Abstract
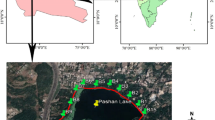
The present study describes generally the ecosystem of Lake Verevi while more detailed approaches are presented in the same issue. The main task of the article is to estimate long-term changes and find the best method for the restoration of good ecological status. Lake Verevi (surface 12.6 ha, mean depth 3.6 m, maximum depth 11 m, drainage area 1.1 km2, water exchange 0.63-times per year) is a hypertrophic hard-water lake located in town Elva (6400 inhabitants). Long-term complex limnological investigations have taken place since 1929. The lake has been contaminated by irregular discharge of urban wastewaters from oxidation ponds since 1978, flood from streets, and infiltrated waters from the surrounding farms. The so-called spring meromixis occurred due to extremely warm springs in recent years. The index value of buffer capacity of Lake Verevi calculated from natural conditions is on the medium level. Water properties were analysed according to the requirements of the EU Water Framework Directive. According to the classification, water quality as a long-term average of surface layers is moderate-good, but the water quality of bottom layers is bad. Values in deeper layers usually exceed 20–30 times the calculated reference values by Vighi and Chiaudani’s model. Naturally, at the beginning of the 20th century the limnological type of the lake was moderately eutrophic. During the 1980s and 1990s the ecosystem was out of balance by abiotic characteristics as well as by plankton indicators. Rapid fluctuations of species composition and abundance can be found in recent years. Seasonal variations are considerable and species composition differs remarkably also in the water column. The dominating macrophyte species vary from year to year. Since the annual amount of precipitation from the atmosphere onto the lake surface is several times higher, the impact of swimmers could be considered irrelevant. Some restoration methods were discussed. The first step, stopping external pollution, was completed by damming the inlet. Drainage (siphoning) of the hypolimnetic water is discussed. Secondary pollution occurs because Fe:P values are below the threshold. The authors propose to use phosphorus precipitation and hypolimnetic aeration instead of siphoning.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekin, O. A., 1959. Metody issledovaniya fizicheskih svojstv i himicheskovo svoistva vody In Pavlovski, E. N. & V. I. Zhadin, (eds), Zhizn’ presnyh vod SSSR. 4, 2: 213–300 [Methods for investigation of physical and chemical properties of water. In Russian].
Berge, D., 1993. Restaureringsstrategi for eutrofierte innsjøer. NIVA – rapport. 73 pp. [Restoration strategies for eutrophied lakes. In Norwegian].
S. Björk (1988) ArticleTitleRedevelopment of lake ecosystems – a case-study Approach –Ambio 17 IssueID2 90–98
Björk, S., 1994a. Planning and accomplishment of redevelopment and restoration projects. In Eiseltova’, M. (ed.), Restoration of Lake Ecosystems, A Holistic Approach, 59–61 pp.
Björk, S., 1994b. Restoration methods and techniques. Sediment removal. In: Eiseltova’, M. (ed.), Restoration of Lake Ecosystems, A Holistic Approach, 82–89 pp.
G. D. Cooke E. B. Welch S. A. Peterson P. R. Newroth (1993) Restoration and Management of Lakes and Reservoirs Lewis Publishers Boca Raton 548
W. G. Crumpton T. M. Isenhart P. D. Mitchell (1992) ArticleTitleNitrate and organic N analyses with second-derivative spectroscopy Limnology and Oceanography 37 IssueID4 907–913
P. Dawidowicz A. Perjs A. Engelmayer A. Martyniak J. Kozlowski L. Kufel M. Paradowska (2002) ArticleTitleHypolimnetic anoxia hampers top-down food-web manipulation in a eutrophic lake Freshwater Biology 47 2401–2409 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.01007.x
Eesti Loodus, 1995. Compiled by A. Raukas. Publishing Office “Valgus”. Tallinn. 606 pp. [Estonia. Nature. In Estonian, Russian and English summary].
Eesti Järved, 1968. Tallinn, “Valgus”. 532 pp. [Estonian lakes. In Estonian].
