Abstract
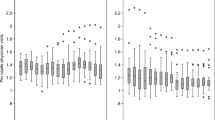
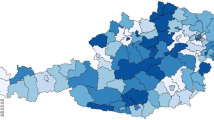
The determinants for the number of outpatient hospital treatments across Danish municipalities are analysed using balanced panel data from the period 1998–2004. The determinants include socio-demographic variables, home help service, residential homes capacity, proxy variables for morbidity, utilisation of primary care services, accessibility of hospitals and a number of other factors. Panel effects in the form of intra-municipal correlation and heterogeneity across years are controlled for. Spatial spillover effects across municipalities will be investigated in order to disclose the spatial dynamics of outpatient treatments. The results reveal substantial heterogeneity and dependency across time, as well as presence of a significant spatial spillover effect. Reverse causalities among the number of hospital outpatient treatments and certain health systems characteristics are further controlled for. The results are shown to be highly sensitive to such adjustments, as the effects of determinants—including those over which the municipalities exert some control—are seriously overestimated if such features are ignored.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abellan, J.J., Richardson, S., Best, N.: Use of space-time models to investigate the stability of patterns of disease. Environ. Health Perspect. 116(8), 1111–1119 (2008)
Anselin, L.: Spatial Econometrics: Methods and Models. Kluwer Academic Publishers, North-Holland (1988)
Banerjee, S., Carlin, B.P., Gelfand, A.E.: Hierarchical Modeling and Analysis for Spatial Data. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL (2004)
Best, N., Arnold, R., Thomas, A., Waller, L., Conlon, E.: Bayesian models for spatially correlated disease and exposure data. In: Bernardo, J., et al. (eds.) Bayesian Statistics, pp. 131–156. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1999)
Bidani, B., Ravallion, M.: Decomposing social indicators using distributional data. J. Econometr. 77(1), 125–139 (1997)
Blais, R.: Variations in surgical rates in Quebec—does access to teaching hospitals make a difference. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 148(10), 1729–1736 (1993)
Brunsdon, C., Fotheringham, A.S., Charlton, M.E.: Geographically weighted regression: a method for exploring spatial nonstationarity. Geographical Anal. 28(4), 281–298 (1996)
Case, A.C., Rosen, H.S., Hines, J.R.: Budget spillovers and fiscal-policy interdependence—evidence from the states. J. Public Econ. 52(3), 285–307 (1993)
Casetti, E.: The expansion method, mathematical modeling, and spatial econometrics. Int. Reg. Sci. Rev. 20(1–2), 9–33 (1997)
Congdon, P., Best, N.: Small area variation in hospital admission rates: Bayesian adjustment for primary care and hospital factors. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. C-Appl. Stat. 49, 207–226 (2000)
Costa-Font, J., Pons-Novell, J.: Public health expenditure and spatial interactions in a decentralized national health system. Health Econ. 16(3), 291–306 (2007)
Costa-Font, J., Rico, A.: Devolution and the interregional inequalities in health and healthcare in Spain. Reg. Stud. 40(8), 875–887 (2006)
Costa-Font, J., Pons-Novell, J.: Public health expenditure and spatial interactions in a decentralized national health system. Health Econ. (2006) (Forthcoming)
Cressie, N., Chan, N.H.: Spatial modeling of regional variables. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 84(406), 393–401 (1989)
Di Matteo, L.: The determinants of the public-private mix in Canadian health care expenditures: 1975–1996. Health Policy 52(2), 87–112 (2000)
Di Matteo, L.: The macro determinants of health expenditure in the United States and Canada: assessing the impact of income, age distribution and time. Health Policy 71(1), 23–42 (2005)
Di Matteo, L., Di Matteo, R.: Evidence on the determinants of Canadian provincial government health expenditures: 1965–1991. J. Health Econ. 17(2), 211–228 (1998)
Elliot, P., Wakefield, J.C., Best, N.G., Briggs, D.J.: Spatial Epidemiology: Methods and Applications. Oxford University Press, Oxford (2000)
Folland, S., Goodman, A.C., Stano, M.: The Economics of Health and Health Care. Pearson Education, Upper Saddle River, NJ (2004)
Fortney, J.C., Steffick, D.E., Burgess J.F., Jr., Maciejewski, M.L., Petersen, L.A.: Are primary care services a substitute or complement for specialty and inpatient services? Health Serv. Res. 40(5 Pt 1), 1422–1442 (2005)
Gerdtham, U.-G., Jönsson, B.: International comparison of health expenditure: theory, data and econometric analysis. In: Culyer, A.J., Newhouse, J.P. (eds.) Handbook of Health Economics, pp. 11–53. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2000)
Giannoni, M., Hitiris, T.: The regional impact of health care expenditure: the case of Italy. Appl. Econ. 34(14), 1829–1836 (2002)
