Abstract
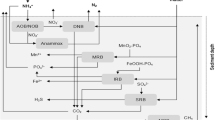
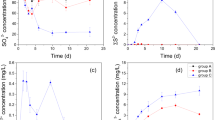
The interactions among sedimentary cycles of sulphur, iron and phosphorus were investigated in the eutrophic Sacca di Goro lagoon (Northern Adriatic coast, Italy) in order to assess the iron buffering capacity of the sediment. Three stations were chosen, which represented different primary producer communities, hydrodynamics and sediment characteristics. Station G was close to the outlet of the Po di Volano river, station 4 was in the central part of the lagoon under tidal influence and station 17, in the sheltered zone, was affected by macroalgal blooms. From January 1997 to January 1998, sediment cores were sampled approximately every 2 months. In parallel, temperature, salinity and dissolved oxygen were determined in the water column. Sedimentary profiles of Eh, pH, dissolved sulphide (DS), acid volatile sulphide (AVS), chromium reducible sulphur (CRS), iron and phosphorus pools were determined in the 0–10 cm sediment horizon. Bacterial sulphate reduction rates were measured only at station 17. Iron pools, AVS and CRS followed similar patterns at all the considered stations, with lower values in the 0–2 cm sediment horizon and peaks in the deepest sediment layer (5–10 cm horizon). Overall, the labile Fe accounted for an annual average of 115.6 ± 3.0 μmol cm−3, with peaks of labile ferric iron up to 40 μmol cm−3. The great iron availability and reactivity accounted for an efficient buffering capacity against sulphides, with the accumulation of AVS and CRS, specially at station G where the iron buffer was replenished by iron-rich freshwaters. At station 17, in spite of a great iron availability the buffering capacity was less efficient due to macroalgal blooms and accumulation of labile organic matter, whose decomposition stimulated bacterial sulfate reduction and the inherent sulphide production both in the pore-water (DS: 4.0 ± 3.7 mM) and in the deepest water column (DS: 85 μM). The iron and sulphur interactions had also implications for P cycling, since in summer the ferric iron reduction was accompanied by a significant increase of pore-water and exchangeable phosphates. The AVS to labile Fe and AVS to TRIS (AVS + CRS) ratios were used to assess the sediment capacity of precipitating and retaining sulphides. These ratios were then compared with the chemical buffer capacity, demonstrating their suitability as indicators of buffering capacity towards sulphides.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Albertazzi R. F. Bopp M. Frignani O. Heike Merlin L. Mengazzo Vituri M. Ravaioli H. J. Simpson L. Tassi Pelati C. Triulzi (1984) ArticleTitleCs-137 as a tracer for processes of marine sedimentation in the vicinity of the Po River Delta (Northern Adriatic Sea) Memorie della Società Geologica Italiana XXVII, 447–459
L. D. Anderson M. L. Delaney (2000) ArticleTitleSequential extraction and analysisi of phosphorus in marine sediments: stremlining of the SEDEX procedure Limnology and Oceanography 45 209–215
K. I. Aspila H. Agemian A. S. Y. Chau (1976) ArticleTitleA semiautomated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments Analyst 101 187–197 Occurrence Handle10.1039/an9760100187 Occurrence Handle1259177
R. Azzoni G. Giordani S. Gazzola M. Bonoli (1999) ArticleTitleAccumulation of phosphorus in relation to iron and sulphur contents in the surficial sediments of three coastal lagoons: Sacca di Goro, Valle Smarlacca (Italy) and Arcachon Bay (France) Proceedings of the Italian Association of Oceanography and Limnology 13 75–84