Eiseltova’, M., (ed.). 1994. Restoration of Lake Ecosystems, A Holistic Approach. Preface, 7–8 pp.
B. A. Faafeng Å. Brabrand (1990) ArticleTitleBiomanipulation of a small, urban lake – removal of fish exclude bluegreen blooms Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 24 597–602
B. A. Faafeng J. P. Nilssen (1981) ArticleTitleA twenty-year study of eutrophication in a deep Soft-water lake Verhandlungen Internationale Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie. 21 412–424
M. J Fall (1996) JENWAY Model 4150 Conductivity Meter manual Jenway Limited Gransmore Green, Felsted, Dunmow, Essex, CM6 3LB, England, 19 pp
Gollerbach, M. (eds), 1977. Zhizn rastenij. Tom Tretij. Vodorosli i lishainiki. Moskva, Prosveshtshenije p. 487 Life of plants. Third part. Algae and Lichens. In Russian.
Gulati, R. D., 1995a. Food-chain manipulation as a tool in management of small lakes in the Netherlands: The Lake Zwemlust example. In: Guidelines for Lake management. Vol. 7. de Bernardi R. & G. Giussani (eds), Biomanipulation in Lakes and Reservoirs management, 147–163 pp.
Gulati, R. D., 1995b. Manipulation of Fish Population for Lake Recovery from Eutrophication in the Temperate Region. In: Guidelines for Lake Management. Vol. 7. de Bernardi R. & G. Giussani (eds), Biomanipulation in Lakes and Reservoirs management, 53–81 pp.
H. P. Hansen F. Koroleff (1999) Determination of nutrients K. Grasshoff K. Kremling M. Ehrhardt (Eds) Methods of Seawater Analysis WILEY-VCH Weinheim. New York. Chichester. Brisbane. Singapore. Toronto 600
Heinonen, P., 1980. Quantity and composition of phytoplankton in Finnish Inland Waters. Publication of Water Research Institute, Helsinki, 37, 91.
K. Hellat A. Malirin L. Mei T. Tenno (1986) ArticleTitleMetrologicheskoe obespechenie sredstv analiza kisloroda v vode Acta et commentationes Universitatis Tartuensis 757 184–193
G. E. Hutchinson (1938) ArticleTitleChemical stratification and lake morphology Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 4 63–69
G. E. Hutchinson (1967) A Treatise on Limnology. II. Introduction to Lake Biology and the Limnoplankton John Wiley and Sons New York, 1115
A. Järvalt T. Krause A. Palm (2005) ArticleTitleDiel migration and spatial distribution of fish in a small stratified lake Hydrobiologia 547 197–203
Järvet, A., 1989. Veekogude kasutamise vastuolud Kavilda oja näitel In: Põllumajandus ja keskkonnakaitse. Tallinn – Elva. pp. 84–90 [Contradictions of management of water bodies on example of Kavilda stream. In Estonian].
H. S. Jensen P. Kristensen E. Jeppesen A. Skytthe (1992) ArticleTitleIron:phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes Hydrobiologia 235/236 731–743 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00026261
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, P. Kristensen, M. Søndergaard, E. Mortensen, O. Sortkjær, K. & Olrik, 1990b. Fish manipulation as a lake restoration tool in shallow, eutrophic, temperate lakes 2: threshold levels, long-term stability and conlusions. – Hydrobiologia 200/201: 219–227. Gulati, R. D., Lammens, E. H. R. R., Meijer, M.-L., van Donk, E (eds), Biomanipulation – Tool for Water Management.
Jeppesen, E., M. Søndergaard, E. Mortensen, P. Kristensen, B. Riemann, H. J. Jensen, J. P. Müller, O. Sortkjær, J. P. Jensen, K. Christofferson, S. Bosselmann, E. Dall, & 1990a. Fish manipulation as a lake restoration tool in shallow, eutrophic, temperate lakes 1: cross– analysis of three Danish case studies. – Hydrobiologia 200/201: 205–218. Gulati, R. D., Lammens, E. H. R. R., Meijer, M.-L., van Donk, E., (eds), Biomanipulation – Tool for Water Management.
