Abstract
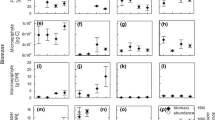
Highly regulated salinity gradients in solar salt pond concentrating sequences provide an opportunity to investigate in situ salinity impacts on aquatic flora and fauna. The Shark Bay Salt solar ponds at Useless Inlet in Western Australia vary in salinity from seawater to four times seawater over the pond sequence. We observed a shift from planktonic to benthic primary productivity as salinity increased. Water column photosynthesis and biomass decreased markedly with increasing salinity, while benthic productivity increased as cyanobacterial mats developed. Correspondingly, productivity shifted from autotrophy to heterotrophy in the water column and from heterotrophy to autotrophy in the benthos. Both shifts occurred at intermediate salinity (S = 110 g kg−1, ρ = 1.087 g cm−3) in the pond sequence, where there was little production by either. Within individual ponds, productivity, algal biomass and physico-chemical conditions were relatively constant over one year, with only water column photosynthesis significantly different between seasons, mostly due to greater winter production. Transitions between benthic and planktonic production and their relative magnitudes appear to be driven mostly by direct responses to salinity stress, but also by changes in nutrient availability and grazing, which are also influenced by salinity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. S. R. Agawin C. M. Duarte S. Agusti (2000) ArticleTitleNutrient and temperature control of picoplankton to phytoplankton biomass and production Limnology and Oceanography 45 591–600 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjsV2ltLc%3D Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.2000.45.3.0591
InstitutionalAuthorNameAmerican Public Health Association (1998) Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater EditionNumber20 APHA, AWA and WEF Washington, DC, USA
J. Bauld (1981) ArticleTitleOccurrence of benthic microbial mats in saline lakes Hydrobiologia 81 87–111 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00048708
J. Bauld (1984) Microbial mats in marginal marine environments: Shark Bay, Western Australia, and Spencer Gulf, South Australia Y. Cohen R. W. Castenholz H. O. Halvorson (Eds) Microbial Mats: Stromatolites Alan R. Liss Inc New York, USA
K. Budd G. W. Kerson (1987) ArticleTitleUptake of phosphate by two cyanophytes: cation effects and energetics Canadian Journal of Botany 65 1901–1907 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXmtlehsrk%3D
L. B. Cahoon J. E. Cooke (1992) ArticleTitleBenthic microalgal production in Onslow Bay, North Carolina, USA Marine Ecology Progress Series 84 185–196
J. A. Davis M. McGuire S. A. Halse D. P. Hamilton P. Horwitz A. J. McComb R. H. Froend M. N. Lyons L. Sim (2003) ArticleTitleWhat happens when you add salt: predicting impacts of secondary salinisation on shallow aquatic ecosystems by using an alternative-states model Australian Journal of Botany 51 715–724 Occurrence Handle10.1071/BT02117
J. S. Davis (1990) Biological management for the production of salt from seawater I. Akatsuka (Eds) Introduction to Applied Phycology SPB Academic Publishing The Hague, The Netherlands 479–488
J. S. Davis (1997) Useless Loop Saltfield: Status Report of the Current Biological Condition Shark Bay Salt Joint Venture Useless Loop, Western Australia
J. S. Davis (1999) Biological Assessment of the Shark Bay Pond System after the Addition of Pond PM1 Shark Bay Salt Joint Venture Useless Loop, Western Australia
J. S. Davis M. Giordano (1996) ArticleTitleBiological and physical events involved in the origin, effects and control of organic matter in solar saltworks International Journal of Salt Lake Research 4 335–347
D. J. Des Marais (1995) ArticleTitleThe biogeochemistry of hypersaline microbial mats Advances in Microbial Ecology 14 251–274 Occurrence Handle11539110 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XhtFOhsb8%3D
T. Fenchel G. M. King T. H. Blackburn (1998) Bacterial Biogeochemistry: The Ecophysiology of Mineral Cycling EditionNumber2 Academic Press San Diego, CA, USA
B. Freedman (1995) Environmental Ecology EditionNumber2 Academic Press San Diego, CA, USA
F. Garcia-Pichel M. Kuhl U. Nubel G. Muyzer (1999) ArticleTitleSalinity-dependent limitation of photosynthesis and oxygen exchange in microbial mats Journal of Phycology 35 227–238 Occurrence Handle10.1046/j.1529-8817.1999.3520227.x
K. Grasshoff (1983) Determination of oxygen K. Grasshoff M. Ehrhardt K. Kremling (Eds) Methods of Seawater Analysis EditionNumber2 Verlag Chimie Weinheim, Germany
G. P. Harris (1999) ArticleTitleComparison of the biogeochemistry of lakes and estuaries: ecosystem processes, functional groups, hysteresis effects and interactions between macro- and microbiology Marine and Freshwater Research 50 791–811 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXks1ymtQ%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1071/MF99111
F. P. Healy (1982) Phosphate (Ch. 5) N. G. Carr B. A. Whitton (Eds) The Biology of Cyanobacteria. Botanical Monographs, Vol. 19 Blackwell Scientific Publications Oxford, UK