R. Azzoni G. Giordani M. Bartoli D.T. Welsh P. Viaroli (2001) ArticleTitleIron, sulphur and phosphorus cycling in the rhyzosphere sediments of a eutrophic Ruppia cirrhosa meadow of the Valle Smarlacca (Italy) Journal of Sea Research 45 15–26 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1385-1101(00)00056-3
A. Barbanti M. C. Bergamini F. Frascari S. G. Miserocchi Rosso (1994) ArticleTitleCritical aspects of sedimentary phosphorus chemical fractionation Journal of Environmental Quality 23 1093–1102
Bartoli M., G. Castaldelli, D. Nizzoli, L. G. Gatti, P. Viaroli, 2001. Benthic fluxes of oxygen, ammonium and nitrate and coupled-uncoupled denitrification rates within communities of three different primary producer growth forms. In Faranda F.M., Guglielmo L., G. Spezie (eds), Mediterranean Ecosystems: Structures and Processes. Springer Verlag, Milano, 29: 225–233
Bondavalli C., 1995. Ciclo di alcuni radionuclidi in un ambiente lagunare stressato. PhD thesis. Institute of Ecology, University of Parma, pp. 96
D. E. Canfield (1989) ArticleTitleReactive iron in sediments Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 53 619–632 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(89)90005-7 Occurrence Handle11539783
D. E Canfield R. Raiswell S. Bottreel (1992) ArticleTitleThe reactivity of sedimentary iron minerals towards sulphide American Journal of Science 292 659–683
Castel J., P. Caumette, R. Herbert, 1996. Eutrophication gradients in coastal lagoons as exemplified by the Bassin d’Arcachon and Étang du Prévost. In Caumette P., J. Castel & R. Herbert (eds), Coastal Lagoon Eutrophication and ANaerobic Processes (C.L.E.AN.). Hydrobiologia 329: ix–xxviii
R. M. Chambers J. W. Fourquren S. A. Macko R. Hoppenot (2001) ArticleTitleBiogeochemical effects of iron availability on primary producers in a shallow marine carbonate environment Limnology and Oceanography 46 IssueID6 1278–1286
J. D. Cline (1969) ArticleTitleSpectrophotometric determination of hydrogen sulphide in natural waters Limnology and Oceanography 14 454–459
J. E. Cloern (2001) ArticleTitleOur evolving conceptual model of the coastal eutrophication problem Marine Ecology Progress Series 210 223–253
R. Dal Cin P. Pambianchi (1991) I sedimenti della Sacca di Goro (Delta del Po) S. Bencivelli N. Castaldi (Eds) Studio Integrato Sull’ecologia Della Sacca di Goro Francoangeli Milano 253–263
C. J. De Groot ParticleDe H. L. Golterman (1990) ArticleTitleSequential fractionation of sediment phosphate Hydrobiologia 192 143–149 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00006010
R. de Wit Particlede L. J. Stal B. Aa. Lomstein R. A. Herbert H. Gemerden Particlevan P. Viaroli V. U. Ceccherelli F. Rodríguez-Valera M. Bartoli G. Giordani R. Azzoni B. Shaub D.T. Welsh A. Donnely A. Cifuentes J. Anton K. Finster L. B. Nielsen A. G. Underlien Pedersen A. T. Neubauer M. A. Colangelo S. K. Heijs (2001) ArticleTitleROBUST: The ROle of BUffering capacities in STabilising coastal lagoon ecosystems Continental Shelf Research 21 2021–2041 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0278-4343(01)00040-1
H. Fossing B. B. Jorgensen (1989) ArticleTitleMeasurement of bacterial sulphate reduction in sediment: evaluation of a single-step chromium reduction method Biogeochemistry 8 205–222 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00002889
G. Giordani M. Bartoli M. Cattadori P. Viaroli (1996) ArticleTitleSulphide release from anoxic sediments in relation to iron availability and organic matter recalcitrance and its effects on inorganic phosphorus recycling Hydrobiologia 329 211–222
G. Giordani R. Azzoni M. Bartoli P. Viaroli (1997) ArticleTitleSeasonal variations of sulphate reduction rates, sulphur pools and iron availability in the sediment of a dystrophic lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy) Water, Air and Soil Pollution 99 363–371