K. Kangro R. Laugaste P. Nõges I. Ott (2005) ArticleTitleLong-term changes and seasonal development of phytoplankton in a strongly stratified hypertrophic lake Hydrobiologia 547 91–103
Kasprzak, P., 1995. Objectives of biomanipulation. In: De Bernardi, R., Giussani, G. (eds), Guidelines of lake management. 7. de Bernardi, R. and Giussani, G. (eds), Biomanipulation in lakes and reservoirs management, 1–15 pp.
P. Kasprzak J. Benndorf T. R. Mehner Koschel (2002) ArticleTitleBiomanipulation of lake ecosystems: an introduction Freshwater Biology 47 2277–2281 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1365-2427.2002.01001.x
A. Kisand (2005) ArticleTitleDistribution of sediment phosphorus fractions in hypertrophic strongly stratified Lake Verevi Hydrobiologia 547 33–39
Koroleff, F., 1982. Total and organic nitrogen. In Grasshoff, K. (ed.), Methods of Seawater Analysis. Verlag chemie, 162–168.
Kört, M., T. Truuts & K. Pajuste, 2002. Õhu saasteainete kaugkande seire. Eesti Keskkonnaseire 2001. 23–25. [Monitoring of long-distance air pollution. In Estonian].
L. Krienitz P. R. Kasprzak Koschkel (1996) ArticleTitleLong term study on the influence of eutrophication, restoration and biomanipulation on the structure and development of phytoplankton communities in Feldberger Haussee (Baltic Lake District, Germany) Hydrobiologia 330 89–110 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00019998
Lampert, W. & U. Sommer, 1997. Limnoecology: The Ecology of Lakes and Streams. Oxford Univeristy Press, 382 pp.
K.-E. Lindenschmidt I. Chorus (1997) ArticleTitleThe effect of aeration on stratification and phytoplankton populations in Lake Tegel Berlin Archiv Für Hydrobiologie 139 IssueID3 317–346
Loopmann, A., 1984. Suuremate Eesti järvede morfomeetrilised andmed ja Veevahetus. Tallinn, 150 lk. [Morphometrical data and water exchange of larger Estonian lakes. In Estonian].
Mäemets, Aare & K. Ennok, 1991. Valgala iseloom, sissevoolude vee keemiline koostis ja järve resotsukoormus. In Timm, H. (ed.), State of Lake Verevi. Hydrobiological researches XVII. pp. 34–44. [Catchment features, chemical composition of water of inflows and pollution loading. In Estonian].
Mäemets, Aime, 1991. Suurtaimestik. In H. Timm (ed.), State of Lake Verevi (Hydrobiological Researches XVII), Tartu: 95–106 [Macrovegetation. In Estonian].
Mäemets, A., I. Ott & A. Mäemets, 1994. Eesti väikejärvede seisundi muutused ja kaitse. Kogumik: Eesti jõgede ja järvede seisund ning kaitse. Toim. A. Järvekülg. Teaduste Akadeemia kirjastus. Tallinn, lk. 32–47. [Changes an protection of Estonian small lakes). In Estonian, English summary].
