D. Peterson (eds), Proceedings of the Gulf of Mexico coastal ecosystems workshop. U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service FWS/OBS-80/30: 103–122
M. L. Quammen C. P. Onuf (1993) ArticleTitleLaguna Madre: seagrass changes continue decades after salinity reduction Estuaries 16 302–310 Occurrence Handle10.2307/1352503
E. E. Quinlan G. A. Baldassarre (1984) ArticleTitleActivity budgets of nonbreeding green-winged teal on playa lakes in Texas Journal of Wildlife Management 48 838–845
D. P. Rave G. A. Baldassarre (1989) ArticleTitleActivity budget of green-winged teal wintering in coastal wetlands of Louisiana Journal of Wildlife Management 53 753–759
K. Schmidt-Nielsen (1975) Animal Physiology: Adaptation and Environment Cambridge University Press London, U.K
W. R. Siegfried (1976) ArticleTitleSegregation in feeding behaviour of four diving ducks in southern Manitoba Canadian Journal of Zoology 54 730–736 Occurrence Handle10.1139/z76-084
Skoruppa, M. K. & M. C. Woodin, 2000. Impact of wintering redhead ducks on pond water quality in southern Texas. In Comín, F. A., J. A. Herrera & J. Ramírez-Ramírez (eds), Limnology and Aquatic Birds: Monitoring, Modelling and Management. Second International Symposium on Limnology and Aquatic Birds: 243–260
N. P. Smith (1978) ArticleTitleIntracoastal tides of upper Laguna Madre, Texas Texas Journal of Science 30 85–95
R. G. D. Steel J. H. Torrie (1980) Principles and Procedures in Statistics EditionNumber2 McGraw-Hill Book Company New York, N.Y
R. Stephenson J. R. Lovvorn M. R. A. Heieis D. R. Jones R. W. Blake (1989) ArticleTitleA hydromechanical estimate of the power requirements of diving and surface swimming in lesser scaup (Aythya affinis) Journal of Experimental Biology 147 507–518
W. O. Stieglitz (1966) ArticleTitleUtilization of available foods by diving ducks on Apalachee Bay, Florida Proceedings of the Southeastern Association of Game and Fish Commissioners 20 42–50
A. Tamisier (1974) ArticleTitleEtho-ecological studies of teal wintering on the Camargue (Rhone Delta, France) Wildfowl 25 107–117
J. D. Thompson G. A. Baldassarre (1991) ArticleTitleActivity patterns of Nearctic dabbling ducks wintering in Yucatan, Mexico Journal of Wildlife Management 108 934–941
J. W. Tunnell SuffixJr. F. W. Judd (Eds) (2002) The Laguna Madre of Texas and Tamaulipas Texas A&M University Press College Station, Texas, U.S.A
Vollenweider, R. A. & J. J. Kerekes, 1980. Synthesis report, cooperative programme on monitoring of inland waters (eutrophication control). Reports prepared on behalf of Technical Bureau, Water Management Sector Group, Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Paris
M. W. Weller (1964) ArticleTitleDistribution and migration of the redhead Journal of Wildlife Management 28 64–103
Whitledge T. E. & W. M. Pulich Jr., 1991. Brown tide symposium and workshop, 15–16 July 1991. The University of Texas Marine Science Institute Technical Report No. TR/91–002, Port Aransas, Texas, U.S.A
M. C. Woodin (1994) ArticleTitleUse of saltwater and freshwater habitats by wintering redheads in southern Texas Hydrobiologia 279/280 279–287 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00027861
M. C. Woodin (1996) ArticleTitleWintering ecology of redheads (Aythya americana) in the western Gulf of Mexico region Gibier Faune Sauvage, Game and Wildlife 13 653–665
Woodin, M. C. & T. C. Michot, 2002. Redhead (Aythya americana). In Poole, A. & F. Gill (eds), The Birds of North America, no. 695
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woodin, M.C., Michot, T.C. Foraging behavior of redheads (Aythya americana) wintering in Texas and Louisiana. Hydrobiologia 567, 129–141 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0057-8
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-006-0057-8