H. L. Golterman (1995) ArticleTitleThe role of the iron hydroxide-phosphate-sulphide system in the phosphate exchange between sediments and water Hydrobiologia 297 43–54 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00033500
H. L. Golterman (2001) ArticleTitlePhosphate release from anoxic sediments or “what did Mortimer really write?” Hydrobiologia 450 99–106 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1017559903404
E. Gomez C. Durillion G. Rofes B. Picot (1999) ArticleTitlePhosphate adsorption and release from sediments of brackish lagoons: pH, O2 and loading influence Water Research 33 2437–2447 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(98)00468-0
S. K. Heijs H. M. Jonkers H. Gemerden Particlevan B. E. M. Schaub L. J. Stal (1999) ArticleTitleThe buffering capacity towards free sulphide in sediment of a coastal lagoon (Bassin d’Arcachon, France): the relative importance of chemical and biological processes Estuarine Coastal Shelf Sciences 49 21–35 Occurrence Handle10.1006/ecss.1999.0482
S. K. Heijs H. Gemerden Particlevan (2000) ArticleTitleMicrobial and environmental variables involved in the sulfide buffering capacity along a eutrophication gradient in a coastal lagoon (Bassin d’Arcachon, France) Hydrobiologia 437 121–131 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1026590520603
S. K. Heijs R. Azzoni G. Giordani H. M. Jonkers D. Nizzoli P. Viaroli H. Gemerden Particlevan (2000) ArticleTitleSulphide-induced release of phosphate from sediments of coastal lagoons and the possible relation to the disappearance of Ruppia sp. Aquatic Microbial Ecology 23 85–95
M. A. Hemminga (1998) ArticleTitleThe root/rhyzome system of seagrasse: an asset and a burden Journal of Sea Research 39 183–196 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S1385-1101(98)00004-5
W. A. House F. H. Denison (2000) ArticleTitleFactors influencing the measurement of equilibrium phosphate concentrations in river sediments Water Research 34 1187–1200 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0043-1354(99)00249-3
R. W. Howarth J. W. B. Stewart (1992) The interactions of sulphur with other element cycles in ecosystems R. W., Howarth J. W. B. Stewart M. U. Ivanov (Eds) Sulphur cycling on the continents: wetlands, terrestrial ecosystems and associated water bodies: SCOPE 33 Wiley and Sons New York 67–84
H. S. Jensen K. J. McGlathery R. Marino R. W. Howarth (1998) ArticleTitleForms and availability of sediment phosphorus in carbonate sand of Bermuda seagrass beds Limnology and Oceanography 43 799–810
B. B. Jørgensen (1982) ArticleTitleMineralization of organic matter in the sea bed – the role of sulfate reduction Nature 296 643–645 Occurrence Handle10.1038/296643a0
M. S. Koch I. A. Mendelssohn K. L. McKee (1990) ArticleTitleMechanism for the hydrogen sulphide growth limitation in wetland macrophytes Limnology and Oceanography 35 399–408
M. D. Krom R. A. Berner (1981) ArticleTitleThe diagenesis of phosphorus in nearshore marine sediment Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 45 207–216 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0016-7037(81)90164-2
M. Kuhl B. B. Jorgensen (1992) ArticleTitleMicrosensor measurements of sulfate reduction and sulphide oxidation in compact microbial communities of aerobic biofilms Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58 1164–1174
D. R. Lovley E. J. P. Phillips (1987) ArticleTitleRapid assay for reducible ferric iron in aquatic sediments Applied and Environmental Microbiology 53 1536–1540
J. R. McLaughlin J. C. Ryden J. K. Syers (1981) ArticleTitleSorption of inorganic phosphate by iron- and aluminium-containing components Journal of Soil Science 32 365–377