H. Mäemets L. Freiberg (2005) ArticleTitleLong- and short-term changes of the macrophyte vegetation in strongly stratified hypertrophic Lake Verevi Hydrobiologia 547 175–184
T. Möls H. Starast A. Milius A. Lindpere (1996) ArticleTitleThe hydrochemical state of Lake Peipsi–Pihkva Hydrobiologia 338 37–47 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00031709
B. Moss D. Stephen C. Alvarez E. Becares W. Bund ParticleVan de S. E. Collings E. Donk ParticleVan E. Eyto ParticleDe T. Feldmann C. Fernández-Aláez M. Fernández-Aláez R. J. M. Frankeng F. García-Criado E. Gross M. Gyllström L.-A. Hansson K. Irvine A. Järvalt J.-P. Jenssen E. Jeppesen T. Kairesalo R. Kornijów T. Krause H. Künnap A. Laas E. Lill B. Lorens H. Luup M. R. Miracle P. Nõges T. Nõges M. Nykänen I. Ott W. Peczula E. T. H. M. Peeters G. Phillips S. Romo V. Russell J. Salujõe M. Scheffer K. Siewertsen H. Smal C. Tesch H. Timm L. Tuvikene I. Tõnno T. Virro D. Wilson (2003) ArticleTitleThe determination of ecological quality in shallow lakes – a tested system (ECOFRAME) for implementation of the European Water Framework Directive Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems 13 507–549 Occurrence Handle10.1002/aqc.592
Nixdorf, B., J. Mischke, U. Hoffmann, A. Hemm, M. & E. Hoehn, 2001. Classification and assessment of lakes in Germany according to the bilogical indicator phytoplankton – first results. Classification of Ecological Statud of Lakes and Rivers. Saara Bäck & Krister Karttunen (eds). TemaNord 2001: 584, 24–27 pp.
P. Nõges (2005) ArticleTitleWater and nutrient mass balance of temperate partly meromictic Lake Verevi Hydrobiologia 547 21–31
T. Nõges K. Kangro (2005) ArticleTitlePrimary production of phytoplankton in a strongly stratified temperate lake Hydrobiologia 547 105–122
G. Nygaard (1949) Hydrobiological Studies on some Danish Ponds and Lakes II: The quotient hypothesis and some little known or new phytoplankton organisms Kunglige Danske Vidensk Selskab. 7 242
Ott, I., 2001. Typology and ecological classification of Estonian lakes. In Classification of ecological status of Lakes and Rivers. TemaNord 2001: 584, 62–64 pp.
Ott, I. & T. Kõiv, 1999. Eesti väikejärvede eripära ja muutused. Estonian Small Lakes: Special Features and Changes. Tallinn. 128 pp.
Ott, I. & R. Laugaste, 1996. Fütoplanktoni koondindeks Üldistus Eesti väikejärvede kohta Eesti vabariigi Keskkonnaministeeriumi Infoleht 3/96. lk. 7–8. [Phytoplankton compound quotient. Conclusion about Estonian small lakes. In Estonian].
Ott, I., R. Laugaste, S. Lokk & A. Mäemets, 1997. Plankton changes in Estonian small lakes in 1951–93. – Proceedings of Estonian Academy of Sciences Biology. Ecology. 46, ½, 58–79.
Ott, I. & S. Lokk, 1996. Viitna Pikkjärv ja puhkajad – Eesti Loodus.174–176. [Lake Viitna Pikkjärv and holidaymakers. In Estonian, English summary].
I. Ott A. Rakko D. Sarik P. Nõges K. Ott (2005) ArticleTitleSedimentation rate of seston during the formation of temperature stratification after ice break-up in the partly meromictic Lake Verevi Hydrobiologia 547 51–61
E. Pihu (1998) ArticleTitleFishes and fisheries management in Lake Võrtsjärv Limnologica 28 IssueID1 91–94
E. Pipp E. Rott (1995) ArticleTitleA phytoplankton compartment model for a small meromictic lake with special reference to species-specific niches and long-term changes Ecological Modellling 78 129–148 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0304-3800(94)00123-Y
Prede, M., I. Ott, A. Kisand, R. Laugaste, H. Mäemets, H. Timm, A. Järvalt, E. Kirt & T. Oja, 1999. A. Maastik (ed.), Lakescape of Otepää: Past, present and future. Tacis–Phare, 24 pp.
Premazzi, G. & G. Chiaudani, 1992. Current approaches to assess water quality in lakes. In ECSC-EEC-EAEC, Brussels, Luxembourg, 249–308.
Reports of the Baltic Intercalibration Workshop, 1977, Kiel: 27–28.