D. B. Herbst (2001) ArticleTitleGradients of salinity stress, environmental stability and water chemistry as a template for defining habitat types and physiological strategies in inland salt waters Hydrobiologia 466 209–219 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjsFaiurk%3D Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1014508026349
B. J. Javor (1983a) Nutrients and ecology of the western salt and exportadora de sal salterns brines B. C. Schreiber H. L. Harner (Eds) Sixth International Symposium on Salt, Vol. 1 The Salt Institute Alexandria, VI, USA 195–205
B. J. Javor (1983b) ArticleTitlePlanktonic standing crop and nutrients in a saltern ecosystem Limnology and Oceanography 28 153–159 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3sXhtFehtr4%3D
B. Javor (1989) Hypersaline Environments: Microbiology and Biogeochemistry Springer-Verlag Berlin, Germany
I. Joint P. Henriksen K. Garde B. Riemann (2002) ArticleTitlePrimary productivity, nutrient assimilation and microzooplankton grazing along a hypersaline gradient FEMS Microbiology Ecology 39 245–257 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD38XjsFOjurg%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0168-6496(02)00178-2 Occurrence Handle19709204
K. J. M. Kramer U. H. Brockman R. M. Warwick (1994) Tidal Estuaries: manual of Sampling and Analytical Procedures AA Balkema Rotterdam, The Netherlands
J. Melack (1988) ArticleTitlePrimary producer dynamics associated with evaporative concentration in a shallow, equatorial soda lake (Lake Elmenteita, Kenya) Hydrobiologia 158 1–14 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL1cXhtlOnt7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00026264
A. Nadler M. Margaritz (1980) Studies of marine solution basins – isotopic and compositional changes during evaporation A. Nissenbaum (Eds) Hypersaline Brines and Evaporitic Environments. Developments in Sedimentology 28 Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company Amsterdam, The Netherlands 115–129
C. Pedros-Alio J. I. Calderon-Paz M. H. MacLean G. Medina C. Marrase J. M. Gasol N. Guixa-Boixereu (2000) ArticleTitleThe microbial food web along salinity gradients FEMS Microbiology Ecology 32 143–155 Occurrence Handle10817867 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXjt1ejt74%3D
J. Pinckney R. G. Zingmark (1993) ArticleTitleBiomass and production of benthic microalgal communities in estuarine habitats Estuaries 16 887–897 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2cXmvVKju7g%3D
J. Pinckney H. W. Paerl (1997) ArticleTitleAnoxygenic photosynthesis and nitrogen fixation by a microbial mat community in a Bahamian hypersaline lagoon Applied and Environmental Microbiology 63 420–426 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXhtVKktLo%3D Occurrence Handle16535506
J. Roux (1991) Microbial Mats in Hypersaline Environments at Dampier Salt, Dampier, Western Australia. MSc Thesis Botany Department, University of Western Australia Perth, Western Australia
J. Roux (1996) ArticleTitleProduction of polysaccharide slime by microbial mats in hypersaline environments of a Western Australian solar saltfield International Journal of Salt Lake Research 5 103–130 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF01995826
M. Scheffer (1998) Ecology of Shallow Lakes Chapman and Hall London, UK
M. Scheffer S. Carpenter J. A. Foley C. Folke B. Walker (2001) ArticleTitleCatastrophic shifts in ecosystems Nature 413 591–596 Occurrence Handle11595939 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXnsleht7c%3D Occurrence Handle10.1038/35098000
D. R. Stenbeck D. A. Horn J. Imberger (1999) Optimisation of Salt Production in the Shark Bay Salt Fields: Feasibility Report Centre for Water Research, University of Western Australia Perth, Western Australia
R. M. Timms B. Moss (1984) ArticleTitlePrevention of growth of potentially dense phytoplankton populations by zooplankton grazing, in the presence of zooplanktivorous fish, in a shallow wetland ecosystem Limnology and Oceanography 29 472–486 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.1984.29.3.0472
G. J. C. Underwood J. Kromkamp (1999) ArticleTitlePrimary production by phytoplankton and microphytobenthos in estuaries Advances in Ecological Research 29 93–153 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXltl2lug%3D%3D Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0065-2504(08)60192-0
Y. Vadeboncoeur E. Jeppensen M. J. Vander Zanden H.-H. Scheirup K. Christoffersen D. M. Lodge (2003) ArticleTitleFrom Greenland to green lakes: cultural eutrophication and the loss of benthic pathways in lakes Limnology and Oceanography 48 1408–1418 Occurrence Handle10.4319/lo.2003.48.4.1408
Williams, W. D., 1998a. Guidelines of Lake Management, Vol. 6: Management of Inland Saline Lakes. International Lake Environment Committee Foundation and the United Nations Environment Programme, Kusatsu, Japan. pp. 1, 39, 63–67.
W. D. Williams (1998b) ArticleTitleSalinity as a determinant of the structure of biological communities in salt lakes Hydrobiologia 381 191–201 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1003287826503
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Segal, R.D., Waite, A.M. & Hamilton, D.P. Transition from Planktonic to Benthic Algal Dominance Along a Salinity Gradient. Hydrobiologia 556, 119–135 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0916-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0916-8