J. Murphy J. P. Riley (1962) ArticleTitleA modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters Analytica Chimica Acta 27 31–36 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0003-2670(00)88444-5
S. W. Nixon (1995) ArticleTitleCoastal marine eutrophication: a definition, social causes and future concerns Ophelia 41 199–219
W. S. Reeburgh (1967) ArticleTitleAn improved interstitial water sampler Limnology and Oceanography 12 163–165
E. E. Roden J. W. Edmonds (1997) ArticleTitlePhosphate mobilization in iron-rich anaerobic sediments: microbial Fe(III) oxides reduction versus iron-sulphide formation Archiv fur Hydrobiologie 139 347–378
T. F. Rozan M. Taillefert R. E. Trouwborst B. T. Glazer S. Ma J. Herszage L. M. Valdes K. S. Price G. W. Luther SuffixIII (2002) ArticleTitleIron–sulphur–phosphorus cycling in the sediments of a shallow coastal bay: Implications for sediment nutrient release and benthic macroalgal blooms Limnology and Oceanography 47 1346–1354
K. C. Ruttemberg (1992) ArticleTitleDevelopment of a sequential extraction method for different forms of phosphorus in marine sediment Limnology and Oceanography 37 1460–1482
Schramm W. & P. H. Nienhuis, 1996. Marine Benthic Vegetation. Recent Changes and the Effects of Eutrophication. Springer, New York, pp. 470
Stal L. J., S. B. Behrens, M. Vilbrant, S. van Bergeijk, & F. Kruying, 1996. The biogeochemistry of two eutrophic marine lagoons and its effects on microphytobenthic communities. In Caumette P., Castel J., R. Herbert (eds), Coastal Lagoon Eutrophication and Anaerobic Processes (C.L.E.AN.). Hydrobiologia 329: 185–198
I. Valiela J. McLelland J. Hauxwell P. J. Behr D. Hersh K. Foreman (1997) ArticleTitleMacroalgal blooms in shallow estuaries: controls and ecophysiological and ecosystem consequences Limnology and Oceanography 42 1105–1118
Viaroli P., R. Azzoni, M. Bartoli, G. Giordani, & L. Tajè, 2001. Evolution of the trophic conditions and Dystrophic Outbreaks in the Sacca di Goro Lagoon (Northern Adriatic Sea). In Faranda F. M., L. Guglielmo, & G. Spezie (eds), Structures and Processes in the Mediterranean Ecosystems. Springer Verlag, Milano, 59: 467–475
P. Viaroli M. Bartoli G. Giordani R. Azzoni D. Nizzoli (2003) ArticleTitleShort term changes of benthic fluxes during clam harvesting in a coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Po river delta) Chemistry and Ecology 19 189–206 Occurrence Handle10.1080/0275754031000119933
P. Viaroli M. Bartoli G. Giordani P. Magni D. T. Welsh (2004) ArticleTitleBiogeochemical indicators as tools for assessing sediment quality/vulnerability in transitional aquatic ecosystems Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 14 S19–S29 Occurrence Handle10.1002/aqc.647
Viaroli P., M. Bartoli, R. Azzoni, G. Giordani, C. Mucchino, M. Naldi, D. Nizzoli, & L. Tajé, 2005. Nutrient and iron limitation to Ulva blooms in an eutrophic coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy). Hydrobiologia 550: 57–71
Viaroli P., G. Giordani, M. Bartoli, M. Naldi, R. Azzoni, D. Nizzoli, I. Ferrari, J. M. Zaldívar, S. Bencivelli, G. Castaldelli, & E. A. Fano. The Sacca di Goro lagoon and an arm of the Po River. In Hutzinger, O., (Ed. in Chief), The Handbook of Environmental Chemistry, Vol. 5. Water pollution: estuaries. Volume editor: P.J. Wangersky, (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azzoni, R., Giordani, G. & Viaroli, P. Iron–sulphur–phosphorus Interactions: Implications for Sediment Buffering Capacity in a Mediterranean Eutrophic Lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Italy). Hydrobiologia 550, 131–148 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4369-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4369-x