A. F. Richter (1986) ArticleTitleBiomanipulation and its feasibility for water quality management in shallow eutrophic management in shallow eutrophic water bodies in the Netherlands Hydrobiological Bulletin 20 IssueID1/2 165–172
H. Riikoja (1930) ArticleTitleZur Morphometrie eineiger Seen Eestis Andmeid Eesti ala järvede uurimiseks 15 116–201
Riikoja, H., 1940. Zur Kenntnis eineiger Seen Ost-Eestis, insbesonderere ihrerWasserchemie. Loodusvarade Instituudi Limnoloogia Laboratooriumi Avaldised, 2.
W. Ripl (1976) ArticleTitleBiochemical oxidation of polluted lake sediment with nitrate A new restoration method. Ambio 5 132–135
Ripl, W., 1994. Restoration methods and techniques. Sediment treatment. In Eiseltova’, M. (ed.), Restoration of Lake Ecosystems, a holistic approach, 75–82 pp.
Rosenström, U. & L. Lepistö, 1996. Phytoplankton indicator species of different types of boreal lakes. Algological Studies 82=Archiv Für Hydrobiologie Supplementum 116, 131–140 pp.
Rummi, P., T. Mägi, J. Ütsi, H. Mäemets, A. Lindpere & A. Mäemets, 1991. Põhjasetted. In Timm, H. (ed.), State of Lake Verevi. Hydrobiological Researches XVII. 22–33 pp. [Bottom sediments. In Estonian].
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of shallow lakes. M.B. Busher (ed.), Population and Community Biology Series. Chapman & Hall Publisher, 357 pp.
Schulz, L., 1981. Nährstoffeintrag in Seen durch Badegäste. Zentralblatt Für Bakteriologie., 1B, 6.
M. Søndergaard P. Kristensen E. Jeppesen (1993) ArticleTitleEight years of internal phosphorus loading and changes in the sediment phosphorus profile of Lake Søbygård Denmark – Hydrobiologia, 253 345–356
Steenberger, C. L. M., J.-P. R. A. Sweerts & T. E. Cappenberg. 1993. Microbial biogeochemical processes in lakes: stratification and eutrophication, 69–99 pp.
Timm, H. (ed.), 1991. Verevi järve seisund. A monograph. Tartu. 139 pp. [State of Lake Verevi. In Estonian, English and Russian summary].
H. Timm T. Möls (2005) ArticleTitleMacrozoobenthos of lake Verevi Hydrobiologia 547 185–195
Unifitsirovannye metody issledovaniya kachestva vod, 1977. I, Moskva: 831 pp. [Standardized methods for investigation of water quality. In Russian].
Van Donk, E., & R. D. Gulati, 1991. Ecological management of aquatic ecosystems: a complementary technique to reduce eutrophication-related preturbians. In Terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems: preturbation and recovery. Published by Ellis Horword Limited, 566–575 pp.
M. Vighi G. Chiaudani (1985) ArticleTitleA simple method to estimate lake phosphorus concentrations resulting from natural background loadings Water Research 19 987–991 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0043-1354(85)90367-7
R. A. Vollenweider (1975) ArticleTitleInput – output models with special reference to the phosphorus loading concept in limnology Scweizerische Zeitschrift für Hydrobiologie 37 53–84
Wetzel, R. G., 1983. Limnology. Saunders College Publishing. 767 pp.
Willen, E., 2000. Phytoplankton in water quality assessment – an indicator concept. In Heinonen, P., G. Ziglio, & A. Van der Beken (eds), Hydrological and limnological aspects of lake monitoring: 58–80. John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Wolter, K.-D., 1994. Restoration methods and techniques. Phosphorus precipitation. In Eiseltova’, M. (ed.), Restoration of Lake Ecosystems, a holistic approach, 63–69 pp.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ott, I., Kõiv, T., Nõges, P. et al. General Description of Partly Meromictic Hypertrophic Lake Verevi, its Ecological Status, Changes during the Past Eight Decades, and Restoration Problems. Hydrobiologia 547, 1–20 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4138-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-4138-x