Gregory, P.M., Malka, E.S., Kostis, J.B., Wilson, A.C., Arora, J.K., Rhoads, G.G.: Impact of geographic proximity to cardiac revascularization services on service utilization. Med. Care 38(1), 45–57 (2000)
Groenewegen, P.P.: Substitution of primary care and specialist care: a regional analysis in Denmark. Soc. Sci. Med. 33(4), 471–476 (1991)
Joines, J.D., Hertz-Picciotto, I., Carey, T.S., Gesler, W., Suchindran, C.: A spatial analysis of county-level variation in hospitalization rates for low back problems in North Carolina. Soc. Sci. Med. 56(12), 2541–2553 (2003)
Jones, J.P., Casetti, E.: Applications of the Expansion Method. Routledge, London (1992)
Lauridsen, J., Bech, M., López, F., Sánchez, M.M.: Geographic and dynamic heterogeneity of public prescription pharmaceutical expenditure in Spain. Rev. Reg. Stud. (2009) (Forthcoming)
Lin, G., Allan, D.E., Penning, M.J.: Examining distance effects on hospitalizations using GIS: a study of three health regions in British Columbia, Canada. Environ. Plan. A 34(11), 2037–2053 (2002)
Linnala, A., Aromaa, A., Mattila, K.: Specialist consultations in primary health care—a possible substitute for hospital care? Health Policy 78(1), 93–100 (2006)
Manning, W.G., Newhouse, J.P., Duan, N., Keeler, E.B., Leibowitz, A., Marquis, M.S.: Health-insurance and the demand for medical-care—evidence from a randomized experiment. Am. Econ. Rev. 77(3), 251–277 (1987)
Mooney, C., Zwanziger, J., Phibbs, C.S., Schmitt, S.: Is travel distance a barrier to veterans’ use of VA hospitals for medical surgical care? Soc. Sci. Med. 50(12), 1743–1755 (2000)
Moscone, F., Knapp, M.: Exploring the spatial pattern of mental health expenditure. J. Ment. Health Policy Econ. 8(4), 205–217 (2005)
Moscone, F., Knapp, M., Tosetti, E.: Mental health expenditure in England: a spatial panel approach. J. Health Econ. 26(4), 842–864 (2007)
Newhouse, J.P.: Medical-care expenditure—cross-national survey. J. Hum. Resour. 12(1), 115–125 (1977)
Newhouse, J.P.: Medical-care costs—how much welfare loss. J. Econ. Perspect. 6(3), 3–21 (1992)
Pedersen, K.M.: Kommunal medfinansiering af sundhedsvæsenet: En idé på sandbund? University Press of Southern Denmark, Odense (2005)
Peeters, L., Chasco, C.: Ecological inference and spatial heterogeneity: an entropy-based distributionally weighted regression approach. Pap. Reg. Sci. 85(2), 257–276 (2006)
Phelps, C.E.: Welfare loss from variations—further considerations. J. Health Econ. 14(2), 253–260 (1995)
Phelps, C.E.: Information diffusion and best practice adoptation. In: Culyer, A.J., Newhouse, J.P. (eds.) Handbook of Health Economics, vol. I, pp. 223–264. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam (2000)
Phelps, C.E.: Health Economics, 3rd edn. Addison Wesley, Boston (2002)
Revelli, F.: Spatial patterns in local taxation: tax mimicking or error mimicking? Appl. Econ. 33(9), 1101–1107 (2001)
Revelli, F.: Testing the tax mimicking versus expenditure spill-over hypotheses using English data. Appl. Econ. 34(14), 1723–1731 (2002)
Ricketts, T.C., Randolph, R., Howard, H.A., Pathman, D., Carey, T.: Hospitalization rates as indicators of access to primary care. Health Place 7(1), 27–38 (2001)
Roemer, M.I.: Bed supply and hospital utiltization: a natural experiment. Hospitals 35(1), 36–42 (1961)
Rosenberger, R.S., Sneh, Y., Phipps, T.T., Gurvitch, R.: A spatial analysis of linkages between health care expenditures, physical inactivity, obesity and recreation supply. J. Leis. Res. 37(2), 216–235 (2005)
Shwartz, M., Ash, A.S., Anderson, J., Iezzoni, L.I., Payne, S.M.C., Restuccia, J.D.: Small-area variations in hospitalization rates—how much you see depends on how you look. Med. Care 32(3), 189–201 (1994)
Thomsen, C.K.: En empirisk model for kommunernes sygehusforbrug. Nationaløkon. Tidsskr. 123(1), 77–93 (1985)
Thomsen, O., Barner-Rasmussen, P.: Sygehusforbrug og brug af praktiserende læge—er der en sammenhæng? Ugeskr. Laeger 154(14), 906–910 (1992)
Wall, M.M.: A close look at the spatial structure implied by the CAR and SAR models. J. Stat. Plan. Inference 121(2), 311–324 (2004)
Wennberg, J., Gittelsohn, A.: Small area variations in health care delivery. Science 182(117), 1102–1107 (1973)
Wennberg, J.E., Barnes, B.A., Zubkoff, M.: Professional uncertainty and the problem of supplier-induced demand. Soc. Sci. Med. 16(7), 811–824 (1982)
Westert, G.P., Groenewegen, P.P., Boshuizen, H.C., Spreeuwenberg, P.M.M., Steultjens, M.P.M.: Medical practice variations in hospital care; time trends of a spatial phenomenon. Health Place 10(3), 215–220 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bech, M., Lauridsen, J. Exploring the small area variation and spatial patterns in outpatient treatments. Health Serv Outcomes Res Method 9, 177–196 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10742-009-0054-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10742-009-0054-2